Robotic Sort
Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1640 Accepted Submission(s): 711
Problem Description
Somewhere deep in the Czech Technical University buildings, there are laboratories for examining mechanical and electrical properties of various materials. In one of yesterday’s presentations, you have seen how was one of the laboratories changed into a new multimedia lab. But there are still others, serving to their original purposes.
In this task, you are to write software for a robot that handles samples in such a laboratory. Imagine there are material samples lined up on a running belt. The samples have different heights, which may cause troubles to the next processing unit. To eliminate such troubles, we need to sort the samples by their height into the ascending order.
Reordering is done by a mechanical robot arm, which is able to pick up any number of consecutive samples and turn them round, such that their mutual order is reversed. In other words, one robot operation can reverse the order of samples on positions between A and B.
A possible way to sort the samples is to find the position of the smallest one (P1) and reverse the order between positions 1 and P1, which causes the smallest sample to become first. Then we find the second one on position P and reverse the order between 2 and P2. Then the third sample is located etc.
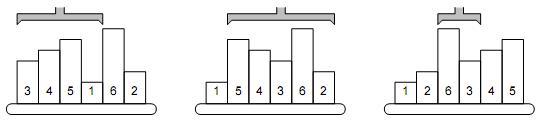
The picture shows a simple example of 6 samples. The smallest one is on the 4th position, therefore, the robot arm reverses the first 4 samples. The second smallest sample is the last one, so the next robot operation will reverse the order of five samples on positions 2–6. The third step will be to reverse the samples 3–4, etc.
Your task is to find the correct sequence of reversal operations that will sort the samples using the above algorithm. If there are more samples with the same height, their mutual order must be preserved: the one that was given first in the initial order must be placed before the others in the final order too.
In this task, you are to write software for a robot that handles samples in such a laboratory. Imagine there are material samples lined up on a running belt. The samples have different heights, which may cause troubles to the next processing unit. To eliminate such troubles, we need to sort the samples by their height into the ascending order.
Reordering is done by a mechanical robot arm, which is able to pick up any number of consecutive samples and turn them round, such that their mutual order is reversed. In other words, one robot operation can reverse the order of samples on positions between A and B.
A possible way to sort the samples is to find the position of the smallest one (P1) and reverse the order between positions 1 and P1, which causes the smallest sample to become first. Then we find the second one on position P and reverse the order between 2 and P2. Then the third sample is located etc.

The picture shows a simple example of 6 samples. The smallest one is on the 4th position, therefore, the robot arm reverses the first 4 samples. The second smallest sample is the last one, so the next robot operation will reverse the order of five samples on positions 2–6. The third step will be to reverse the samples 3–4, etc.
Your task is to find the correct sequence of reversal operations that will sort the samples using the above algorithm. If there are more samples with the same height, their mutual order must be preserved: the one that was given first in the initial order must be placed before the others in the final order too.
Input
The input consists of several scenarios. Each scenario is described by two lines. The first line contains one integer number N , the number of samples, 1 ≤ N ≤ 100 000. The second line lists exactly N space-separated positive integers, they specify the heights of individual samples and their initial order.
The last scenario is followed by a line containing zero.
The last scenario is followed by a line containing zero.
Output
For each scenario, output one line with exactly N integers P1 , P1 , . . . PN ,separated by a space.
Each Pi must be an integer (1 ≤ Pi ≤ N ) giving the position of the i-th sample just before the i-th reversal operation.
Note that if a sample is already on its correct position Pi , you should output the number Pi anyway, indicating that the “interval between Pi and Pi ” (a single sample) should be reversed.
Each Pi must be an integer (1 ≤ Pi ≤ N ) giving the position of the i-th sample just before the i-th reversal operation.
Note that if a sample is already on its correct position Pi , you should output the number Pi anyway, indicating that the “interval between Pi and Pi ” (a single sample) should be reversed.
