作者:李春港
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/lcgbk/p/14792404.html
一、数据结构
数据结构:在计算机中对数据按一定的方式进行组织
数据结构:线性关系 链式存储
链式存储:单向链表(v) 单向循环链表 双向链表 双向循环链表(v) 内核循环链表(v)
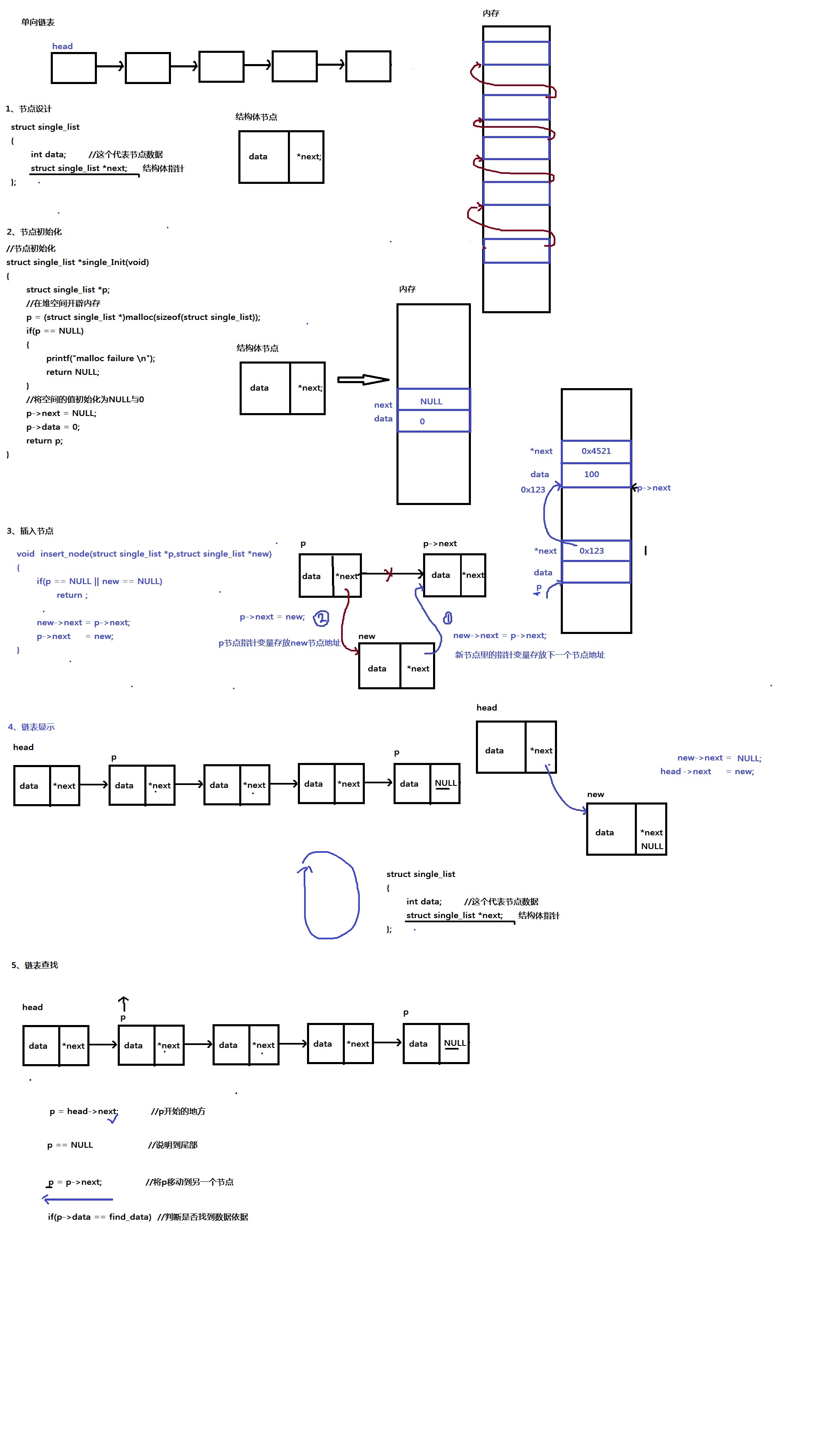
1、单向链表
1. 节点设计
struct single_list
{
int data;
struct single_list *next;
};
书上写法
typedef struct single_list
{
int data;
struct single_list *next;
}listnode,*singly_list;
//listnode == struct single_list
//singly_list == struct single_list *
2. 节点初始化
struct single_list *single_Init(void)
{
struct single_list *p;
//在堆空间开辟内存
p = (struct single_list *)malloc(sizeof(struct single_list));
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("malloc failure
");
return NULL;
}
//将空间的值初始化为NULL与0
p->next = NULL;
p->data = 0;
return p;
}
3.插入节点
void insert_node(struct single_list *p,struct single_list *new)
{
if(p == NULL || new == NULL)
return ;
new->next = p->next; //结合单向链表.jpg中的插入节点图进行理解
p->next = new; //结合单向链表.jpg中的插入节点图进行理解
}
4、显示节点
void display_node(struct single_list *head)
{
struct single_list *p;
p = head->next; //p指向第一个有数据的节点
while(p != NULL)
{
printf("%d ",p->data);
p = p->next; //将p移动到下一个节点
}
printf("
");
}
5、查找节点
struct single_list *find_node(struct single_list *head, int find_data)
{
struct single_list *p;
p = head->next; //p指向第一个有数据的节点
