1 概述
1-1 成分分析
前置知识ExecutorService:
常识:ExecutorService是线程池生命周期管理(创建,执行,关闭)的工具类
JDK中ExecutorService接口的实现类
AbstractExecutorService,
ForkJoinPool,
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor,
ThreadPoolExecutor
接口方法定义:
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout,
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
boolean isShutdown()
boolean isTerminated()
void shutdown()
List<Runnable> shutdownNow()
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task)
Future<?> submit(Runnable task)
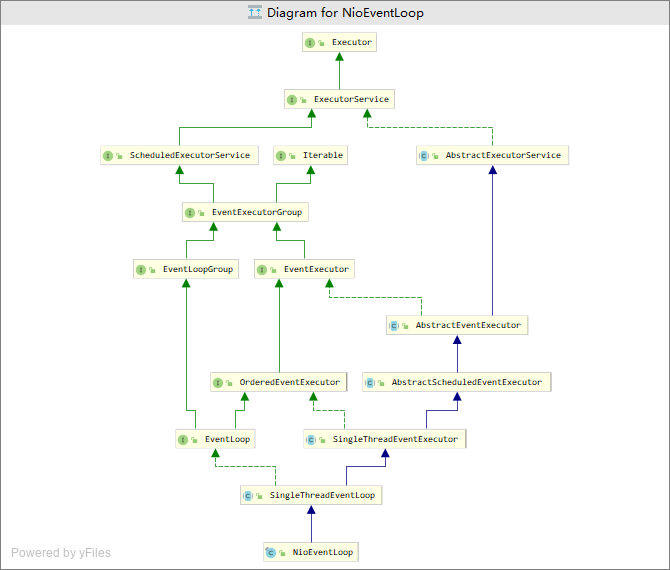
显然:Netty框架中NioEventLoop实现了JDK中的ExecutorService接口,而ExecutorService是用于管理线程池的,因此能NioEventLoop中必定有线程池所包含的线程对象和任务队列。
从图中自下而上阅读相关类的源码,可以发现以下重要属性
| 类名称 | 特有属性 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| NioEventLoop | private Selector selector; private Selector unwrappedSelector; private SelectedSelectionKeySet selectedKeys; |
|
| SingleThreadEventExecutor | private final Queue private volatile Thread thread; |
任务队列 |
| AbstractScheduledEventExecutor | PriorityQueue<ScheduledFutureTask<?>> scheduledTaskQueue; | 定时任务队列 |
=总结=====
NioEventLoop中由线程对象、Selector对象和多个任务队列(普通/定时任务队列)组成,因此这个类可以处理IO事件,也可以处理所提交的普通任务和定时任务
1-2 部分方法
| 说明 | 所对应的小节 | |
|---|---|---|
int getIoRatio() |
获得网络IO占所有任务执行时间的比率 | 3-3-5 |
rebuildSelector() |
重新构建selector,用于解决空轮询bug) | 3-3-4 |
run() |
nio线程运行的核心方法 | 1-3-2 |
selectorProvider() |
提供用于注册的selector对象 | 2 |
setIoRatio(int ioRatio) |
设置期望用于网络IO的时间比率 | 3-3-5 |
wakeup(boolean inEventLoop) |
唤醒阻塞的NIO线程 | 3-3-2 |
总结:在NioEventLoop中任务执行的入口函数就是run方法,在run方法中实现对网络IO,以及其他线程提交给EventLoop线程池的普通任务和定时任务处理。因此NioEventLoop可以看作能够监控网络连接并且处理网络连接事件的单线程线程池,其中监控功能由selector对象提供,任务的处理则是线程池本身的作用。NioEventLoop的核心在于多线程环境中如何协调处理网络IO事件和其他线程提交的普通任务和定时任务,总体来看有两点:
- 线程间交互:通过selector.select(time)和selector.wakeup方法灵活的控制nio线程的阻塞与运行(有点类似于wait/notify的同步机制),使得该线程能够有任务时执行任务,没任务时阻塞在那监控网络IO事件
- 通过ioRatio控制网络IO事件和其他任务处理时间的比例。
源码阅读时从NioEventLoop中的run方法和select方法进行展开阅读。
2 构造方法
NioEventLoop(NioEventLoopGroup parent, Executor executor, SelectorProvider selectorProvider,
SelectStrategy strategy, RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler,
EventLoopTaskQueueFactory queueFactory) {
super(parent, executor, false, newTaskQueue(queueFactory), newTaskQueue(queueFactory),
rejectedExecutionHandler);
if (selectorProvider == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("selectorProvider");
}
if (strategy == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("selectStrategy");
}
provider = selectorProvider;
final SelectorTuple selectorTuple = openSelector();
