The gray code is a binary numeral system where two successive values differ in only one bit.
Given a non-negative integer n representing the total number of bits in the code, print the sequence of gray code. A gray code sequence must begin with 0.
For example, given n = 2, return [0,1,3,2]. Its gray code sequence is:
00 - 0 01 - 1 11 - 3 10 - 2
Note:
For a given n, a gray code sequence is not uniquely defined.
For example, [0,2,3,1] is also a valid gray code sequence according to the above definition.
For now, the judge is able to judge based on one instance of gray code sequence. Sorry about that.
解法1 dp+非位运算
规律: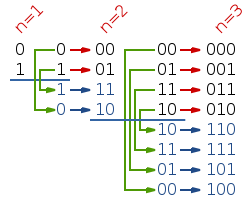
public class Solution { public List<Integer> grayCode(int n) { if(n == 0) { List<Integer> l1 = new ArrayList<>(); l1.add(0); return l1; } List<List<String>> list = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> l1 = new ArrayList<>(); List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); l1.add("0"); l1.add("1"); list.add(l1); for(int i = 1 ; i < n ; i++){ List<String> member = list.get(i-1); List<String> next = new ArrayList<>(); for(String s : member){ String newS = "0"+ s; next.add(newS); } for(int j = member.size() -1 ; j >= 0; j--){ String newS = "1"+ member.get(j); next.add(newS); } list.add(next); } List<String> l = list.get(n-1); for(String str : l){ res.add(getValueofBit(str)); } return res; } public int getValueofBit(String s){ int res = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i < s.length() ; i++){ res += Math.pow(2, s.length()-1-i) * (s.charAt(i) -'0'); } return res; } }
bit运算
public class Solution { public List<Integer> grayCode(int n) { int count = (int) Math.pow(2, n); List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i = 0; i < count ; i++){ res.add(i ^ (i >> 1)); } return res; } }