1. 采用的方案:冒泡排序
和数组的冒泡排序的思想没有很大的区别。直接 看代码吧。
定义一下数据结构:
typedef struct student
{
int num;
float score;
struct student *pre;
struct student *pnext;
}node,*Node;
排序代码:
Node sortt(Node head)
{
Node p=head,pn=head;
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)
{
p=head->next;
pn=p->next;//p和pn总是两个相邻的节点,且pn在p之后
for(int j=0;j<n-i-1;j++)
{
if(p->score > pn->score)
{
if(pn->next==NULL)
{
p->next=NULL;
pn->pre=p->pre;
p->pre->next=pn;
pn->nextt=p;
p->pre=pn;
}
else
{
p->next=pn->next;
pn->pre=p->pre;
p->pre->next=pn;
pn->next->pre=p;
p->pre=pn;
pn->next=p;
//位置交换结束
pn=p->next;//位置交换结束之后进行指针偏移,pn指向p的下一个节点
}
}
else
{
p=p->next;
pn=pn->next;
}
}
}
return head;
}
void TwoWayBubbleSort(LinkList &L)
{
int exchange = 1;//设标记
LinkList head = L;//双向链表头,算法过程中是向下起泡的开始结点
LinkList tail = NULL;//双向链表尾,算法过程中是向上起泡的开始结点
while(exchange)
{
LinkList p = head->next;
exchange = 0;
while (p->next != tail)
{
if (p->data > p->next->data)
{
LinkList temp = p->next; exchange = 1;
p->next = temp->next;
if(temp->next)temp->next->prior = p;
temp->next = p; p->prior->next = temp;
temp->prior = p->prior; p->prior = temp;
}
else p = p->next;
}
tail = p;
p = tail->prior;
while (exchange&&p->prior != head)
{
if (p->data < p->prior->data)
{
LinkList temp = p->prior; exchange = 1;
p->prior = temp->prior; temp->prior->next = p;
temp->prior = p; p->next->prior = temp;
temp->next = p->next; p->next = temp;
}
else p = p->prior;
}
head = p;
}
}
2. 保证不断链,每遍历一下就变换链的方向
定义数据结构:
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
代码:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *ans=NULL;
ListNode *pre=NULL;
ListNode *temp=head;
while(temp!=NULL)
{
ListNode *nextt=temp->next;
if(nextt==NULL)
ans=temp;
temp->next=pre;
pre=temp;
temp=nextt;
}
return ans;
}
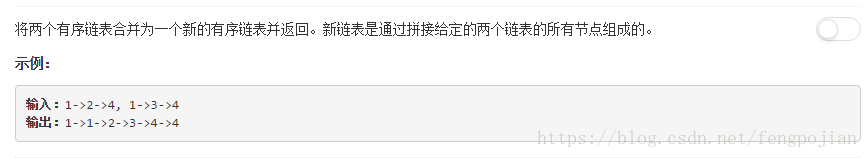
3. 合并两个有序链表
/**
*Definition for singly-linked list
*/
class ListNode{
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x){
val = x;
}
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) return l2;
if (l2 == null) return l1;
ListNode head = null;
if (l1.val <= l2.val){
head = l1;
head.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
} else {
head = l2;
head.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
}
return head;
}
4. 单链表的快排
struct Node
{
int key;
Node* next;
Node(int nKey, Node* pNext)
: key(nKey)
, next(pNext)
{}
};
Node* GetPartion(Node* pBegin, Node* pEnd)
{
int key = pBegin->key;
Node* p = pBegin;
Node* q = p->next;
while(q != pEnd)
{
if(q->key < key)
{
p = p->next;
swap(p->key,q->key);
}
q = q->next;
}
swap(p->key,pBegin->key);
return p;
}
void QuickSort(Node* pBeign, Node* pEnd)
{
if(pBeign != pEnd)
{
Node* partion = GetPartion(pBeign,pEnd);
QuickSort(pBeign,partion);
QuickSort(partion->next,pEnd);
}
}