// 下面两个创建selector对象
selector = selectorTuple.selector;
unwrappedSelector = selectorTuple.unwrappedSelector;
selectStrategy = strategy;
}
注意:NioEventLoop在执行构造函数时创建selector
2-1 selector中key的优化
selector实现
- 从反编译的源码中可以看到keys和selectedKeys是hashset,set中的元素是key对象
// package sun.nio.ch中对于selector的实现的反编译文件
public abstract class SelectorImpl extends AbstractSelector {
protected Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = new HashSet();
protected HashSet<SelectionKey> keys = new HashSet();
private Set<SelectionKey> publicKeys;
private Set<SelectionKey> publicSelectedKeys;
....
}
SelectionKeys实现
- 从反编译的源码中可以看到key包含channel,selecotr,index,interestOps(关注的事件类型)
public class SelectionKeyImpl extends AbstractSelectionKey { // openjdk的反编译源码
final SelChImpl channel;
public final SelectorImpl selector;
private int index;
private volatile int interestOps;
private int readyOps;
阅读构造方法中的openSelector()源码可以发现,采用两个selector主要目的是为了优化selector的key集合,原始的selector即unwrappedSelector中key的集合是基于hashset实现,集合在遍历时的开销要高于数组实现的集合开销,因此如果开启keyset的优化,那么就会有两个selector
selector = selectorTuple.selector;
// keyset是基于数组实现,迭代的效率要高于基于hashset的实现版本
unwrappedSelector = selectorTuple.unwrappedSelector;
// keyset基于hashset实现,用于快速删除和添加
openSelector源码
private SelectorTuple openSelector() {
final Selector unwrappedSelector;
try {
// unwrappedSelector是原始的selector对象
unwrappedSelector = provider.openSelector();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException("failed to open a new selector", e);
}
// 如果关闭keyset的优化,则直接返回
if (DISABLE_KEY_SET_OPTIMIZATION) {
return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector);
}
....... // 后续还有代码,通过反射的方式将selectKeySet由HashSet<>()实现替换为数组实现,得到一个新的selector对象
}
3 EventLoop中Thread
3-3-1 线程创建流程
package CodeAnalyze;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoop;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
public class TestEventLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventLoop eventLoop = new NioEventLoopGroup().next();
eventLoop.execute(()->{
log.error("hello");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
eventLoop.submit(()->{
log.error("hello again");
});
}
}
执行结果:执行完提交的两个任务后,程序不会停止,一直在运行
16:27:59 [ERROR] [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] C.TestEventLoop - hello
16:28:00 [ERROR] [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] C.TestEventLoop - hello again
- 从日志中可以看出执行两个任务的是同一线程nioEventLoopGroup-2-1、
引申的问题:
1.NioEventLoop中的单个线程是何时被启动的?
2.NioEventLoop中如何保证只有单个线程被启动。
3.NioEventLoop执行完所有任务后,一直在运行的过程是怎样的?
