一、weak_ptr出现的意义
上一节提到过shared_ptr,它会自动释放“不再需要使用的对象”的相应的资源,但是它不是万能的,在某些时候(比如说循环引用),它会显得力不从心,这就是weak_ptr出现的意义;
1.1 weak_ptr 使用特性
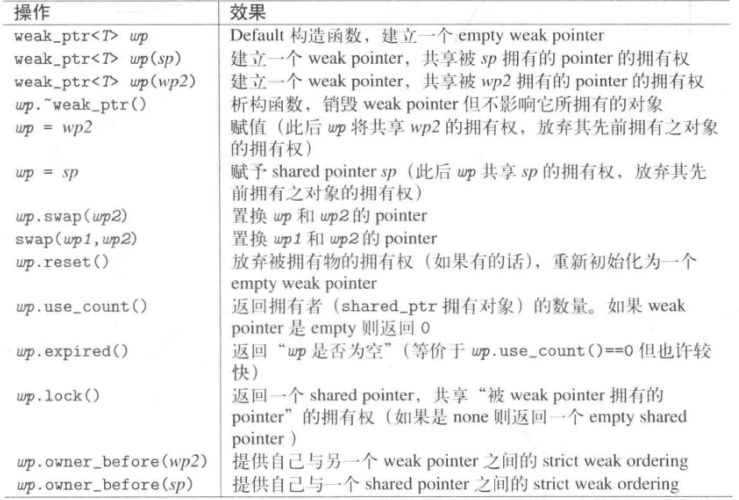
weak_ptr也是一个模板,只提供能接受一个shared_ptr的构造函数或者另一个weak_ptr的赋值,也就是说不能直接用它定义一个智能指针对象,它是为了搭配shared_ptr使用的,weak_ptr提供lock、swap、reset、expired、operator=、use_count等函数,相对shared_ptr多了lock、expired函数,却少了get函数,也不支持operator* 和 operator->
二、weak_ptr使用测试
2.1 以下例子在shared_ptr循环引用时的弊端
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <memory> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 class Person { 8 public: 9 string name; 10 shared_ptr<Person> mother; 11 shared_ptr<Person> father; 12 vector<shared_ptr<Person>> kids; 13 14 Person(const string& n, 15 shared_ptr<Person> m = nullptr, 16 shared_ptr<Person> f = nullptr) 17 : name(n), mother(m), father(f) { 18 } 19 20 ~Person() { 21 cout << "delete " << name << endl; 22 } 23 }; 24 25 shared_ptr<Person> initFamily(const string& name) 26 { 27 shared_ptr<Person> mom(new Person(name + "'s mom")); 28 shared_ptr<Person> dad(new Person(name + "'s dad")); 29 shared_ptr<Person> kid(new Person(name, mom, dad)); 30 //以下是为了统计引用次数 31 cout << "1 mom is shared " << mom.use_count() << " times" << endl; 32 cout << "1 dad is shared " << dad.use_count() << " times" << endl; 33 cout << "1 kid is shared " << kid.use_count() << " times" << endl; 34 mom->kids.push_back(kid); 35 dad->kids.push_back(kid); 36 cout << "mom is shared " << mom.use_count() << " times" << endl; 37 cout << "dad is shared " << dad.use_count() << " times" << endl; 38 cout << "kid is shared " << kid.use_count() << " times" << endl; 39 return kid; 40 } 41 42 int main() 43 { 44 shared_ptr<Person> p = initFamily("nico"); 45 46 cout << "nico's family exists" << endl; 47 cout << "- nico is shared " << p.use_count() << " times" << endl; 48 cout << "- name of 1st kid of nico's mom: " 49 << p->mother->kids[0]->name << endl; 50 51 p = initFamily("jim"); 52 cout << "jim's family exists" << endl; 53 }

上述例子解释:首先我们initFamily函数建立Person:mom 、dad和kid,根据传入的实参将所有姓名初始化,并且还将kid插入到其父母的容器中,最终initFamily函数返回kid并赋值给p,p其实指向上述家庭的最后一个handle,因此在p被赋值之前nico共被共享3次,现在如果我们释放这个p(释放方式:(1)给p指向一个新的person或者赋值为nullptr;(2)main()函数结束时离开p的作用域),但是我们看到程序输出的结果是没有任何person被释放(没有执行析构函数),因为他们都至少被一个shared_ptr指向,于是析构函数都无法执行,这就是循环指向的问题。