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p->data == find_data) //判断节点里的数据是否与你要查找的数据相等
{
return p; //把找到数据的节点地址返回
}
p = p->next; //将p移动到下一个节点
}
return NULL;
}
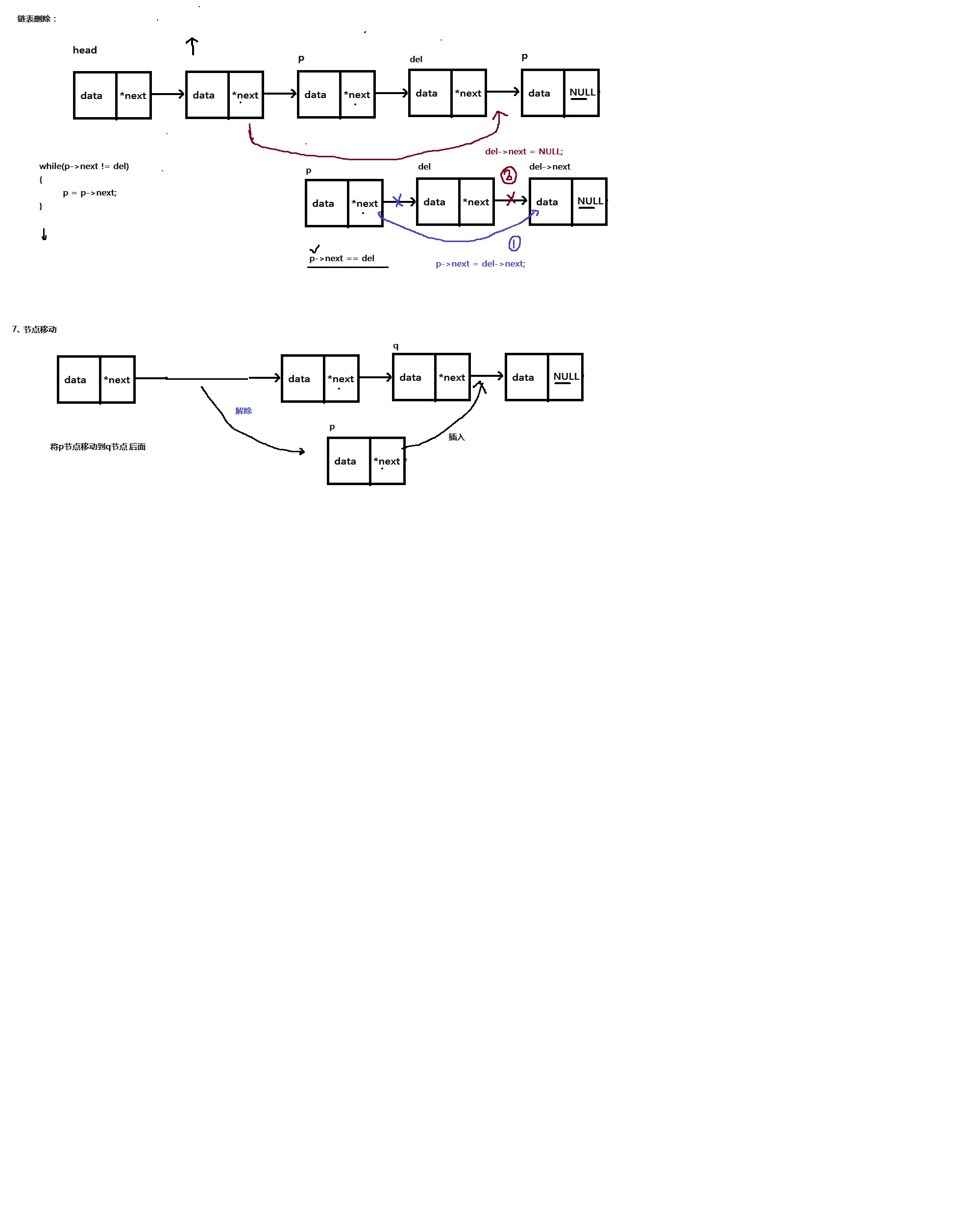
6、解除节点
void del_node(struct single_list *head, struct single_list *del)
{
struct single_list *p;
if(del == NULL)
return;
p = head; //p指向头节点
//遍历查找del前面节点
while(p->next != del)
{
p = p->next;
}
p->next = del->next; //del前面节点的next存放del后面节点地址
del->next = NULL; //del里面的next指向NULL
}
图解
-
数据结构
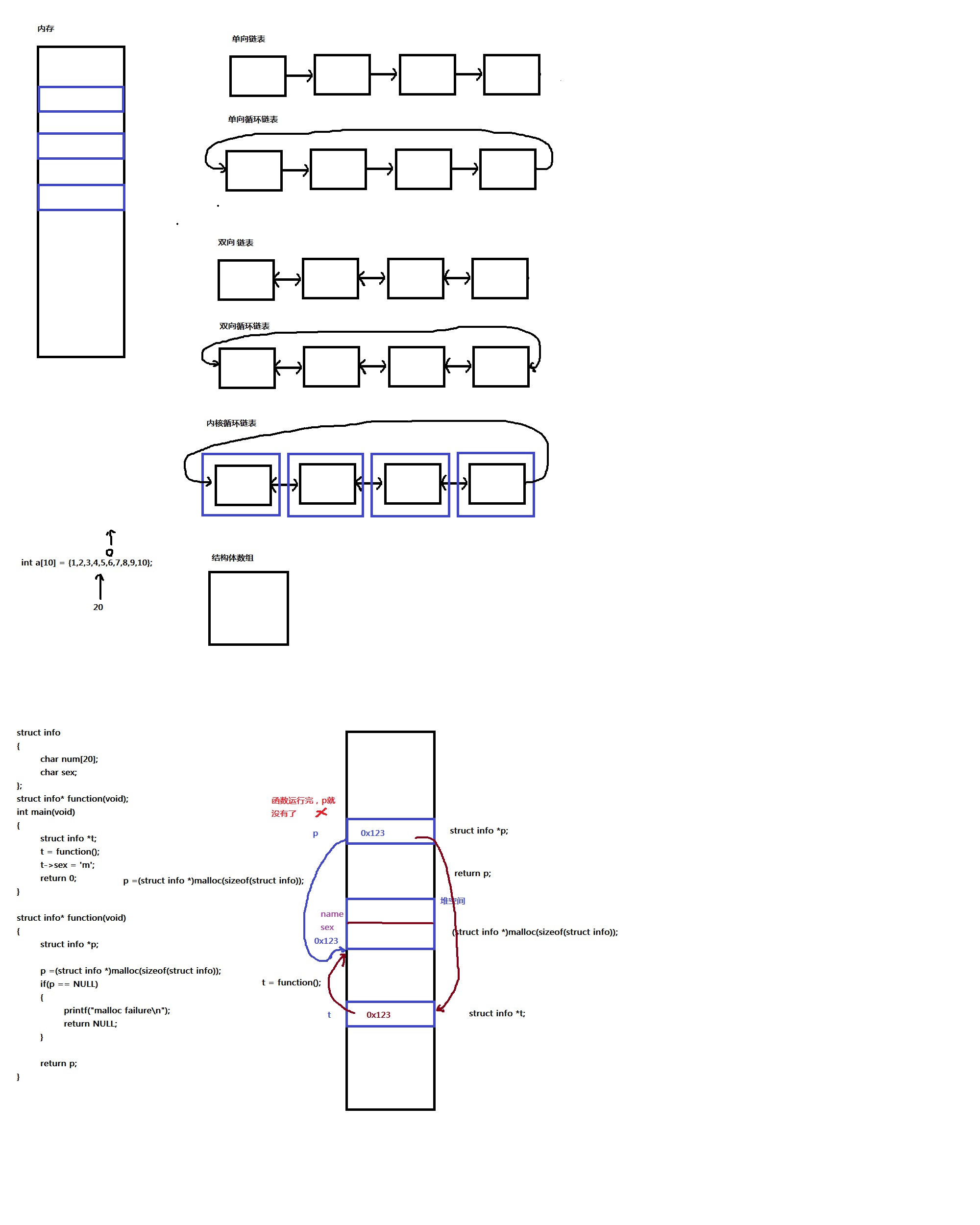
-
单向链表
2、双向循环链表
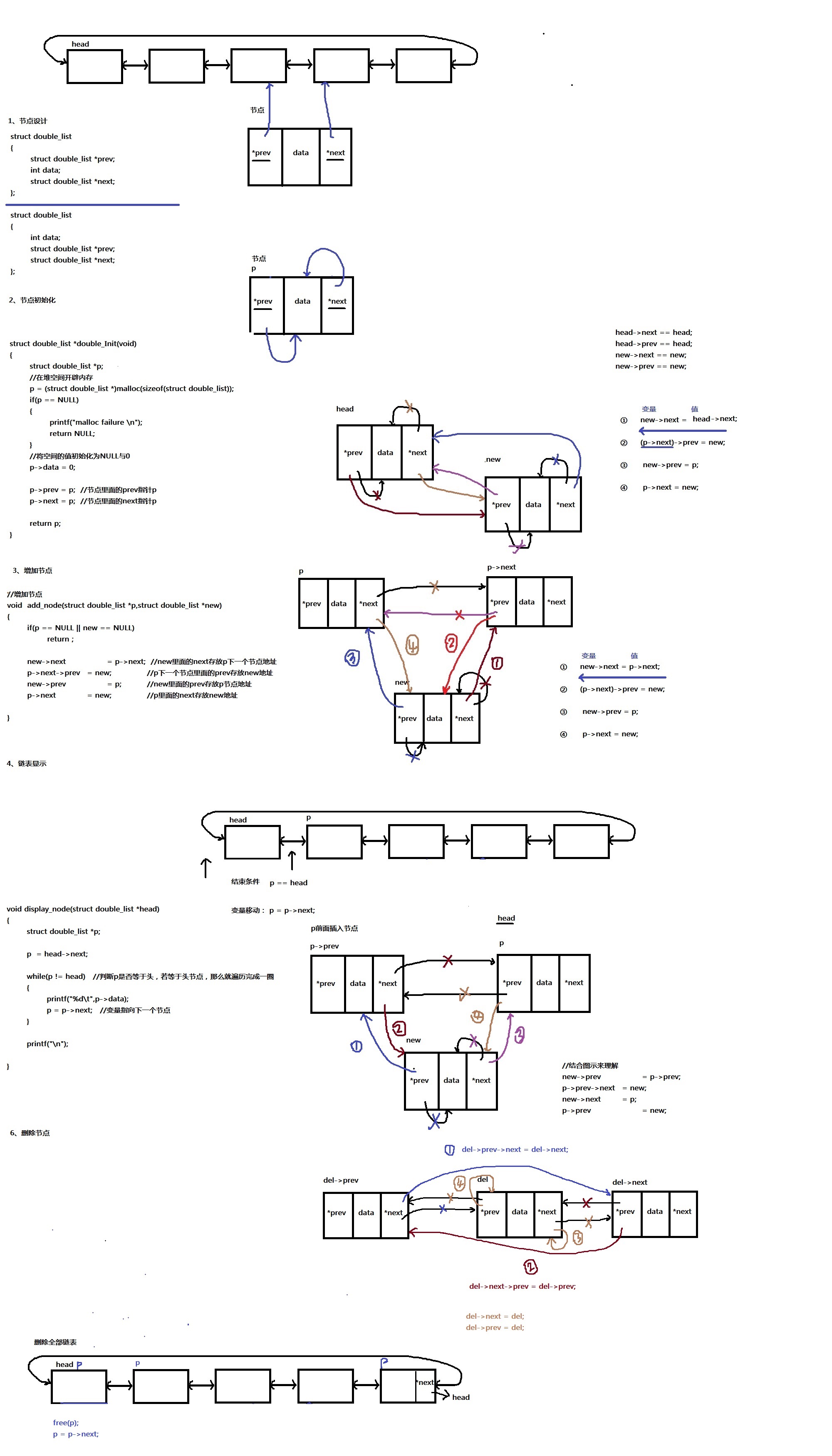
双向链表:可以通过当前的节点找到前缀节点或者后缀节点
1、节点设计
struct double_list
{
int data;
struct double_list *prev;
struct double_list *next;
};
2、节点初始化
struct double_list *double_Init(void)
{
struct double_list *p;
//在堆空间开辟内存
p = (struct double_list *)malloc(sizeof(struct double_list));
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("malloc failure
");
return NULL;
}
//将空间的值初始化为NULL与0
p->data = 0;
p->prev = p; //节点里面的prev指针p
p->next = p; //节点里面的next指针p
return p;
}
3、增加节点
//增加节点
void insert_node(struct double_list *p,struct double_list *new)
{
if(p == NULL || new == NULL)
return ;
new->next = p->next; //new里面的next存放p下一个节点地址
p->next->prev = new; //p下一个节点里面的prev存放new地址
new->prev = p; //new里面的prev存放p节点地址
p->next = new; //p里面的next存放new地址
}
//增加尾部节点
