1. 综述
SRS 中使用了 State Threads 协程库,该库对信号的处理是将信号事件转换为 I/O 事件。主要做法是:对关注的信号设置同样地信号处理函数 sig_catcher(),该函数捕获信号,并将信号写入管道,然后由创建的信号线程 signal 不断循环读取该管道,读取到事件并做相应的处理。
2. 信号管理器之创建
信号管理器的定义是在 SrsServer 类下的:
/**
* SRS RTMP server, initialize and listen,
* start connection service thread, destroy client.
*/
class SrsServer : virtual public ISrsReloadHandler
, virtual public ISrsSourceHandler
, virtual public IConnectionManager
{
...
private:
...
/**
* signal manager which convert signal to io message.
*/
SrsSignalManager* signal_manager;
...
};
2.1 SrsSignalManager 类
位于 srs_app_server.hpp:
/**
* convert signal to io,
* @see: st-1.9/docs/notes.html
*/
class SrsSignalManager : public ISrsEndlessThreadHandler
{
private:
/* Per-process pipe which is used as a signal queue. */
/* Up to PIPE_BUF/sizeof(int) signals can be queued up. */
int sig_pipe[2];
st_netfd_t signal_read_stfd;
private:
SrsServer* _server;
SrsEndlessThread* pthread;
public:
SrsSignalManager(SrsServer* server);
virtual ~SrsSignalManager();
public:
virtual int initialize();
virtual int start();
// interface ISrsEndlessThreadHandler.
public:
virtual int cycle();
private:
// global singleton instance
static SrsSignalManager* instance;
/* Signal catching function. */
/* Converts signal event to I/O event. */
static void sig_catcher(int signo);
};
SrsSignalManager 类继承自 ISrsEndlessThreadHandler 类。
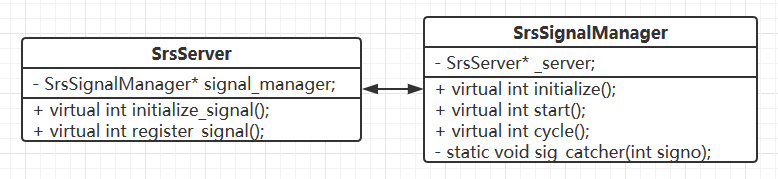
SrsServer 与 SrsSignalManager 之间的关系图 1(双向关联)
2.2 ISrsEndlessThreadHandler
位于 srs_app_thread.hpp:
/**
* the endless thread is a loop thread never quit.
* user can create thread always running util server terminate.
* the step to create a thread never stop:
* 1. create SrsEndlessThread field.
* for example:
* class SrsStreamCache: public ISrsEndlessThreadHandler {
* public: SrsStreamCache() {
* pthread = new SrsEndlessThread("http-stream", this);
* }
* public: virtual int cycle() {
* // do some work never end.
* }
}
* }
* @remark user must use block method in cycle method, for example, sleep or socket io.
*/
class ISrsEndlessThreadHandler
{
public:
ISrsEndlessThreadHandler();
virtual ~ISrsEndlessThreadHandler();
public:
/**
* the cycle method for the common thread.
* @remark user must use block method in cycle method, for example, sleep or socket io.
*/
virtual int cycle() = 0;
public:
/**
* other callback for handler.
* @remark all callback is optional, handler can ignore it.
*/
virtual void on_thread_start();
virtual int on_before_cycle();
virtual int on_end_cycle();
virtual void on_thread_stop();
}
该类是用于创建一个无限循环、从不退出的线程,直到 server 终止。
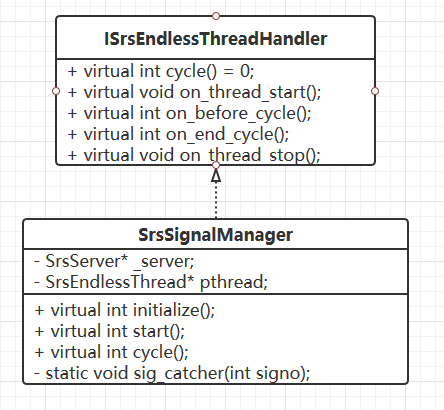
SrsSignalManager 与 ISrsEndlessThreadHandler 之间的关系图 2(继承)
2.3 SrsSignalManager 构造函数
SrsSignalManager* SrsSignalManager::instance = NULL;
SrsSignalManager::SrsSignalManager(SrsServer* server)
{
SrsSignalManager::instance = this;
_server = server;
sig_pipe[0] = sig_pipe[1] = -1;
/* 创建一个无线循环且永不退出的线程 */
pthread = new SrsEndlessThread("signal", this);
signal_read_stfd = NULL;
}
2.4 SrsEndlessThread
2.4.1 SrsEndlessThread 类定义
class SrsEndlessThread : public internal::ISrsThreadHandler
{
private:
internal::SrsThread* pthread;
ISrsEndlessThreadHandler* handler;
public:
SrsEndlessThread(const char* n, ISrsEndlessThreadHandler* h);
virtual ~SrsEndlessThread();
public:
/**
* for the endless thread, never quit.
