快速排序:
def quick_sort(array, left, right): """ :type array: list :type left: int :type right: int :return:type list """ if left < right: i = partition(array, left, right) quick_sort(array, left, i) quick_sort(array, i+1, right) return array def partition(a, left, right): middle = (left + right) / 2 # the middle element is the pivot pivot = a[middle] a[middle], a[right-1] = a[right-1], a[middle] # swap middle element with the last element i = left - 1 for j in range(left, right): if a[j] > pivot: i += 1 a[j], a[i] = a[i], a[j] a[i+1], a[right-1] = a[right-1], a[i+1] return i+1 ar = [2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 234, 123, 324, 52, 423, 42, 4, 23, 4, 5, 12, 5, 15, 1, 5, 51, 142] print quick_sort(ar, 0, len(ar))
采用in_place方法,选取数组中间元素作为基准值,首先将基准值换到数组最后,然后遍历数组,有一个指针i记录分割位置,遍历结束i指在大于基准值和小于等于基准值的分界点,最后将基准值与i+1元素换位从而完成基准值的位置确定,然后递归解决问题。
树 前,中,后序遍历:
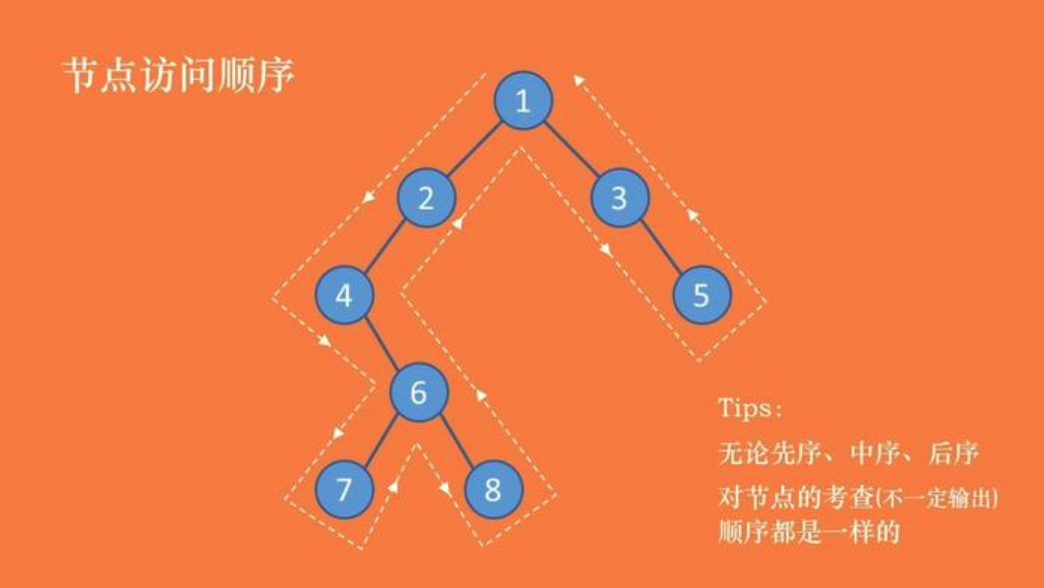
图片选自 https://www.jianshu.com/p/456af5480cee
上图顺序很好理解,就是从左到右终极描边。
前序:就按终极描边的顺序来。 所以结果是:12467835
中序:按终极描边来,只要有左节点就跳过,没有就输出。 所有结果是:47682135
后序:按终极描边来,有子节点就跳过,没有就输出。 所以结果是:78642531