Sample Input
6
3 4 5 1 6 2
4
3 3 2 1
0
Sample Output
4 6 4 5 6 6
4 2 4 4
Source
Recommend
linle
splay tree
旋转操作
1 /* *********************************************** 2 Author :kuangbin 3 Created Time :2013/8/24 23:28:43 4 File Name :F:2013ACM练习专题学习splay_tree_2HDU1890.cpp 5 ************************************************ */ 6 7 #include <stdio.h> 8 #include <string.h> 9 #include <iostream> 10 #include <algorithm> 11 #include <vector> 12 #include <queue> 13 #include <set> 14 #include <map> 15 #include <string> 16 #include <math.h> 17 #include <stdlib.h> 18 #include <time.h> 19 using namespace std; 20 21 #define Key_value ch[ch[root][1]][0] 22 const int MAXN = 100010; 23 int pre[MAXN],ch[MAXN][2],root,tot1; 24 int size[MAXN];//子树规模 25 int rev[MAXN];//反转标记 26 int s[MAXN],tot2;//内存池和容量 27 28 //debug部分********************************** 29 void Treavel(int x) 30 { 31 if(x) 32 { 33 Treavel(ch[x][0]); 34 printf("结点:%2d: 左儿子 %2d 右儿子 %2d 父结点 %2d size = %2d rev = %2d ",x,ch[x][0],ch[x][1],pre[x],size[x],rev[x]); 35 Treavel(ch[x][1]); 36 } 37 } 38 void debug() 39 { 40 printf("root:%d ",root); 41 Treavel(root); 42 } 43 //以上是debug部分************************************** 44 45 46 void NewNode(int &r,int father,int k) 47 { 48 r = k; 49 pre[r] = father; 50 ch[r][0] = ch[r][1] = 0; 51 size[r] = 1; 52 rev[r] = 0; 53 } 54 //反转的更新 55 void Update_Rev(int r) 56 { 57 if(!r)return; 58 swap(ch[r][0],ch[r][1]); 59 rev[r] ^= 1; 60 } 61 inline void push_up(int r) 62 { 63 size[r] = size[ch[r][0]] + size[ch[r][1]] + 1; 64 } 65 inline void push_down(int r) 66 { 67 if(rev[r]) 68 { 69 Update_Rev(ch[r][0]); 70 Update_Rev(ch[r][1]); 71 rev[r] = 0; 72 } 73 } 74 void Build(int &x,int l,int r,int father) 75 { 76 if(l > r)return; 77 int mid = (l+r)/2; 78 NewNode(x,father,mid); 79 Build(ch[x][0],l,mid-1,x); 80 Build(ch[x][1],mid+1,r,x); 81 push_up(x); 82 } 83 int n; 84 void Init() 85 { 86 root = tot1 = tot2 = 0; 87 ch[root][0] = ch[root][1] = pre[root] = size[root] = rev[root] = 0; 88 NewNode(root,0,n+1); 89 NewNode(ch[root][1],root,n+2); 90 Build(Key_value,1,n,ch[root][1]); 91 push_up(ch[root][1]); 92 push_up(root); 93 } 94 //旋转,0为左旋,1为右旋 95 inline void Rotate(int x,int kind) 96 { 97 int y = pre[x]; 98 push_down(y); 99 push_down(x);//先把y的标记下传,在把x的标记下传 100 ch[y][!kind] = ch[x][kind]; 101 pre[ch[x][kind]] = y; 102 if(pre[y]) 103 ch[pre[y]][ch[pre[y]][1]==y] = x; 104 pre[x] = pre[y]; 105 ch[x][kind] = y; 106 pre[y] = x; 107 push_up(y); 108 } 109 //Splay调整,将r结点调整到goal下面 110 inline void Splay(int r,int goal) 111 { 112 push_down(r); 113 while(pre[r] != goal) 114 { 115 if(pre[pre[r]] == goal) 116 { 117 //有反转操作,需要先push_down,再判断左右孩子 118 push_down(pre[r]); 119 push_down(r); 120 Rotate(r,ch[pre[r]][0]==r); 121 } 122 else 123 { 124 //有反转操作,需要先push_down 125 push_down(pre[pre[r]]); 126 push_down(pre[r]); 127 push_down(r); 128 int y = pre[r]; 129 int kind = ch[pre[y]][0]==y; 130 if(ch[y][kind] == r) 131 { 132 Rotate(r,!kind); 133 Rotate(r,kind); 134 } 135 else 136 { 137 Rotate(y,kind); 138 Rotate(r,kind); 139 } 140 } 141 } 142 push_up(r); 143 if(goal == 0) root = r; 144 } 145 //得到第k个结点(需要push_down) 146 inline int Get_kth(int r,int k) 147 { 148 push_down(r); 149 int t = size[ch[r][0]] + 1; 150 if(t == k)return r; 151 if(t > k)return Get_kth(ch[r][0],k); 152 else return Get_kth(ch[r][1],k-t); 153 } 154 //找前驱(需要push_down) 155 inline int Get_pre(int r) 156 { 157 push_down(r); 158 if(ch[r][0] == 0)return -1;//不存在 159 r = ch[r][0]; 160 while(ch[r][1]) 161 { 162 r = ch[r][1]; 163 push_down(r); 164 } 165 return r; 166 } 167 //找后继(需要push_down) 168 inline int Get_next(int r) 169 { 170 push_down(r); 171 if(ch[r][1] == 0)return -1; 172 r = ch[r][1]; 173 while(ch[r][0]) 174 { 175 r = ch[r][0]; 176 push_down(r); 177 } 178 return r; 179 } 180 181 struct Node 182 { 183 int id,val; 184 }node[MAXN]; 185 bool cmp(Node a,Node b) 186 { 187 if(a.val != b.val)return a.val < b.val; 188 else return a.id < b.id; 189 } 190 int main() 191 { 192 //freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); 193 //freopen("out.txt","w",stdout); 194 while(scanf("%d",&n) == 1 && n) 195 { 196 for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) 197 { 198 scanf("%d",&node[i].val); 199 node[i].id = i; 200 } 201 sort(node+1,node+n+1,cmp); 202 Init(); 203 for(int i = 1; i <= n;i++) 204 { 205 Splay(node[i].id,0); 206 printf("%d",size[ch[root][0]]); 207 if(i < n)printf(" "); 208 else printf(" "); 209 Splay(Get_kth(root,i),0); 210 Splay(Get_next(node[i].id),root); 211 Update_Rev(Key_value); 212 } 213 } 214 return 0; 215 }