代码赏析(SingleThreadEventExecutor.Execute源码)
execute源码
@Override
public void execute(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) { //参数校验
throw new NullPointerException("task");
}
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop(); // 判断当前线程是否是EventLoop中线程
addTask(task); // 在任务队列中添加任务
if (!inEventLoop) { // 非当前线程,
startThread(); // 则调用startThread()启动新线程
if (isShutdown()) {
boolean reject = false;
try {
if (removeTask(task)) {
reject = true;
}
} catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) {
if (reject) {
reject();
}
}
}
if (!addTaskWakesUp && wakesUpForTask(task)) {
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
}
private void startThread() {
if (state == ST_NOT_STARTED) { // 检测状态位
// 通过CAS(Compare and Swap)更改状态位,确保线程不会被重复创建
if (STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, ST_NOT_STARTED, ST_STARTED)) {
boolean success = false;
try {
doStartThread();
success = true;
} finally {
if (!success) {
STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, ST_STARTED, ST_NOT_STARTED);
}
}
}
}
}
private void doStartThread() {
assert thread == null;
// =================此时由executor的execute方法创建新的线程对象并提交任务===================
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// ==========================NioEventLoop的成员被赋值位当前创建的线程!!!!===============
thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (interrupted) {
thread.interrupt();
}
boolean success = false;
updateLastExecutionTime();
try {
// 该run方法内部是死循环(此处执行的是NioEventLoop的run方法)
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run();
......
}
总结:从上面的源码中可以看到EventLoop会在首次提交任务时创建并设置Thread对象,通过CAS(Compare and Swap)保证线程不会重复启动。在线程创建后提交的任务块代码中包含有for的死循环代码块,该代码块中会检查任务队列中是否有任务并执行。
NioEventLoop的run方法(死循环代码块):
@Override
protected void run() {
for (;;) {
........ // 省略代码
}
}
- 该死循环中会处理IO事件,定时任务,普通任务
小结:
1.NioEventLoop中的单个线程是何时被启动的?
首次调用execute方法,会创建新的线程对象
2.NioEventLoop中如何保证只有单个线程被启动。
startThread() 中通过标志位的CAS机制确保线程不会被重复创建(调用execute),
从而保证只有单个线程对象被创建。
3.NioEventLoop执行完所有任务后,一直在运行的过程是怎样的?
运行过程中会不断检查是否有网络IO触发的任务、用户提交的普通任务和定时任务。
3-3-2 非NIO线程任务提交执行流程
背景:单个EventLoop对象可以看成是单线程执行器,除了能够处理来自网络的IO任务外,还能够处理其他线程提交的普通任务和定时任务,当nio线程调用select方法后处于阻塞状态,该如何执行其他线程提交的任务,netty中是通过其他线程调用NioEventLoop中定义wakeup方法来唤醒阻塞中的nio线程,让其执行提交的任务。
| java.nio.channels.Selector的 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| select() | 获取所关联的channel有I/O操作的key的集合,注意该方法是阻塞(blocking)调用 |
| select(long timeout) | 带有超时时间的阻塞调用 |
| selectNow() | 非阻塞调用 |
| wakeup() | 让select()调用立刻返回 |
NIO线程创建完成后会执行下面的run方法循环逻辑:
// io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop的run方法源码如下(外层循环):
@Override
protected void run() {
for (;;) {
try {
try {
switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
case SelectStrategy.BUSY_WAIT:
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
// 关键:执行select方法处理入站的网络IO事件
select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false));
if (wakenUp.get()) {
selector.wakeup();
}
default:
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// (出现IO异常则重新构建selector)https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/8566
rebuildSelector0();
handleLoopException(e);
continue;
}
cancelledKeys = 0;
needsToSelectAgain = false;
final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;
if (ioRatio == 100) {
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
runAllTasks();
}
} else {
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