void insert_node_tail(struct double_list *p,struct double_list *new)
{
if(p == NULL || new == NULL)
return ;
//结合图示来理解
new->prev = p->prev;
p->prev->next = new;
new->next = p;
p->prev = new;
}
4、显示链表所有节点
void display_node(struct double_list *head)
{
struct double_list *p;
p = head->next;
while(p != head) //判断p是否等于头,若等于头节点,那么就遍历完成一圈
{
printf("%d ",p->data);
p = p->next; //变量指向下一个节点
}
printf("
");
}
5、查找节点
struct double_list *find_node(struct double_list *head,int find_data)
{
struct double_list *p;
p=head->next;
while(p != head)
{
if(p->data == find_data)
return p; //返回找到的节点数据地址
p=p->next; //将p移动到下一个节点
}
return NULL;
}
6、删除整个链表
void del_node(struct double_list *del) //将节点地址传递过去
{
del->prev->next = del->next; //del前缀节点里的next存放del后缀节点地址
del->next->prev = del->prev; //del后缀节点里的prev存放del前缀节点地址
del->next = del; //del里面的next指向自己
del->prev = del; //del里面的prev指向自己
}
void free_all_node(struct double_list *head) //将节点地址传递过去
{
struct double_list *p, *del;
p = head->next; //p第一个有数据的节点
while(p != head)
{
del_node(p); //将节点地址传递过去
free(p);
p = head->next; //p第一个有数据的节点
}
free(head); //释放头节点
}
图解
3、内核链表
内核链表:/home/gec/Download/linux-2.6.35.7-gec/include/linux/list.h
内核链表其实就是一个双向循环链表
记得:内核链表操作都是小结构体
内核链表函数说明
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list) //初始小结体
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head) //将节点插入链表当中
