1 线程初步
进程->多进程。单核CPU时,多进程资源抢占,一个时间点只能有一个进程执行。
线程是在进程基础上划分得更小的单元。
多线程是java的优势。
1.1 继承Thread类实现多线程
class MyThread extends Thread{ private String title; public MyThread(String title) { this.title = title; } @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { System.out.println(this.title + "运行。 i="+i); } } }
1.1.1 使用start()方法开始执行
使用run()会顺序执行。
public class ThreadDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) { new MyThread("ThreadA").run(); new MyThread("ThreadB").run(); new MyThread("ThreadC").run(); } }
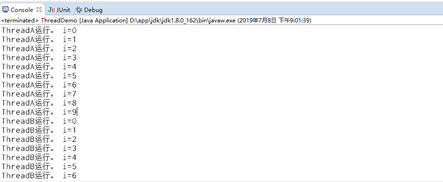
1.1.2 start()
每一个线程类只会执行一次,重复执行就会抛出IllegalThreadStateException()异常
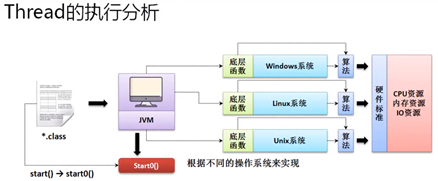
JNI(Java Native Inteface)技术,Thread的native需要依托于操作系统执行。
任何情况下,只要定义了多线程,多线程的启动永远只有一种方案:Thread类中的start() 方法。
public synchronized void start() { if (threadStatus != 0) throw new IllegalThreadStateException(); group.add(this); boolean started = false; try { start0(); started = true; } finally { try { if (!started) { group.threadStartFailed(this); } } catch (Throwable ignore) { } } }
1.2 基于Runnable接口实现多线程
1.2.1 没有单继承的局限
@FunctionalInterface public interface Runnable { public abstract void run(); }
class MyThread implements Runnable{ private String title; public MyThread(String title) { this.title = title; } @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { System.out.println(this.title + "运行。 i="+i); } } }
public class ThreadDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) { new Thread(new MyThread("ThreadA")).start(); new Thread(new MyThread("ThreadB")).start(); new Thread(new MyThread("ThreadC")).start(); } }
1.2.2 Runnable接口使用了函数式的接口定义
public class ThreadDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) { for(int x=0;x<3;x++) { String title = "线程对象-"+x; new Thread(()->{ for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { System.out.println(title + "运行。 i="+i); } }).start(); } } }
1.3 小结
以后的开发中对于多线程的实现,优先考虑Runnable接口实现,并且永恒都是通过Thread类对象启动多线程
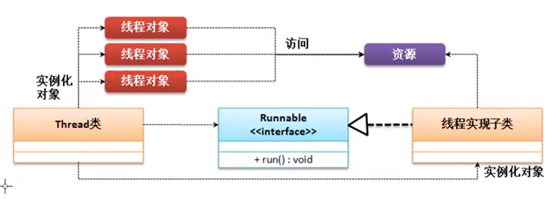
1.4 Thread与Runnable关系
1.4.1 Thread 是Runnable的实现类
public class Thread implements Runnable {}
1.4.2 多线程设计中使用了代理设计模式
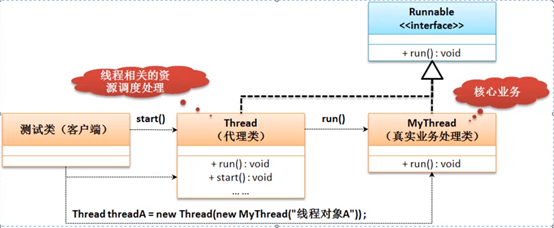
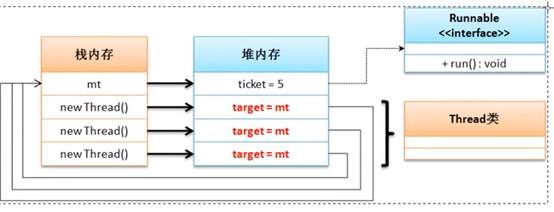
1.4.3 多线程访问同一资源
通过Thread类的构造方法传入runnable接口对象时,会将runnable对象保存到target对象,run()时执行target的run()方法。
class MyThread implements Runnable{ private int ticket = 5 ; private String title; @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<100;i++) { if(this.ticket>0) { System.out.println(this.title + "卖票。 i="+this.ticket --); } } } } public class ThreadDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread mt = new MyThread(); new Thread(mt).start(); new Thread(mt).start(); new Thread(mt).start(); } }
1.5 Callable接口实现多线程
@FunctionalInterface public interface Callable<V> { V call() throws Exception; }
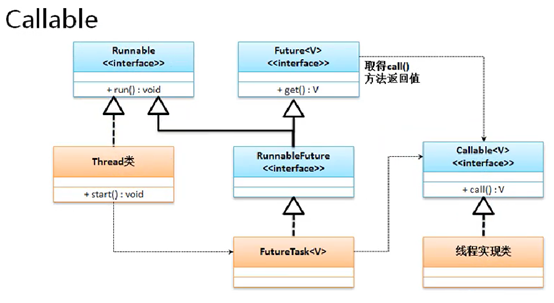
Runnable和Callable的区别:
- Runnable是在JDK1.0+实现,Callable是在JDK1.5+实现。
- Runnable接口中有一个run()方法,无返回值。
- Callable接口提供call()方法,有返回值。
class MyThread implements Callable<String>{ @Override public String call() throws Exception { for(int x =0;x<10;x++) { System.out.println("线程执行,x="+x); } return "线程执行完毕"; } } public class ThreadDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { FutureTask<String> task = new FutureTask<>(new MyThread()); new Thread(task).start(); System.out.println("线程返回数据:"+task.get()); } }
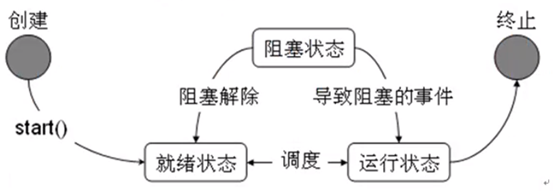
1.6 多线程运行状态