介绍
tp是PHP框架thinkphp 的简称。tp的model 时thinkphp框架中mvc结构中m与数据交互的最重要的一环。
本文以提出的几个问题为线索,简要分析了tp框架中model的实现逻辑。
问题
如何连接数据库?
如何将方法转化为sql?
使用了什么设计模式?
分析
先查看一下tp版本。在框架源码根目录下composer.lock 文件中搜索thinkphp。

我电脑的框架版本有点低了,最新的是thinkphp6了。
首先我们根目录下搜索model方法,thinkphp/helper.php文件中
function model($name = '', $layer = 'model', $appendSuffix = false)
{
return Loader::model($name, $layer, $appendSuffix);
}
thinkphp/library/think/Loader.php 文件中
public static function model($name = '', $layer = 'model', $appendSuffix = false, $common = 'common')
{
$uid = $name . $layer;
// 这里使用了创建型的设计模式-单例模式
if (isset(self::$instance[$uid])) {
return self::$instance[$uid];
}
list($module, $class) = self::getModuleAndClass($name, $layer, $appendSuffix);
if (class_exists($class)) {
$model = new $class();
} else {
$class = str_replace('\' . $module . '\', '\' . $common . '\', $class);
if (class_exists($class)) {
$model = new $class();
} else {
throw new ClassNotFoundException('class not exists:' . $class, $class);
}
}
return self::$instance[$uid] = $model;
}
接下来就是同个$model = new $class(); 实力化具体的model了。
我们随便打开一个model文件 找到他的父类,thinkphp/library/think/Model.php。这里开头定义了连接属性。

搜索 $connection 找到如下代码
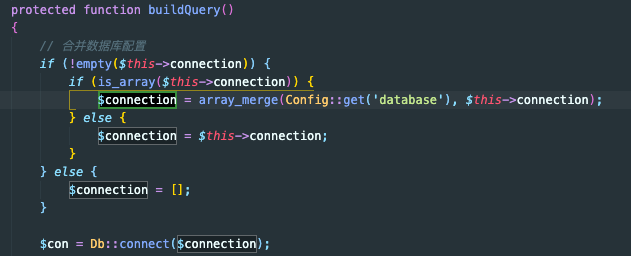
这里就找到了数据库链接了, 在 thinkphp/library/think/Db.php 文件的,connect函数接收的参数是在config.php 中配置的数据库链接信息。
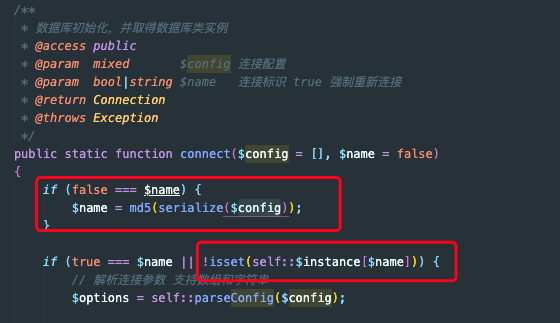
$name是以数据库配置数组序列化得到的字符串md5加密后作为单例的key,如果数据库配置信息不变,我们在一次请求周期内,只进行一次链接,这就是单例模式的好处。
接下来就是根据配置的type 找到类 比如配置的是mysql,那找到文件 thinkphp/library/think/db/connector/Mysql.php。
但是在Mysql类中没有找到怎么根据配置链接的,打开Mysql的父类,thinkphp/library/think/db/Connection.php
父类方法connect,找到具体连接数据库的方式:PDO。
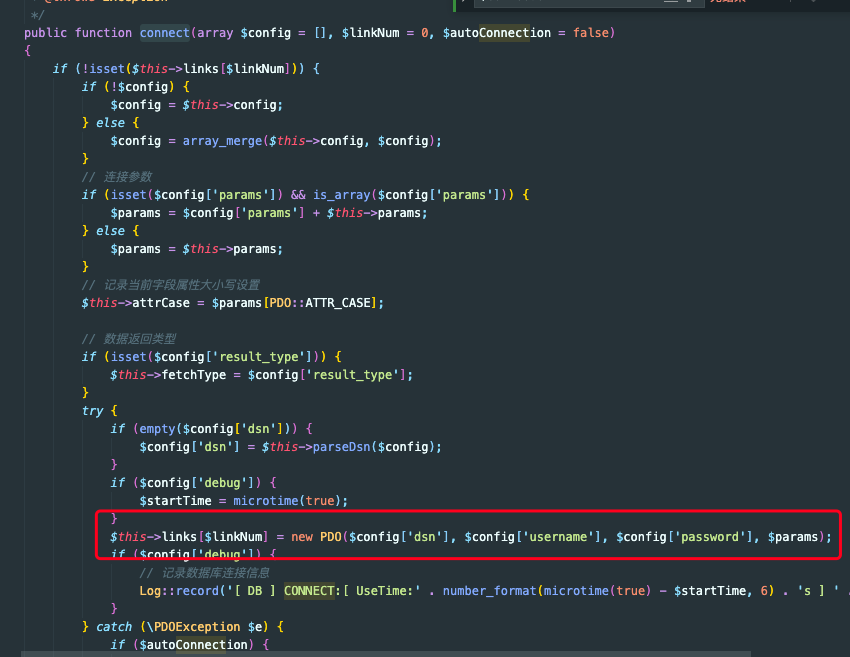
最后返回
return $this->links[$linkNum];
至此,第一个问题解决。
我们找一个方法来分析如何将方法转化为sql, delete方法。
/**
* 删除当前的记录
* @access public
* @return integer
*/
public function delete()
{
if (false === $this->trigger('before_delete', $this)) {
return false;
}
// 删除条件
$where = $this->getWhere();
// 删除当前模型数据
$result = $this->getQuery()->where($where)->delete();
// 关联删除
if (!empty($this->relationWrite)) {
foreach ($this->relationWrite as $key => $name) {
$name = is_numeric($key) ? $name : $key;
$model = $this->getAttr($name);
if ($model instanceof Model) {
$model->delete();
}
}
}
$this->trigger('after_delete', $this);
// 清空原始数据
$this->origin = [];
return $result;
}
主要流程就是获取删除条件和删除当前模型数据
获取删除条件
protected function buildQuery()
{
// 合并数据库配置
if (!empty($this->connection)) {
if (is_array($this->connection)) {
$connection = array_merge(Config::get('database'), $this->connection);
} else {
$connection = $this->connection;
}
} else {
$connection = [];
}
$con = Db::connect($connection);
// 设置当前模型 确保查询返回模型对象
$queryClass = $this->query ?: $con->getConfig('query');
$query = new $queryClass($con, $this);
// 设置当前数据表和模型名
if (!empty($this->table)) {
$query->setTable($this->table);
} else {