list_for_each(pos, head) //往后遍历链表,pos是遍历过程的各个大结构体的小结构体的地址,head是大结构体头的小结构体
list_entry(ptr, type, member)通过小结构得到大结构体地址,member是大结构里小结构的名称
list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) 直接遍历得到大结构体,member是大结构里小结构的名称,pos是遍历过程的各个大结构体的小结构体的地址
list_for_each_prev(pos, head) 往前面遍历链表
void list_del(struct list_head *entry)删除节点(解除节点)
list_del_init(struct list_head *entry)删除节点并让节点指向自己(解除节点)
list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) //内核链表移动
list_cut_position(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry) //链表分解
list_splice_init(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)//链表合成
1、内核链表节点设计
struct kernel_node
{
int data;
struct list_head list;
};
2、节点初始化
struct kernel_node *kernel_Init(void)
{
struct kernel_node *p;
//在堆空间开辟内存
p = (struct kernel_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct kernel_node));
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("malloc failure
");
return NULL;
}
p->data = 0;
//小结构初始化
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->list);
return p;
}
3、显示所有节点
void display_node(struct kernel_node *head)
{
struct kernel_node *tmp;//用于存储大结构体指针
list_for_each_entry(tmp, &head->list, list)
{
printf("%d ",tmp->data);
}
printf("
");
}
4、查找结点
struct kernel_node *find_node(struct kernel_node *head,int find_data)
{
struct list_head *pos;
