坚持到第10章了,继续努力!
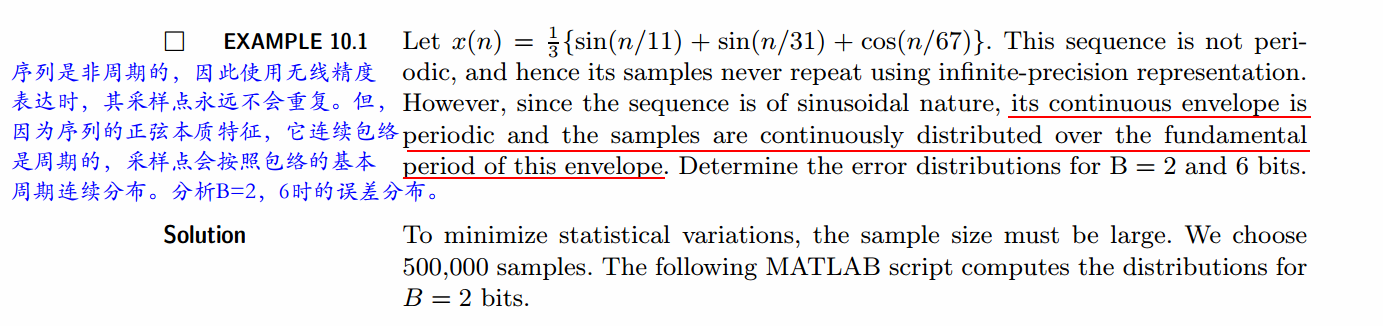
代码:
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% Output Info about this m-file
fprintf('
***********************************************************
');
fprintf(' <DSP using MATLAB> Exameple 10.1
');
time_stamp = datestr(now, 31);
[wkd1, wkd2] = weekday(today, 'long');
fprintf(' Now is %20s, and it is %7s
', time_stamp, wkd2);
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
clear; close all;
% Example parameters
B = 2; N = 500000; n = [1:N];
xn = (1/3)*(sin(n/11) + sin(n/31) + cos(n/67)); clear n;
% Quantization error analysis
[H1, H2, Q, estat] = StatModelR(xn, B, N); % Compute histograms
H1max = max(H1); H1min = min(H1); % Max and Min of H1
H2max = max(H2); H2min = min(H2); % Max and Min of H2
Hf1 = figure('units', 'inches', 'position', [1, 1, 8, 6], ...
'paperunits', 'inches', 'paperposition', [0, 0, 6, 4], ...
'NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Exameple 10.1a');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
TF = 10;
title('Normalized error e1 and e2');
subplot(2, 1, 1);
bar(Q, H1); axis([-0.5, 0.5, -0.001, 4/128]); grid on;
xlabel('Normalized error e1'); ylabel('Distribution of e1 ', 'vertical', 'baseline');
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, [1:1:4]/128] );
text(-0.45, 0.030, sprintf('SAMPLE SIZE N = %d', N));
text(-0.45, 0.025, sprintf(' ROUNDED TO B = %d BITS', B));
text(-0.45, 0.020, sprintf(' MEAN = %.4e', estat(1)));
text(0.10, 0.030, sprintf('MIN PROB BAR HEIGHT = %f', H1min)) ;
text(0.10, 0.025, sprintf('MAX PROB BAR HEIGHT = %f', H1max)) ;
text(0.10, 0.020, sprintf(' SIGMA = %f', estat(2))) ;
subplot(2, 1, 2);
bar(Q, H2); axis([-0.5, 0.5, -0.001, 4/128]); grid on;
%title('Normalized error e2');
xlabel('Normalized error e2'); ylabel('Distribution of e2', 'vertical', 'baseline');
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, 1:1:4]/128 );
text(-0.45, 0.030, sprintf('SAMPLE SIZE N = %d', N));
text(-0.45, 0.025, sprintf(' ROUNDED TO B = %d BITS', B));
text(-0.45, 0.020, sprintf(' MEAN = %.4e', estat(3)));
text(0.10, 0.030, sprintf('MIN PROB BAR HEIGHT = %f', H2min)) ;
text(0.10, 0.025, sprintf('MAX PROB BAR HEIGHT = %f', H2max)) ;
text(0.10, 0.020, sprintf(' SIGMA = %f', estat(4))) ;
%% ---------------------------------------------------------------------
%% B = 6
%% ---------------------------------------------------------------------
% Example parameters
B = 6; N = 500000; n = [1:N];
xn = (1/3)*(sin(n/11) + sin(n/31) + cos(n/67)); clear n;
% Quantization error analysis
[H1, H2, Q, estat] = StatModelR(xn, B, N); % Compute histograms
H1max = max(H1); H1min = min(H1); % Max and Min of H1
H2max = max(H2); H2min = min(H2); % Max and Min of H2
Hf2 = figure('units', 'inches', 'position', [1, 1, 8, 6], ...
