分为数值类型,非数值类型。
数值类型包括,整形int,短整形short int,长整形long int,单精度浮点型float,双精度浮点型double。
其他的,比如数组,结构体,枚举。
非数值类型包括,char字符型。
字符串,封装了的字符数组。
整型,int,32位。
11111111 8 bit (比特) = 1 byte(字节)
11111111
11111111
11111111
几进制就没有几,二进制没有二,十进制没有十,八进制没有八,都变成10了。
8bit的最大值是2的8次方-1。也就是255。
短整型,short int,16位。
长整型,long int,32位。
float 32。
double 64。
字符型 char 8位。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// standared 标准
// input output 输入/输出
// header 头 .h头文件
int main() // 返回int,如果是void表示没有返回
{
int salary = 2500;
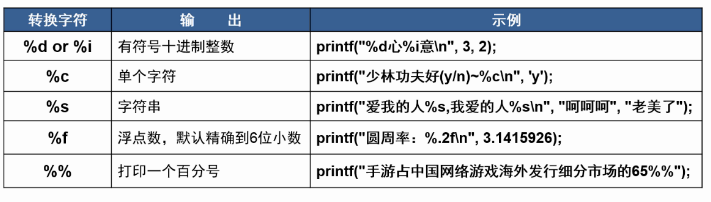
printf("小明的月薪是 %d
",salary);
return 0;
}
float小例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 已知长方形宽和高,求长方形的面积
int main()
{
float width = 2.5f;
float height= 3.5f;
float s = width*height;
printf("长方形的面积:%f
",s);
return 0;
}
double小例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 已知圆的半径,求圆的面积
int main()
{
double radius = 3.0;
double area = 3.141592653*radius*radius;
printf("圆的面积:%lf
",area);
return 0;
}
微调一下,小数显示两位数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 已知圆的半径,求圆的面积
int main()
{
double radius = 3.0;
double area = 3.141592653*radius*radius;
printf("圆的面积:%.2lf
",area); // .2lf表示保留两位小数
return 0;
}
char小例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 打印字符对应的ASCII码
int main()
{
char a = 'a';
char A = 'A';
printf("字符的ASCII码:
");
printf("%c %d
",a,a);
printf("%c %d
",A,A);
printf("%c %d
",a-32,a-32);
return 0;
}
// 结果
字符的ASCII码:
a 97
A 65
A 65
调整:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 打印字符对应的ASCII码
int main()
{
char a = 'a';
char ch = 97;
printf("字符的ASCII码:
");
printf("%c %d
",a,a);
printf("%c %d
",ch,ch);
return 0;
}
结果:
字符的ASCII码:
a 97
a 97
从上面可以看出,用'a',97效果都是一样的。
有符号的char类型指向-128到127之间,无符号的char类型指向0到255之间。
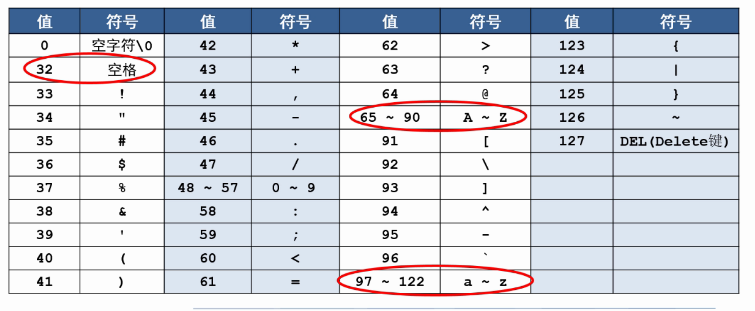
转换练习
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 接收用户输入的小写字母,输出大写字母
int main()
{
char ch = 'a';
printf("小写字母%c对应的大写字母位%c",ch,ch-32);
return 0;
}
九老师语录,不要钻牛角尖。有些东西一时半会理解不了正常,因为你还没到那个程序。等学到那个程度,回头会发现原来如此简单。