缓存
一级缓存(Local cache)
- 作用范围:单个SqlSession,与SqlSeesion中的Executor组合在一起(当前SqlSession执行select语句则发生缓存写入,发生update类语句则发生缓存清空)
- 弊端:不能跨会话共享,无法感知到其他SqlSession发生的update类语句,可能获取到的缓存为过时数据
二级缓存(namespace cache)
- 作用范围:单个namespace,通过TransactionalCacheManager对象(全局)管理,只有当事务被commit或rollback,且之后没有update类语句时,才会将缓存写入,而update类语句发生commit则缓存清空
- tips 1:二级缓存的开启,需要configuration配置中
cacheEnabled=true,且Mapper.xml文件中显示定义标签 - tips 2: 二级缓存的实现,是通过CachingExecutor代理BaseExecutor实现的
others
- 缓存的实现是基于PerpetualCache类的,通过代理的方式实现功能增强,二级缓存默认大小为1024,采用LRU算法
- Mybatis提供了对第三方缓存的支持,如:redis(需引入mybatis-redis相关依赖)
插件
demo(逻辑翻页转换为物理翻页)
① 实现Interceptor接口,② 在mybatis-config.xml文件中通过
// @Intercepts注解中配置需要拦截的对象类型,以及拦截的方法和参数
@Intercepts(
{@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class})
})
@Intercepts({@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class})
})
public class MyPageInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 将逻辑分页(全部查询出来抛弃多余数据)处理成物理翻页(limit字段定向查询)
Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();
MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement)args[0]; // MappedStatement
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(args[1]); // Object parameter
RowBounds rb = (RowBounds)args[2]; // RowBounds
// 1. 若RowBounds为空,无需分页
if (rb == RowBounds.DEFAULT) {
return invocation.proceed();
}
// 否则 - 重置RowBounds参数对象,将翻页设置取消
args[2] = RowBounds.DEFAULT;
// 并在SQL后加上limit语句
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
String limit = String.format("LIMIT %d,%d", rb.getOffset(), rb.getLimit());
sql = sql + " " + limit;
// 重构SqlSource,置换原来的SqlSource
SqlSource sqlSource = new StaticSqlSource(ms.getConfiguration(), sql, boundSql.getParameterMappings());
// 通过反射修改参数
Field field = MappedStatement.class.getDeclaredField("sqlSource");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(ms, sqlSource);
// 执行被拦截方法
return invocation.proceed();
}
}
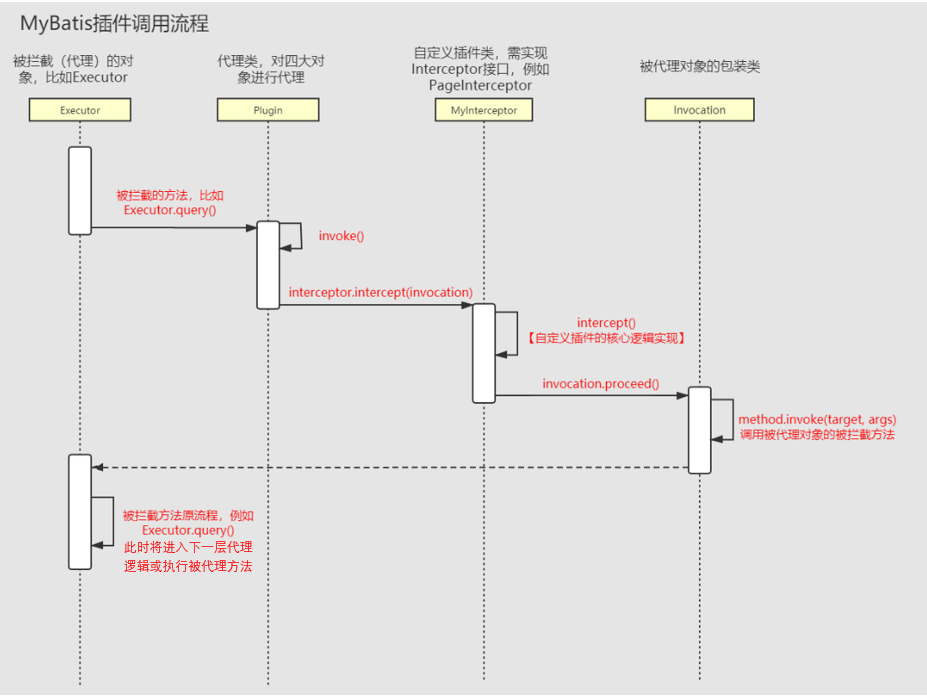
插件原理
解析:SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象解析配置文件时,会将对应的插件类注册到configration对象的InterceptorChain中
创建:获取sqlSession时,对于四大对象,会调用InterceptorChain.pluginAll(target)方法,通过代理的方式,实现intercept(逐层代理形成intercept链)
调用:
①代理对象被拦截的方法 -> ②plugins.invoke()方法
-> ③invoke内部调用Interceptor.intercept(Invocation invocation)方法,执行拦截逻辑
-> ④调用invocation.proceed()进入下一层逻辑
// Plugin对象
public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler {
private final Object target;
private final Interceptor interceptor;
private final Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap;
private Plugin(Object target, Interceptor interceptor, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
this.target = target;
this.interceptor = interceptor;
this.signatureMap = signatureMap;
}
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
// 构建代理对象:通过对象类型和方法签名获取到接口,为该接口生成代理类,以Plugin对象为invokeHandler
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
}
// 调用step2:通过代理对象方法进入到InvocationHandler类的invoke方法,再调用interceptor.intercept()实现插件逻辑
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
...
}
// Invocation对象
public class Invocation {
private final Object target;
private final Method method;
private final Object[] args;
public Invocation(Object target, Method method, Object[] args) {
this.target = target;
this.method = method;
this.args = args;
}
public Object getTarget() { return target;}
public Method getMethod() { return method;}
public Object[] getArgs() { return args;}
public Object proceed() throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
return method.invoke(target, args);
}
}
tips 1: mybatis通过将Plugin与Interceptor对象组合,将InvocationHandler.invoke()方法中的细节实现抽取到Interceptor.intercept()中(桥接模式,使控制维度与实现维度解耦)
tips 2: mybatis插件的代理顺序与mybatis-config.xml的定义顺序一致,而插件的执行顺序将从最外层代理往里执行(先执行最后定义的插件逻辑)
四大对象(可被拦截的)
Executor:update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback, getTransaction, close, isClosed
ExecutorType.SIMPLE:普通执行器,为每个语句的执行创建一个新的预处理语句ExecutorType.REUSE:statement缓存,该类型的执行器会复用预处理语句ExecutorType.BATCH:批量执行器,该类型的执行器会批量执行所有更新语句
ParameterHandler:getParameterObject, setParameters
ResultSetHandler:handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters
StatementHandler:prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query