Description
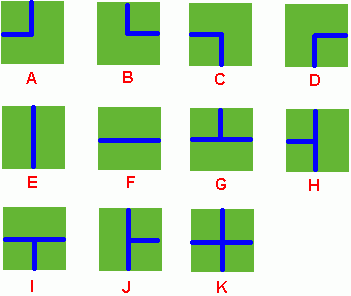
Benny has a map of his farm, which is an array of marks denoting the distribution of water pipes over the whole farm. For example, if he has a map
ADC
FJK
IHE
then the water pipes are distributed like
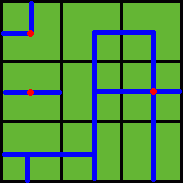
Several wellsprings are found in the center of some squares, so water can flow along the pipes from one square to another. If water flow crosses one square, the whole farm land in this square is irrigated and will have a good harvest in autumn.
Now Benny wants to know at least how many wellsprings should be found to have the whole farm land irrigated. Can you help him?
Note: In the above example, at least 3 wellsprings are needed, as those red points in Figure 2 show.
Input
Output
Sample Input
2 2 DK HF 3 3 ADC FJK IHE -1 -1
Sample Output
2 3
Hint
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[500][500],p[500][500];
int n1,n2;
int map[11][4]={
{1,0,0,1},
{1,1,0,0},
{0,0,1,1},
{0,1,1,0},
{1,0,1,0},
{0,1,0,1},
{1,1,0,1},
{1,0,1,1},
{0,1,1,1},
{1,1,1,0},
{1,1,1,1}
};
int p1(int q)
{if(p[q/n2][q%n2]==q)
return q;
else return p[q/n2][q%n2]=p1(p[q/n2][q%n2]);
}
void v(int i,int j)
{
if(map[a[i][j]][1]==1&&j<n2-1)
if(map[a[i][j+1]][3]==1)
{p[p1(p[i][j])/n2][p1(p[i][j])%n2]=p1(p[i][j+1]);
v(i,j+1);}
if(map[a[i][j]][2]==1&&i<n1-1)
if(map[a[i+1][j]][0]==1)
{p[p1(p[i][j])/n2][p1(p[i][j])%n2]=p1(p[i+1][j]);v(i+1,j);}
return;}
void set()
{int i,j;
for(i=0;i<n1;i++)
for(j=0;j<n2;j++)
{p[i][j]=i*n2+j;}
}
void c()
{int y[2500];
int t=0,i,j;
for(i=0;i<n1;i++)
for(j=0;j<n2;j++)
{y[t]=p1(p[i][j]);t++;}
sort(y,y+n1*n2);
t=0;
for(i=1;i<n1*n2;i++)
if( y[i]!=y[i-1] )
t++;
printf( "%d
", (t+1) );
}
int main()
{
int i,j;
char l;
while( scanf( "%d %d", &n1, &n2 ), n1>0&& n2> 0 )
{
for(i=0;i<n1;i++)
for(j=0;j<n2;j++)
{ cin>>l;
a[i][j]=int(l-'A');}
set();
for(i=0;i<n1;i++)
for(j=0;j<n2;j++)
{
v(i,j);}
c();
}
return 0; }