// 即便抛出异常也要处理shut down
try {
if (isShuttingDown()) {
closeAll();
if (confirmShutdown()) {
return;
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
}
}
// io.nettty.channel.NioEventLoop的select方法源码(内层循环)
private void select(boolean oldWakenUp) throws IOException {
Selector selector = this.selector;
try {
int selectCnt = 0;
long currentTimeNanos = System.nanoTime();
long selectDeadLineNanos = currentTimeNanos + delayNanos(currentTimeNanos);
for (;;) {
long timeoutMillis = (selectDeadLineNanos - currentTimeNanos + 500000L) / 1000000L;
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
if (selectCnt == 0) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
}
break;
}
/*==================================================================
当wakeUp value == true时1个task已经提交,那么该task不会得到机会调用,
因此再执行select操作前,再次检查task queue进行执行,
动机:如果不进行检查,那么该task会被阻塞,直到select方法调用超时之后才有机会得到执行,
这对于IdleStateHandler会产生影响
IdleStateHandler:能够检测出入站数据,并发送定时心跳包,该handler如果提交
任务,应该得到立即响应
=====================================================================*/
if (hasTasks() && wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
int selectedKeys = selector.select(timeoutMillis);
selectCnt ++;
if (selectedKeys != 0 || oldWakenUp || wakenUp.get() || hasTasks() || hasScheduledTasks()) {
// - Selected something,
// - waken up by user, or
// - the task queue has a pending task.
// - a scheduled task is ready for processing
break;
}
// 线程被打断,因此重置选择的key并且跳出循环,这样就不会陷入busy loop
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
// 日志输出
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely because " +
"Thread.currentThread().interrupt() was called. Use " +
"NioEventLoop.shutdownGracefully() to shutdown the NioEventLoop.");
}
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
long time = System.nanoTime();
if (time - TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(timeoutMillis) >= currentTimeNanos) {
selectCnt = 1;
} else if (SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD > 0 &&
selectCnt >= SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD) {
selector = selectRebuildSelector(selectCnt);
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
currentTimeNanos = time;
}
if (selectCnt > MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row for Selector {}.",
selectCnt - 1, selector);
}
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) { // Harmless exception - log anyway
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(CancelledKeyException.class.getSimpleName() + " raised by a Selector {} - JDK bug?",
selector, e);
}
}
}
注意:程序中使用NioEventLoop的execute方法执行任务,而NioEventLoop中的Nio线程正处于selector.select(timeoutMillis)的阻塞调用状态,那么此时会通过selector.wakeup()让阻塞调用返回从而能够及时执行所提交的任务。
// io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop中execute和wakeup源码!!!
@Override
public void execute(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) { //参数校验
throw new NullPointerException("task");
}
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop(); // 判断当前线程是否是EventLoop中线程
addTask(task); // 在任务队列中添加任务!!!
if (!inEventLoop) { // 非当前线程,
...... // 省略代码
}
if (!addTaskWakesUp && wakesUpForTask(task)) {
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
}
@Override
protected void wakeup(boolean inEventLoop) {
if (!inEventLoop && wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
selector.wakeup(); // 停止selector的阻塞调用!!!!!
