1.边框渐变
如:
.arrow div {transition: border-color 0.5s ease-in-out; }
.arrow div:hover {border-color: #009688; }
flex的兼容性在pc端还算阔以,但是在移动端,那就呵呵了。今天我们只是学习学习,忽略一些不重要的东西。
首先flex的使用需要有一个父容器,父容器中有几个items.
父容器:container
属性:
display:flex;/*flex块级,inline-flex:行内快*/
justify-content:space-around;/*center:水平居中,flex-start:靠左;flex-end:靠右;space-between:两边的向两边靠,中间等分;space-around:完美的平均分配*/
align-items:stretch;/*center:垂直居中、flex-start:至顶、flex-end:至底、space-between、space-around*/
flex-direction: row;/*column从上向下的排列,column-reverse、row:从左到右,row-reverse:从右向左*/
flex-wrap:wrap;/*wrap多行显示(父容器不够显示的时候,从上到下)、nowrap(当容器不够宽的时候,子元素会平分父容器的宽或者高)、wrap-reverse:从下向上*/
/*flex-flow是flex-direction、flex-wrap的缩写*/
这里给出一个简单的demo:
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="Generator" content="EditPlus®"> <style> .container{ width:600px; height:400px; border:1px solid #000; display:flex;/*flex块级,inline-flex:行内快*/ justify-content:space-around;/*center:水平居中,flex-start:靠左;flex-end:靠右;space-between:两边的向两边靠,中间等分;space-around:完美的平均分配*/ align-items:stretch;/*center:垂直居中、flex-start,至顶,flex-end:至底*,space-between、space-around*/ flex-direction: row;/*column从上向下的排列,column-reverse,,,,row:从左到右,row-reverse:从右向左*/ flex-wrap:wrap;/*wrap多行显示(父容器不够显示的时候,从上到下)、nowrap(当容器不够宽的时候,子元素会平分父容器的宽或者高)、wrap-reverse:从下向上*/ /*flex-flow是flex-direction、flex-wrap的缩写*/ } .box{ width:200px; height:100px; border:1px solid #000; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="box">这是中间的box1</div> <div class="box">这是中间的box2</div> </div> </body> </html>
子元素的属性:
order:设置元素的顺序
例如:我么想要将本来第二个元素排在第一,将排在第一的元素设置为第二。
我们可以设置他们的order值。
.box1{order:1;} .box2{order:0;} <div class="container"> <div class="box box1">这是中间的box1</div> <div class="box box2">这是中间的box2</div> </div>
flex:指定可伸缩长度的部件,是flex-shrink,flex-grow,flex-basis这三个属性的缩写。
他可以指定一个子元素的占据父元素的宽度或者高度的比例。(前提是在子元素还没有占满父级元素的情况下)
demo:
<style> .container{ width:800px; height:600px; border:1px solid red; display:flex; align-items:center; justify-content:center; flex-direction:row; flex-wrap:wrap; } .box{ width:200px; height:200px; border:1px solid blue; } .box1{ flex:2 } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class= " box box1">1</div> <div class="box box2">2</div> <div class="box box3">3</div> <div class="box box4">4</div> </div> </body>
最终效果如下:因为子元素占满父级元素。
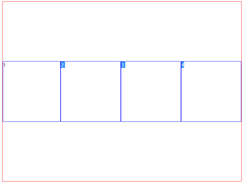
进一步验证:
<style> .container{ width:800px; height:600px; border:1px solid red; display:flex; align-items:center; justify-content:center; flex-direction:row; flex-wrap:wrap; } .box{ width:200px; height:200px; border:1px solid blue; } .box1{ flex:2 } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class= " box box1">1</div> <div class="box box2">2</div> </div> </body>
很明显的阔以看到,box1占据了600px宽度
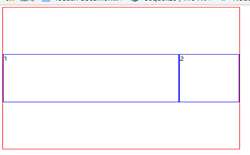
align-self:用来单独设置子元素的对齐方式(可将默认的对齐方式进行覆盖)
例如:我们已经在父元素中设置了align-items:center.(将子元素设置为垂直居中显示)
这个时候我们想单独更改某个子元素的对齐方式,就可以使用align-self
<style> .container{ width:800px; height:600px; border:1px solid red; display:flex; align-items:center; justify-content:center; flex-direction:row; flex-wrap:wrap; } .box{ width:100px; height:100px; border:1px solid blue; } .box1{ flex:2 } /* .box4{ align-self:flex-end; } */ </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class= " box box1">1</div> <div class="box box2">2</div> <div class="box box3">3</div> <div class="box box4">4</div> </div> </body>
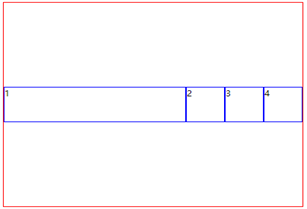
假如我们设置 box4:align-self:flex-end;呢
.box4{ align-self:flex-end; }
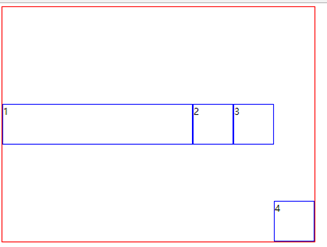
好了,已经改变了box4的对齐方式。
如果想兼容更多的浏览器,可以采用优雅降级的方式,例如sass-flex-mixin