一:
To create a new branch and switch to it at the same time, you can run the git checkout command with the -b switch:
$ git checkout -b iss53
Switched to a new branch "iss53"
This is shorthand for:
$ git branch iss53
$ git checkout iss53
https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Git-Branching-Basic-Branching-and-Merging
二:The iss53 branch has moved forward with your work
However, before you do that, note that if your working directory or staging area has uncommitted changes that conflict with the branch you’re checking out, Git won’t let you switch branches. It’s best to have a clean working state when you switch branches。
You can run your tests, make sure the hotfix is what you want, and finally merge the hotfixbranch back into your master branch to deploy to production. You do this with the git mergecommand:
$ git checkout master
$ git merge hotfix
Updating f42c576..3a0874c
Fast-forward
index.html | 2 ++
1 file changed, 2 insertions(+)
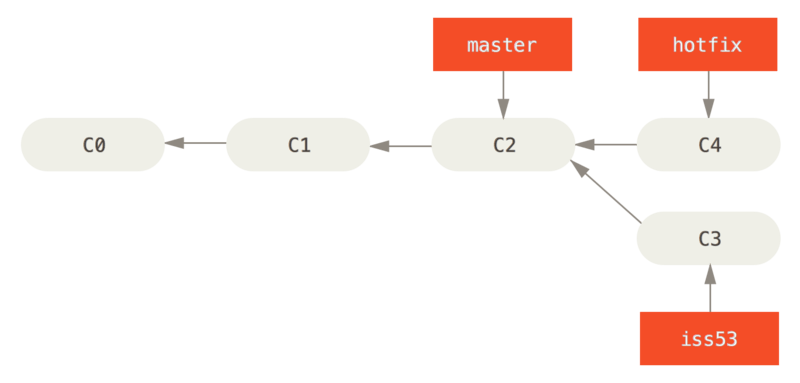
You’ll notice the phrase “fast-forward” in that merge. Because the commit C4 pointed to by the branch hotfix you merged in was directly ahead of the commit C2 you’re on, Git simply moves the pointer forward. To phrase that another way, when you try to merge one commit with a commit that can be reached by following the first commit’s history, Git simplifies things by moving the pointer forward because there is no divergent work to merge together — this is called a “fast-forward.”
三:
Suppose you’ve decided that your issue #53 work is complete and ready to be merged into your master branch. In order to do that, you’ll merge your iss53 branch into master, much like you merged your hotfix branch earlier. All you have to do is check out the branch you wish to merge into and then run the git merge command:
$ git checkout master
Switched to branch 'master'
$ git merge iss53
Merge made by the 'recursive' strategy.
index.html | 1 +
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
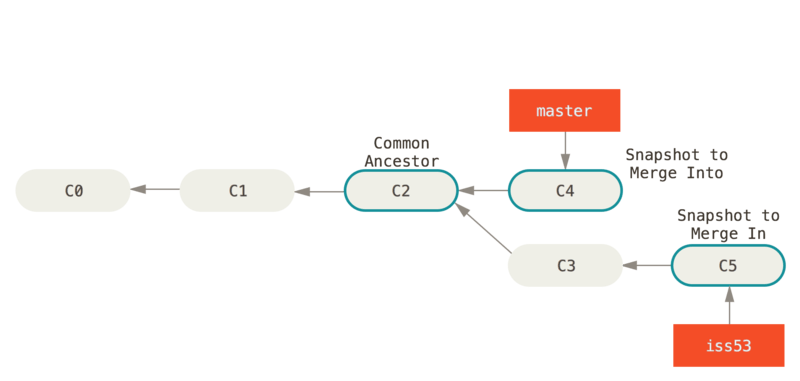
This looks a bit different than the hotfix merge you did earlier. In this case, your development history has diverged from some older point. Because the commit on the branch you’re on isn’t a direct ancestor of the branch you’re merging in, Git has to do some work. In this case, Git does a simple three-way merge, using the two snapshots pointed to by the branch tips and the common ancestor of the two.