}
}
注意:上述代码反应执行selector.wakeup()(其他线程让NioEventLoop中阻塞的NIO线程继续执行)需同时满足以下两个条件:
1)当前线程不是nio线程(非EventLoop中Thread,是提交任务的线程)
2) CAS修改wakeUp标志位成功(保证多线程情况下selector.wakeup被频繁的无效调用)
总结
每个EventLoop线程对象创建后,该nio线程会执行一段循环逻辑代码监控网络IO时间,该循环中会不断调用
// io.nettty.channel.NioEventLoop.select方法内部代码
int selectedKeys = selector.select(timeoutMillis);
上述方法是带有超时时间的阻塞方法,如果其他线程使用该EventLoop的线程执行任务,如果调用Selector.select方法处于阻塞状态就无法及时处理其他线程提交的任务,因此netty中使用Selector.wakeup方法方法唤醒阻塞的线程,从而让线程能够及时处理任务队列中其他线程提交的任务。
selector.wakeup(); // 停止selector的阻塞调用!!!!! (io.nettty.channel.NioEventLoop.wakeup方法内部代码)
超时时间计算策略:
long currentTimeNanos = System.nanoTime();
// 截止时间 = 当前时间 + 延迟时间 (单位是纳秒)
long selectDeadLineNanos = currentTimeNanos + delayNanos(currentTimeNanos);
for (;;) {
// 超时时间 = (截止时间 - 当前时间 + 0.5 毫秒) / 1毫秒 (毫秒为最小单位)
long timeoutMillis = (selectDeadLineNanos - currentTimeNanos + 500000L) / 1000000L;
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
if (selectCnt == 0) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
}
break;
}
select的超时时间计算方法
情况1:无定时任务,返回1s
情况2:有定时任务,则等于定时任务的截止时间
private static final long SCHEDULE_PURGE_INTERVAL = TimeUnit.SECONDS.toNanos(1); // 1s转化为纳秒为单位
// NioEventLoop的delayNanos方法
protected long delayNanos(long currentTimeNanos) {
ScheduledFutureTask<?> scheduledTask = peekScheduledTask();
if (scheduledTask == null) {
return SCHEDULE_PURGE_INTERVAL;
}
return scheduledTask.delayNanos(currentTimeNanos);
}
// ScheduledFutureTask的delayNanos方法
public long delayNanos(long currentTimeNanos) {
return Math.max(0, deadlineNanos() - (currentTimeNanos - START_TIME));
}
select的超时时间计算总结:在没有定时任务的情况下,超时时间大约为1s左右,有定时任务则是定时任务的截止时间减去当前时间。
3-3-3 EventLoop调用select()的时机
在NioEventLoop的run方法循环中下面代码展示线程进行select的条件:
switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
case SelectStrategy.BUSY_WAIT: // NioEventLoop中不支持busy wait策略(盲等策略)
case SelectStrategy.SELECT: // 进入select分支
select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false)); // 原子boolean变量wakenUp设置为false,并返回先前值
if (wakenUp.get()) {
selector.wakeup();
}
default:
}
可以看出当swith分支满足SelectStrategy.SELECT时,会调用NioEventLoop的select方法去查看key
| 属性 | 值 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| SelectStrategy.CONTINUE | -1 | Indicates a blocking select should follow. |
| SelectStrategy.BUSY_WAIT | -2 | Indicates the IO loop should be retried, no blocking select to follow directly |
| SelectStrategy.SELECT | -3 | Indicates the IO loop to poll for new events without blocking. |
注意:calculateStrategy方法只会-3或者一个非负数表示key的数目(后文提到),其余两个分支在NioEventLoop中没有被用到
SelectStrategy.SELECT条件出现的时机:
情况1:当前任务队列中没有任务,满足SelectStrategy.SELECT条件
情况2:当前任务队列中有任务,则通过selector.selectNow方法获取key的数目并返回
final class DefaultSelectStrategy implements SelectStrategy {
static final SelectStrategy INSTANCE = new DefaultSelectStrategy();
private DefaultSelectStrategy() { }
@Override
public int calculateStrategy(IntSupplier selectSupplier, boolean hasTasks) throws Exception {
return hasTasks ? selectSupplier.get() : SelectStrategy.SELECT;
}
}
selectSupplier.get()作用解析
private final IntSupplier selectNowSupplier = new IntSupplier() {
@Override
public int get() throws Exception {
return selectNow();
}
};
int selectNow() throws IOException {
try {
return selector.selectNow();
} finally {
// restore wakeup state if needed
if (wakenUp.get()) {
selector.wakeup();
}
}
}
多线程环境下,该方法执行后首先查看key的数目并返回,同时检查wakenUp标志位确定是否唤醒阻塞的nio线程。
a) 非EventLoop中的nio线程执行selectNow(),则会通过标志设置唤醒nio线程从而处理任务队列中积压的任务
b) EventLoop中的nio线程执行selectNow(),表示位肯定为false,不会执行selector.wakeup();
3-3-4 内循环流程select方法总结
// io.nettty.channel.NioEventLoop的select方法源码(内层循环)
private void select(boolean oldWakenUp) throws IOException {
Selector selector = this.selector;
try {
int selectCnt = 0; // 统计selector.select方法调用次数
long currentTimeNanos = System.nanoTime();