struct kernel_node *tmp;//用于存储大结构体指针
list_for_each(pos, &head->list) //通过小结构体遍历链表
{
tmp = list_entry(pos,struct kernel_node,list); //通过小结构体得到大结构体
if(tmp->data == find_data)
return tmp;
}
return NULL;
}
内核链表头文件kernel_list.h
#ifndef __LIST_H
#define __LIST_H
/* This file is from Linux Kernel (include/linux/list.h)
* and modified by simply removing hardware prefetching of list items.
* Here by copyright, credits attributed to wherever they belong.
* Kulesh Shanmugasundaram (kulesh [squiggly] isis.poly.edu)
*/
/*
* Simple doubly linked list implementation.
*
* Some of the internal functions (“__xxx”) are useful when
* manipulating whole lists rather than single entries, as
* sometimes we already know the next/prev entries and we can
* generate better code by using them directly rather than
* using the generic single-entry routines.
*/
/**
* container_of - cast a member of a structure out to the containing structure
*
* @ptr: the pointer to the member.
* @type: the type of the container struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the member within the struct.
*
*/
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER)
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({
const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr);
(type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );})
/*
* These are non-NULL pointers that will result in page faults
* under normal circumstances, used to verify that nobody uses
* non-initialized list entries.
*/
#define LIST_POISON1 ((void *) 0x00100100)
#define LIST_POISON2 ((void *) 0x00200)
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next;
struct list_head *prev;
};
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
#define LIST_HEAD(name)
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{
list->next = list;
list->prev = list;
}
/*
* Insert a new entry between two known consecutive entries.
*
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
* the prev/next entries already!
*/
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new, // 要插入的节点
struct list_head *prev,// 前节点 before
struct list_head *next) // 后节点 after
{
next->prev = new; // 后节点的上家为new
new->next = next;
new->prev = prev;
prev->next = new;
}
/**
* list_add – add a new entry
* @new: new entry to be added
* @head: list head to add it after
*
* Insert a new entry after the specified head.
* This is good for implementing stacks.
*/
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head, head->next);
}
/**
* list_add_tail – add a new entry
* @new: new entry to be added
* @head: list head to add it before
*
* Insert a new entry before the specified head.