如下是引入weak_ptr来解决循环指向的问题:我们可以把kid申明为一个类型为weak_ptr类型的vector。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <memory> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 class Person { 8 public: 9 string name; 10 shared_ptr<Person> mother; 11 shared_ptr<Person> father; 12 vector<weak_ptr<Person>> kids; // weak pointer !!! 13 14 Person(const string& n, 15 shared_ptr<Person> m = nullptr, 16 shared_ptr<Person> f = nullptr) 17 : name(n), mother(m), father(f) { 18 } 19 20 ~Person() { 21 cout << "delete " << name << endl; 22 } 23 }; 24 25 shared_ptr<Person> initFamily(const string& name) 26 { 27 shared_ptr<Person> mom(new Person(name + "'s mom")); 28 shared_ptr<Person> dad(new Person(name + "'s dad")); 29 shared_ptr<Person> kid(new Person(name, mom, dad)); 30 //以下是为了统计引用次数 31 cout << "1 mom is shared " << mom.use_count() << " times" << endl; 32 cout << "1 dad is shared " << dad.use_count() << " times" << endl; 33 cout << "1 kid is shared " << kid.use_count() << " times" << endl; 34 mom->kids.push_back(kid); 35 dad->kids.push_back(kid); 36 cout << "mom is shared " << mom.use_count() << " times" << endl; 37 cout << "dad is shared " << dad.use_count() << " times" << endl; 38 cout << "kid is shared " << kid.use_count() << " times" << endl; 39 return kid; 40 } 41 42 int main() 43 { 44 shared_ptr<Person> p = initFamily("nico"); 45 46 cout << "nico's family exists" << endl; 47 cout << "- nico is shared " << p.use_count() << " times" << endl; 48 cout << "- name of 1st kid of nico's mom: " 49 << p->mother->kids[0].lock()->name << endl;
//上述使用了lock函数,lock函数来获取其对应的shared_ptr对象,下面详细解释 50 51 p = initFamily("jim"); 52 cout << "jim's family exists" << endl; 53 }
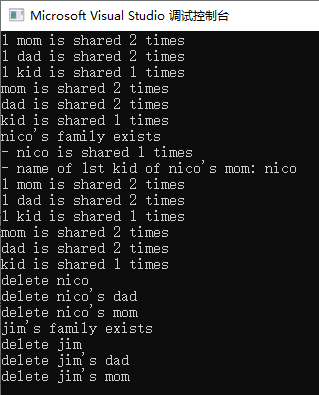
上述解析:关键就在于使用的weak_ptr相比于shared_ptr,没有增加kid的引用计数,所以再最后离开main作用域后能准确调用析构函数,上面例子重要的函数时lock,我们可以将mon(shared_ptr)指针直接赋值给weak_ptr(反之不行),其实weak_ptr 最重要的函数只有lock和expired两个函数,因为weak_ptr本身不会增加引用计数,所以当我们要使用时就要用lock函数,lock()会产生出一个shared_ptr(也就说使用之前必须复制到 shared_ptr)进而像普通指针一样使用。
关键函数解析:
-
operator=
void operator=(std::weak_ptr<T> desired) noexcept;为weak_ptr赋值,weak_ptr接受shared_ptr类型的变量赋值,但是反过来是行不通的,需要使用lock函数。
-
reset
void reset() noexcept;释放被管理对象的所有权。调用后 *this 不管理对象。
-
swap
void swap( weak_ptr& r ) noexcept;交换 *this 与 r 的内容。
-
use_count
long use_count() const noexcept;返回共享被管理对象所有权的 shared_ptr 实例数量,或 0 ,若被管理对象已被删除,即 *this 为空。
-
expired
bool expired() const noexcept;检查被引用的对象是否已删除,等价于 use_count() == 0,但是比use_count快,若被管理对象已被删除则为 true ,否则为 false 。由于不知道对象是否已经被析构,最好使用之前先使用expired函数检测一下。
-
lock
std::shared_ptr<T> lock() const noexcept;创建新的 std::shared_ptr 对象,它共享被管理对象的所有权。若无被管理对象,即 *this 为空,则返回亦为空的 shared_ptr ,等效地返回 expired() ? shared_ptr<T>() : shared_ptr<T>(*this) ,原子地执行。
2.2 常见成员函数以及分类介绍