long selectDeadLineNanos = currentTimeNanos + delayNanos(currentTimeNanos);
for (;;) {
long timeoutMillis = (selectDeadLineNanos - currentTimeNanos + 500000L) / 1000000L;
// 1)超时时间小于0,跳出循环
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
if (selectCnt == 0) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
}
break;
}
// 2) 存在普通任务则跳出循环
if (hasTasks() && wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
int selectedKeys = selector.select(timeoutMillis);
selectCnt ++;
// 3) key的数量大于0(有事件发生) || WakenUp为true || 存在普通任务 || 存在定时任务 跳出循环
if (selectedKeys != 0 || oldWakenUp || wakenUp.get() || hasTasks() || hasScheduledTasks()) {
break;
}
// 4)线程被打断,跳出循环
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely because " +
"Thread.currentThread().interrupt() was called. Use " +
"NioEventLoop.shutdownGracefully() to shutdown the NioEventLoop.");
}
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
// 5) selector.select方法调用次数超过SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD,跳出循环
long time = System.nanoTime();
if (time - TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(timeoutMillis) >= currentTimeNanos) {
selectCnt = 1;
} else if (SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD > 0 &&
selectCnt >= SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD) {
selector = selectRebuildSelector(selectCnt);
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
currentTimeNanos = time;
}
// 6) selector.select方法调用次数超过MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS,跳出循环
if (selectCnt > MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row for Selector {}.",
selectCnt - 1, selector);
}
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) { // Harmless exception - log anyway
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(CancelledKeyException.class.getSimpleName() + " raised by a Selector {} - JDK bug?",
selector, e);
}
}
}
总结:上述代码的select方法基本思路是在截止时间到达前循环调用带有超时时间的selector.select方法,由于nio线程不仅仅需要监控keys获取时间,因此以下几种情况需要跳出循环:
1)超时时间小于0,跳出循环
2) 存在普通任务则跳出循环
3)就绪的key的数量大于0(有事件发生) || WakenUp为true || 存在普通任务 || 存在定时任务 跳出循环
4)线程被打断,跳出循环
5)selector.select方法调用次数超过SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD,跳出循环
6)selector.select方法调用次数超过MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS,跳出循环 // premature:过早的,提前的,早产的
其中5)是用于处理空轮询bug(NIO selector wakes up with 0 selected keys infinitely),当bug发生时,可以通过判定计数次数来rebuild selector并跳出空轮询循环。可以通过环境参数io.netty.selectorAutoRebuildThreshold配置阈值
int selectorAutoRebuildThreshold = SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.selectorAutoRebuildThreshold", 512);
if (selectorAutoRebuildThreshold < MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS) {
selectorAutoRebuildThreshold = 0;
}
SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD = selectorAutoRebuildThreshold;
这种bug非常严重,违背了“selector在没有事件发生时阻塞的原则”,nio线程没有做任何工作但确占用cpu资源,浪费了宝贵的计算资源。
3-3-5 普通/网络IO任务的时间分配
// io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop的run方法源码如下(外层循环):
private volatile int ioRatio = 50;
@Override
protected void run() {
for (;;) {
try {
try {
switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
case SelectStrategy.BUSY_WAIT:
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false)); // 关键:执行select方法获取网络IO事件
if (wakenUp.get()) {
selector.wakeup();
}
default:
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// (出现IO异常则重新构建selector)https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/8566
rebuildSelector0();
handleLoopException(e);
continue;
}
cancelledKeys = 0;
needsToSelectAgain = false;
final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio; // 定义网络IO任务处理时间占所有任务的比例
if (ioRatio == 100) {
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
runAllTasks();
}
} else {
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
processSelectedKeys(); // 处理key集合中关联的所有网络IO事件