堆排序:
#!/usr/bin/env python #-*-coding:utf-8-*- def heap_sort(lst): def sift_down(start, end): """最大堆调整""" root = start while True: child = 2 * root + 1 if child > end: break if child + 1 <= end and lst[child] < lst[child + 1]: child += 1 if lst[root] < lst[child]: lst[root], lst[child] = lst[child], lst[root] root = child else: break # 创建最大堆 for start in xrange((len(lst) - 2) // 2, -1, -1): sift_down(start, len(lst) - 1) # 堆排序 for end in xrange(len(lst) - 1, 0, -1): lst[0], lst[end] = lst[end], lst[0] sift_down(0, end - 1) return lst def main(): l = [9,2,1,7,6,8,5,3,4] heap_sort(l) if __name__ == "__main__": main()
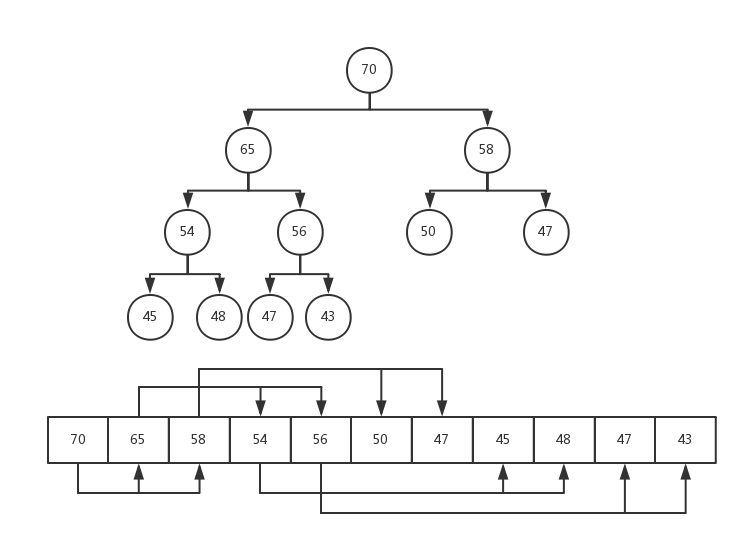
上图解释了heap_sort函数中第一个循环的索引计算。下图为堆调整的过程,代码主要思路是首先先将数组按照最大堆的规则进行排序,而排序是从最后一个节点的父节点开始,依次到达root节点。之后将符合最大堆规则的数组的第一个元素移除,代码中表现为将第一个元素与最后一个元素交换位置,然后将小一号的数组进行最大堆的调整,然后继续将第一个最后一个换位置,如此循环。最后数组为从小到大依次排序的。
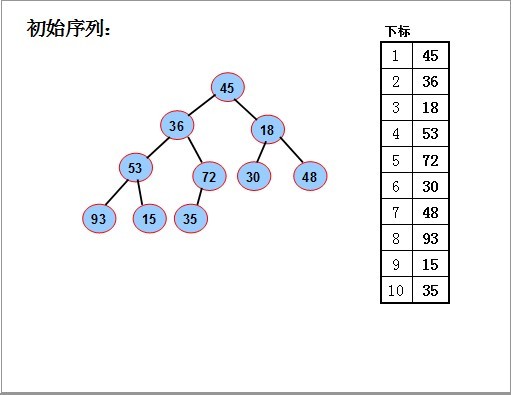
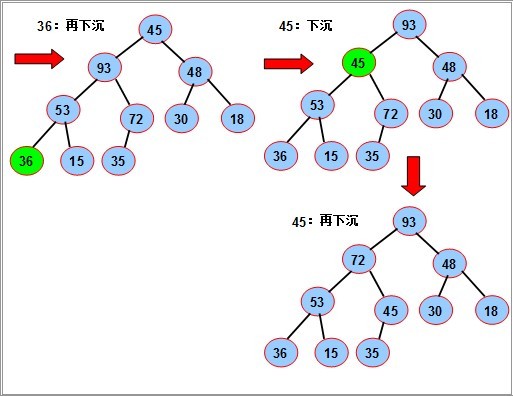
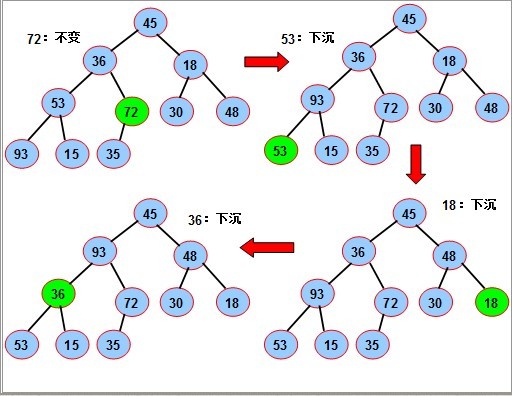
图片来自 http://128kj.iteye.com/blog/1728555 结合代码和图片可以很好理解
关于二叉搜索树:https://www.61mon.com/index.php/archives/191/ 详细问题及解法