*/
virtual int start();
// interface internal::ISrsThreadHandler
public:
virtual int cycle();
virtual void on_thread_start();
virtual int on_before_cycle();
virtual int on_end_cycle();
virtual void on_thread_stop();
};
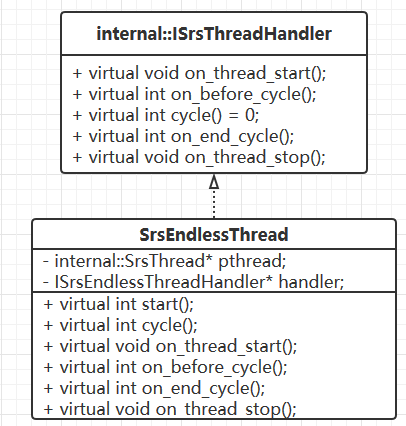
该 SrsEndlessThread 类继承自命名空间 internal 下的 ISrsThreadHandler 类。
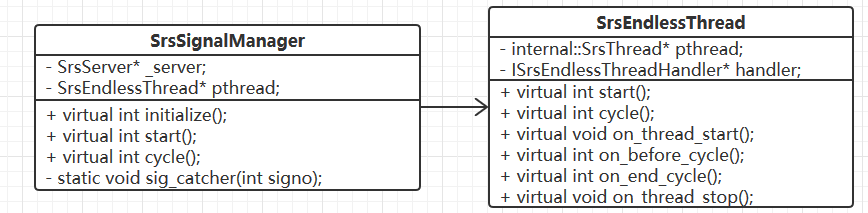
SrsEndlessThread 与 SrsSignalManager 之间的关系图 3(单向关联)
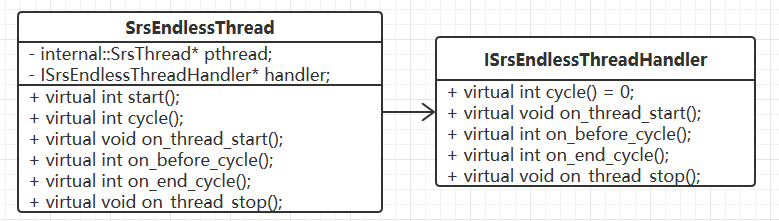
SrsEndlessThread 与 ISrsEndlessThreadHandler 之间的关系 4(单向关联)
2.4.2 ISrsThreadHandler 类定义
// the internal classes, user should never use it.
// user should use the public classes at the bellow:
// @see SrsEndlessThread, SrsOneCycleThread, SrsReusableThread
namestacp internal {
/**
* the handler for the thread, callback interface.
* the thread model defines as:
* handler->on_thread_start()
* while loop:
* handler->on_before_cycle()
* handler->cycle()
* handler->on_end_cycle()
* if !loop then break for user stop thread.
* sleep(CycleIntervalMilliseconds)
* handler->on_thread_stop()
* when stop, the thread will interrupt the st_thread,
* which will cause the socket to return error and
* terminater the cycle thread.
*
* @remark why should check can_loop() in cycle method?
* when thread interrupt, the socket maybe not got EINT,
* espectially on st_usleep(), so the cycle must check the loop,
* when handler->cycle() has loop itself, for example:
* while (true):
* if (read_from_socket(skt) < 0) break;
* if thread stop when read_from_socket, it's ok, the loop will break,
* but when thread stop interrupt the st_usleep(0), then the loop is
* death loop.
* in a word, the handler->cycle() must:
* while (pthread->can_loop()):
* if (read_from_socket(skt) < 0) break;
* check the loop, then it works.
*
* @remark why should use stop_loop() to terminate thread in itself?