* This is useful for implementing queues.
*/
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head) //
{
__list_add(new, head->prev, head);
}
/*
* Delete a list entry by making the prev/next entries
* point to each other.
*
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
* the prev/next entries already!
*/
static inline void __list_del(struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = prev;
prev->next = next;
}
/**
* list_del – deletes entry from list.
* @entry: the element to delete from the list.
* Note: list_empty on entry does not return true after this, the entry is in an undefined state.
*/
static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
entry->next = (void *) 0;
entry->prev = (void *) 0;
}
/**
* list_del_init – deletes entry from list and reinitialize it.
* @entry: the element to delete from the list.
*/
static inline void list_del_init(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry);
}
/**
* list_move – delete from one list and add as another’s head
* @list: the entry to move
* @head: the head that will precede our entry
*/
static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del(list->prev, list->next);
list_add(list, head);
}
/**
* list_move_tail – delete from one list and add as another’s tail
* @list: the entry to move
* @head: the head that will follow our entry
*/
static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del(list->prev, list->next);
list_add_tail(list, head);
}
/**
* list_empty – tests whether a list is empty
* @head: the list to test.
*/
static inline int list_empty(struct list_head *head)
{
return head->next == head;
}
static inline void __list_splice(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
struct list_head *first = list->next;
struct list_head *last = list->prev;
struct list_head *at = head->next;
first->prev = head;
head->next = first;
last->next = at;
at->prev = last;
}
/**
* list_splice – join two lists
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*/
static inline void list_splice(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list))
__list_splice(list, head);
}
/**
* list_splice_init – join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list.
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*
* The list at @list is reinitialised
*/
static inline void list_splice_init(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list)) {
__list_splice(list, head);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
}
}
static inline int list_is_singular( struct list_head *head)
{
return !list_empty(head) && (head->next == head->prev);
}
static inline void __list_cut_position(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry)
{
struct list_head *new_first = entry->next;
list->next = head->next;
list->next->prev = list;
list->prev = entry;
entry->next = list;
head->next = new_first;
new_first->prev = head;
}
/**
* list_cut_position - cut a list into two
* @list: a new list to add all removed entries
* @head: a list with entries
* @entry: an entry within head, could be the head itself
* and if so we won't cut the list
*
* This helper moves the initial part of @head, up to and
* including @entry, from @head to @list. You should
* pass on @entry an element you know is on @head. @list
* should be an empty list or a list you do not care about
* losing its data.
*
*/
static inline void list_cut_position(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry)
{
if (list_empty(head))
return;
if (list_is_singular(head) &&
(head->next != entry && head != entry))
return;
if (entry == head)
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
else
__list_cut_position(list, head, entry);
}
/**
* list_entry – get the struct for this entry
* @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer. 移动的小结构体对应的地址
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in. 大结构体类型 (struct info)
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 小结构体在大结构体里面的成员名list
*///返回值为大结构体地址
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member)
((type *)((char *)(ptr)-(size_t)(&((type *)0)->member)))
/**
* list_for_each - iterate over a list
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop counter. // p
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define list_for_each(pos, head)
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head);
pos = pos->next)
/**
* list_for_each_prev - iterate over a list backwards
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop counter.
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
//向前遍历
#define list_for_each_prev(pos, head)
for (pos = (head)->prev; pos != (head);
pos = pos->prev)
/**
* list_for_each_safe - iterate over a list safe against removal of list entry
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop counter.
* @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
//安全的遍历删除
#define list_for_each_safe(pos, n, head)
for (pos = (head)->next, n = pos->next; pos != (head);
pos = n, n = pos->next)
/**
* list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop counter. 大结构体指针
* @head: the head for your list. 小结构体指针
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 小结构体在大结构体里面的成员名list
*/
//向后直接遍历得到大结构体
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member)
for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member);
&pos->member != (head);
pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_safe – iterate over list of given type safe against removal of list entry
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop counter.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, n, head, member)
for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member),
n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member);
&pos->member != (head);
pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member))
#endif
内核链表图解