$query->name($this->name);
}
if (!empty($this->pk)) {
$query->pk($this->pk);
}
return $query;
}
new $queryClass($con, $this); 实际上是创建了如下对象。
thinkphp/library/think/db/Query.php 类中找到where whereOr等一系列方法。这里的大部分方法最后都retrun $this;从而实现了链式调用。
public function where($field, $op = null, $condition = null)
{
$param = func_get_args();
array_shift($param);
$this->parseWhereExp('AND', $field, $op, $condition, $param);
return $this;
}
通过搜索,我们找到此类中的delete方法
public function delete($data = null)
{
// 分析查询表达式
$options = $this->parseExpress();
$pk = $this->getPk($options);
if (isset($options['cache']) && is_string($options['cache']['key'])) {
$key = $options['cache']['key'];
}
if (!is_null($data) && true !== $data) {
if (!isset($key) && !is_array($data)) {
// 缓存标识
$key = 'think:' . $options['table'] . '|' . $data;
}
// AR模式分析主键条件
$this->parsePkWhere($data, $options);
} elseif (!isset($key) && is_string($pk) && isset($options['where']['AND'][$pk])) {
$key = $this->getCacheKey($options['where']['AND'][$pk], $options, $this->bind);
}
if (true !== $data && empty($options['where'])) {
// 如果条件为空 不进行删除操作 除非设置 1=1
throw new Exception('delete without condition');
}
// 生成删除SQL语句
$sql = $this->builder->delete($options);
// 获取参数绑定
$bind = $this->getBind();
if ($options['fetch_sql']) {
// 获取实际执行的SQL语句
return $this->connection->getRealSql($sql, $bind);
}
// 检测缓存
if (isset($key) && Cache::get($key)) {
// 删除缓存
Cache::rm($key);
} elseif (!empty($options['cache']['tag'])) {
Cache::clear($options['cache']['tag']);
}
// 执行操作
$result = $this->execute($sql, $bind);
if ($result) {
if (!is_array($data) && is_string($pk) && isset($key) && strpos($key, '|')) {
list($a, $val) = explode('|', $key);
$item[$pk] = $val;
$data = $item;
}
$options['data'] = $data;
$this->trigger('after_delete', $options);
}
return $result;
}
execute();解析出sql后调用此方法。实际到
thinkphp/library/think/db/Connection.php
中执行execute();方法。
// 预处理
if (empty($this->PDOStatement)) {
$this->PDOStatement = $this->linkID->prepare($sql);
}
但是sql是怎么生成的呢
$sql = $this->builder->delete($options);
在这里thinkphp/library/think/db/Builder.php
protected $deleteSql = 'DELETE FROM %TABLE% %USING% %JOIN% %WHERE% %ORDER%%LIMIT% %LOCK%%COMMENT%';
public function delete($options)
{
$sql = str_replace(
['%TABLE%', '%USING%', '%JOIN%', '%WHERE%', '%ORDER%', '%LIMIT%', '%LOCK%', '%COMMENT%'],
[
$this->parseTable($options['table'], $options),
!empty($options['using']) ? ' USING ' . $this->parseTable($options['using'], $options) . ' ' : '',
$this->parseJoin($options['join'], $options),
$this->parseWhere($options['where'], $options),
$this->parseOrder($options['order'], $options),
$this->parseLimit($options['limit']),
$this->parseLock($options['lock']),
$this->parseComment($options['comment']),
], $this->deleteSql);
return $sql;
}
本质上是字符匹配替换。
至此,条件转化为sql问题解决。
设计模式后续分析。