Function 函数式接口
使用注解@FunctionalInterface标识,并且只包含一个抽象方法的接口是函数式接口。函数式接口主要分为:
- Supplier供给型函数:Supplier的表现形式为不接受参数、只返回数据。
- Consumer消费型函数:Consumer接收一个参数,没有返回值。
- Runnable无参无返回型函数:Runnable的表现形式为即没有参数也没有返回值。
- Function有参有返回型函数:Function函数的表现形式为接收一个参数,并返回一个值。
1、处理业务异常
示例:
public void isTrue(String msg){
// 业务处理...
boolean conditon;
if(conditon){
throw new RuntimeException(msg);
}
}
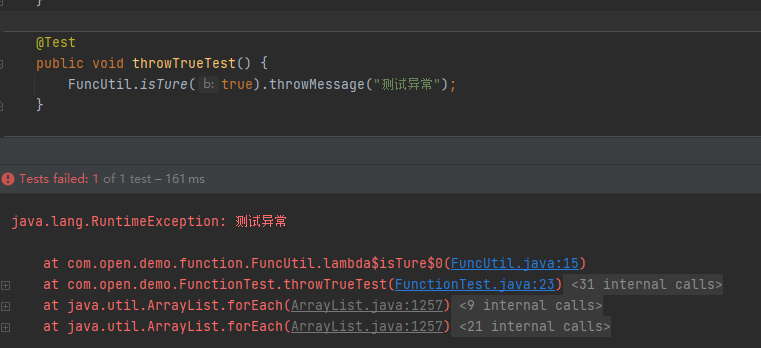
Function函数式编程:
FuncUtil.isTure(conditon).throwMessage("测试异常");
第一步:定义一个抛出异常的函数式接口, 消费型接口:只有参数没有返回值
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ThrowExceptionFunction {
/**
* 抛出异常信息
*
* @param message 异常信息
**/
void throwMessage(String message);
}
第二步:定义一个工具类 FuncUtil.isTure(boolean b)
/**
* 处理抛出异常
*/
public static ThrowExceptionFunction isTure(boolean b) {
return (errorMessage) -> {
if (b) {
throw new RuntimeException(errorMessage);
}
};
}
2、处理if...else...分支操作
示例:
public void isTureOrFalse(){
// 业务处理...
boolean a;
if(a){
System.out.println("true 逻辑");
} else {
System.out.println("false 逻辑");
}
}
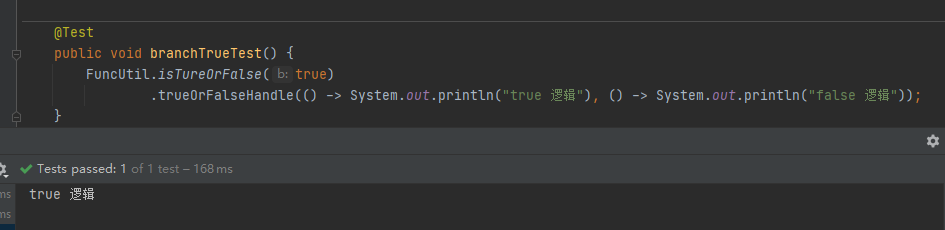
Function函数式编程:
FuncUtil.isTureOrFalse(true)
.trueOrFalseHandle(() -> System.out.println("true 逻辑"), () -> System.out.println("false 逻辑"));
第一步:定义一个分支处理函数式接口,接口的参数为两个Runnable接口。这两个两个Runnable接口分别代表了为true或false时要进行的操作
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BranchFunction {
/**
* 分支操作
*
* @param trueHandle 为true时要进行的操作
* @param falseHandle 为false时要进行的操作
**/
void trueOrFalseHandle(Runnable trueHandle, Runnable falseHandle);
}
第二步:定义一个工具类 FuncUtil.isTureOrFalse(boolean b)
/**
* 参数为true或false时,分别进行不同的操作
*/
public static BranchFunction isTureOrFalse(boolean b) {
return (trueHandle, falseHandle) -> {
if (b) {
trueHandle.run();
} else {
falseHandle.run();
}
};
}
3、处理if...else...分支操作,并消费输入参数
示例:
public void isBlankOrNoBlank(String msg){
if(null==msg || ''==msg){
System.out.println("msg为空");
} else {
System.out.println("msg is:"+msg);
}
}
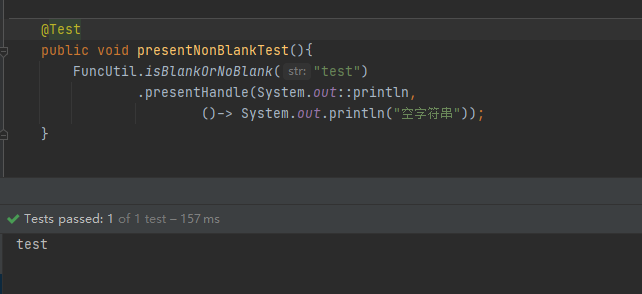
Function函数式编程:
FuncUtil.isBlankOrNoBlank("test")
.presentHandle(System.out::println,
()-> System.out.println("空字符串"));
第一步:定义一个PresentFunction的函数式接口,接口的参数一个为Consumer接口。一个为Runnable,分别代表值不为空时执行消费操作和值为空时执行的其他操作
public interface PresentFunction<T extends Object> {
/**
* 值不为空时执行消费操作
* 值为空时执行其他的操作
*
* @param action 值不为空时,执行的消费操作
* @param emptyAction 值为空时,执行的操作
**/
void presentHandle(Consumer<? super T> action, Runnable emptyAction);
}
第二步:定义一个工具类 FuncUtil.isTureOrFalse(boolean b)
/**
* 参数为true或false时,分别进行不同的操作
*/
public static PresentFunction<?> isBlankOrNoBlank(String str) {
return (consumer, runnable) -> {
if (str == null || str.length() == 0) {
runnable.run();
} else {
consumer.accept(str);
}
};
}
更多高级用法详见github:https://gitee.com/open-cloud-framework/open-demo.git