'paperunits', 'inches', 'paperposition', [0, 0, 6, 4], ...
'NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Exameple 10.1b');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
TF = 10;
subplot(2, 1, 1);
bar(Q, H1); axis([-0.5, 0.5, -0.001, 4/128]); grid on;
title('Normalized error e1'); ylabel('Distribution of e1 ', 'vertical', 'baseline');
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, 1:1:4]/128 );
text(-0.45, 0.030, sprintf('SAMPLE SIZE N = %d', N));
text(-0.45, 0.025, sprintf(' ROUNDED TO B = %d BITS', B));
text(-0.45, 0.020, sprintf(' MEAN = %.4e', estat(1)));
text(0.10, 0.030, sprintf('MIN PROB BAR HEIGHT = %f', H1min)) ;
text(0.10, 0.025, sprintf('MAX PROB BAR HEIGHT = %f', H1max)) ;
text(0.10, 0.020, sprintf(' SIGMA = %.7f', estat(2))) ;
subplot(2, 1, 2);
bar(Q, H2); axis([-0.5, 0.5, -0.001, 4/128]); grid on;
title('Normalized error e2'); ylabel('Distribution of e2', 'vertical', 'baseline');
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, 1:1:4]/128 );
text(-0.45, 0.030, sprintf('SAMPLE SIZE N = %d', N));
text(-0.45, 0.025, sprintf(' ROUNDED TO B = %d BITS', B));
text(-0.45, 0.020, sprintf(' MEAN = %.4e', estat(3)));
text(0.10, 0.030, sprintf('MIN PROB BAR HEIGHT = %f', H2min)) ;
text(0.10, 0.025, sprintf('MAX PROB BAR HEIGHT = %f', H2max)) ;
text(0.10, 0.020, sprintf(' SIGMA = %.7f', estat(4))) ;
运行结果:
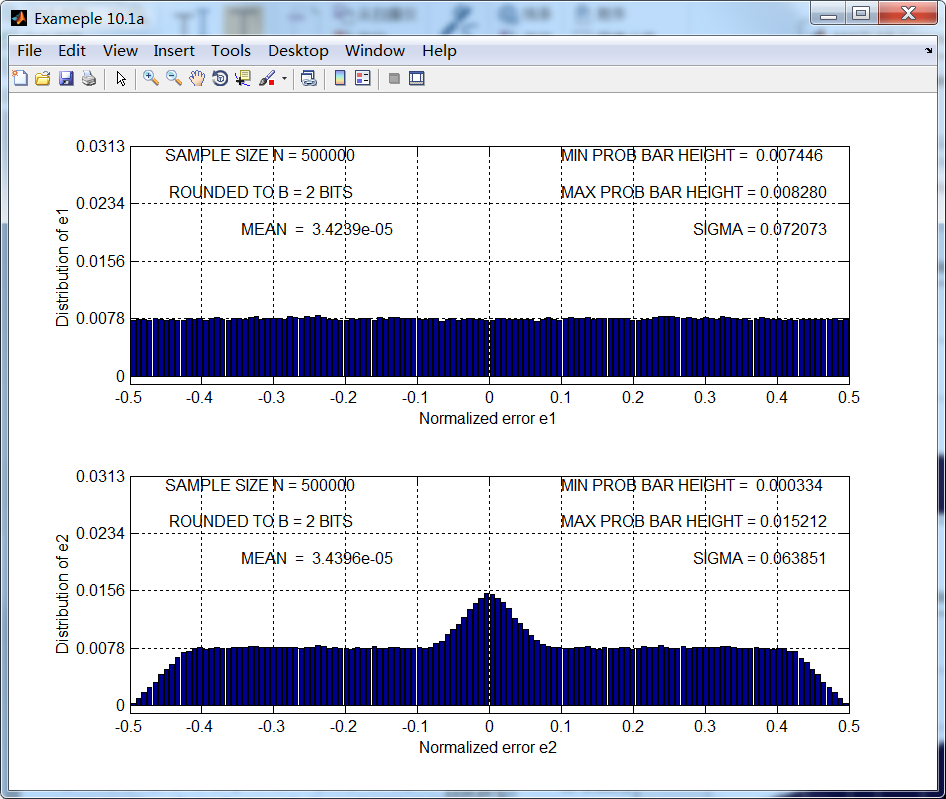
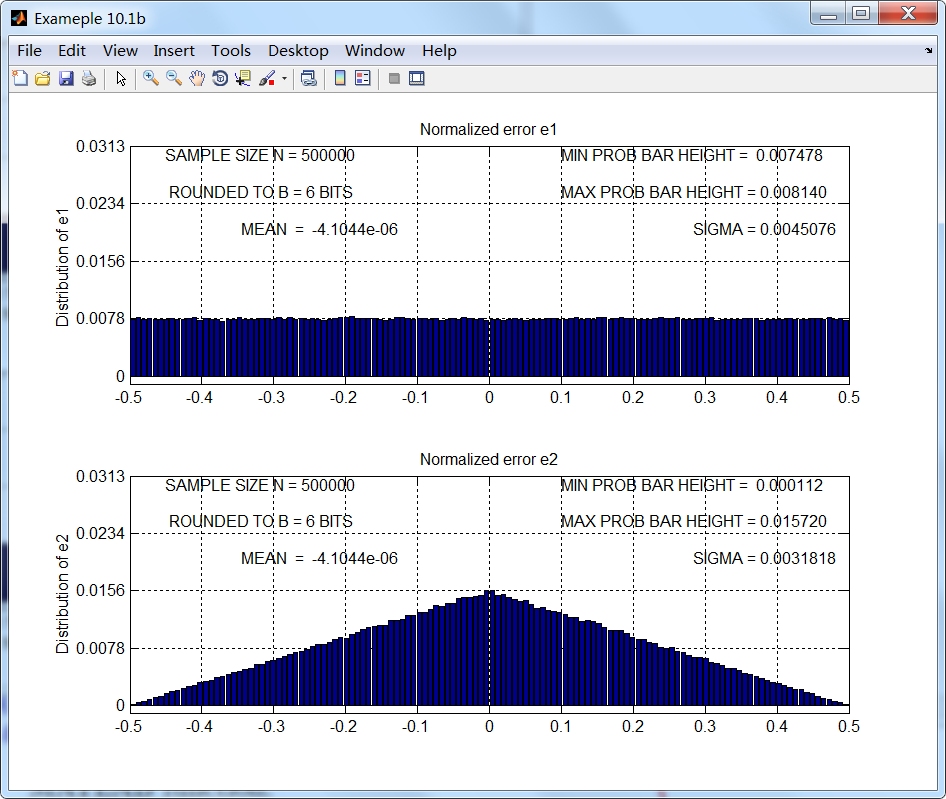
B=2的结果如第1张图所示,很明显,即使误差看起来均匀分布,但误差采样序列不是独立的。对应B=6的
结果如第2张图所示,当B≥6时,结果满足误差模型假设条件。