} finally {
final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
try {
if (isShuttingDown()) {
closeAll();
if (confirmShutdown()) {
return;
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
}
}
总结:上述内循环代码中netty中通过ioRatio的设置来控制网络IO和其他任务时间的分配比例,基本思路如下所示。初始化 ioRatio = 50,即处理网络IO和其他任务的时间对半,各占50%。需要注意的是,如果ioRatio = 100,则先处理完所有IO事件,然后再处理完所有任务。
// 首先处理所有key中的关联时间,并计算处理时间ioTime,然后根据公式ioTime/ioRatio*(1-ioRatio)计算处理其他任务最多用多少时间。
// ioRatio=100,则先processSelectedKeys(),然后调用没有超时时间的runAllTasks
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
}
// io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadExecutor中带有超时时间的runAllTasks源码
protected boolean runAllTasks(long timeoutNanos) {
fetchFromScheduledTaskQueue();
Runnable task = pollTask();
if (task == null) {
afterRunningAllTasks();
return false;
}
final long deadline = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime() + timeoutNanos;
long runTasks = 0;
long lastExecutionTime;
for (;;) {
safeExecute(task);
runTasks ++;
// Check timeout every 64 tasks because nanoTime() is relatively expensive.
// XXX: Hard-coded value - will make it configurable if it is really a problem.
if ((runTasks & 0x3F) == 0) {
lastExecutionTime = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime();
if (lastExecutionTime >= deadline) { // 超时,跳出循环,不再处理任务队列中的任务
break;
}
}
task = pollTask();
if (task == null) {
lastExecutionTime = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime();
break;
}
}
afterRunningAllTasks();
this.lastExecutionTime = lastExecutionTime;
return true;
}
可以看到传入的时间用于计算deadline,当超过deadline会停止处理任务队列中的任务。
3-3-6 key中关联事件类型的区分
// io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop的processSelectedKeys和processSelectedKeysOptimized源码如下
private void processSelectedKeys() {
// 判断key是否为优化后的key集合(数组实现/hashset)
if (selectedKeys != null) {
processSelectedKeysOptimized();
} else {
processSelectedKeysPlain(selector.selectedKeys());
}
}
private void processSelectedKeysOptimized() {
for (int i = 0; i < selectedKeys.size; ++i) {
final SelectionKey k = selectedKeys.keys[i];
// null out entry in the array to allow to have it GC'ed once the Channel close
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2363
selectedKeys.keys[i] = null;
final Object a = k.attachment(); // key关联的channel实例
if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) {
processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a);
} else {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
NioTask<SelectableChannel> task = (NioTask<SelectableChannel>) a;
processSelectedKey(k, task);
}
if (needsToSelectAgain) {
// null out entries in the array to allow to have it GC'ed once the Channel close
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2363
selectedKeys.reset(i + 1);
selectAgain();
i = -1;
}
}
}
private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) {
final AbstractNioChannel.NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe();
if (!k.isValid()) { // 参数校验
final EventLoop eventLoop;
try {
eventLoop = ch.eventLoop();
} catch (Throwable ignored) {
return;
}
if (eventLoop != this || eventLoop == null) {
return;
}
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
return;
}
// 根据事件类型调用不同的底层API进行处理
try {
int readyOps = k.readyOps();
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) { // 连接关闭
int ops = k.interestOps();
ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;
k.interestOps(ops);
unsafe.finishConnect();
}
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) { // write事件写入
ch.unsafe().forceFlush();
}
// accept事件和read事件处理
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) { //
unsafe.read();
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) {
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
}
}
总结:从源码中可以看到netty一次性获取所有有就绪事件的key,然后根据key的属性判断事件类型。