* in the thread itself, that is the cycle method,
* if itself want to terminater the thread, should never use stop(),
* but use stop_loop() to set the loop to false and terminater normally.
*
* @remark when should set the interval_us, and when not?
* the cycle will invoke util cannot loop, eventhough the return code of cycle
* is error, so the interval_us used to sleep for each cycle.
*
*/
class ISrsThreadHandler
{
public:
ISrsThreadHandler();
virtual ~ISrsThreadHandler();
public:
virtual void on_thread_start();
virtual int on_before_cycle();
virtual int cycle() = 0;
virtual int on_end_cycle();
virtual void on_thread_stop();
};
}
SrsEndlessThread 与 internal::ISrsThreadHandler 之间的关系图 5(继承)
2.4.3 SrsEndlessThread 构造函数
SrsEndlessThread::SrsEndlessThread(const char* n, ISrsEndlessThreadHandler* h)
{
handler = h;
/*
* @n: 线程的名字,由前面可知为 signal
* @this: 线程循环的处理程序
* @0: 线程循环后休眠的时间,这里为 0,即不休眠
* @false: 该线程是否可 joinable,这里为 false,即表示不可以被其他线程终止
*/
pthread = new internal::SrsThread(n, this, 0, false);
}
在该构造函数中,创建了一个 SrsThread 类的线程,这里为 signal,该线程是一个无限循环且永不退出的线程。
2.4.4 SrsThread 类定义
namespace internal {
...
/**
* provides services from st_thread_t,
* for common thread usage.
*/
class SrsThread
{
private:
st_thread_t tid;
int _cid;
bool loop;
bool can_run;
bool really_terminated;
bool _joinable;
const char* _name;
bool disposed;
private:
ISrsThreadHandler* handler;
int64_t cycle_interval_us;
public:
/**
* initialize the thread.
* @param name, human readable name for st debug.
* @param thread_handler, the cycle handler for the thread.
* @param interval_us, the sleep inteval when cycle finished.
* @param joinable, if joinable, other thread must stop the thread.
* @remark if joinable, thread never quit itself, or memory leak.
* @see: https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/78
* #remark about st debug, see st-1.9/README, _st_iterate_threads_flag
*/
/**
* TODO: FIXME: maybe all thread must be reap by others threads,
* @see: https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/77
*/
SrsThread(const char* name, ISrsThreadHandler* thread_handler,
int64_t interval_us, bool joinable);
virtual ~SrsThread();
public:
/**
* get the context id. @see: ISrsThreadContext.get_id().
* used for parent thread to get thd id.
* @remark when start thread, parent thread will block and wait for this id ready.
*/
virtual int cid();
/**
* start the thread, invoke the cycle of handler util
* user stop the thread.
* @remark ignore any error of cycle of handler.
* @remark user can start multiple times, ignore if already started.
* @remark wait for the cid is set by thread pfn.
*/
virtual int start();
/**
* stop the thread, wait for the thread to terminate.
* @remark user can stop multiple times, ignore if already stopped.
*/
virtual void stop();
public:
/**
* whether the thread should loop,
* used for handler->cycle() which has a loop method,
* to check this method, break if false.
*/
virtual bool can_loop();
/**
* for the loop thread to stop the loop.
* other thread can directly use stop() to stop loop and wait for quit.
* this stop loop method only set loop to false.
*/
virtual void stop_loop();
private:
virtual void dispose();
virtual void thread_cycle();
static void* thread_fun(void* arg);
};
}
该类定义了一个线程,用于提供来自 st_thread_t 的服务,便于通用的线程使用。
SrsEndlessThread 与 SrsThread 之间的关系图 6(单向关联)

2.4.5 SrsThread 构造函数
SrsThread::SrsThread(const char* name, ISrsThreadHandler* thread_handler,
int64_t interval_us, bool joinable)
{
_name = name;
handler = thread_handler;
cycle_interval_us = interval_us;
tid = NULL;
loop = false;
really_terminated = true;
_cid = -1;
_joinable = joinable;
disposed = false;
/*
* in start(), the thread cycle method maybe stop the remove the thread itself,
* and the thread start(0 is waiting for the _cid, and sement fault then.
* @see https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/110
* thread will set _cid, callback on_thread_start(), then wait for the can_run signal.
*/
can_run = false;
}
以上即为 SrsSignalManager 信号管理器的构造过程:主要就是创建一个无线循环且永不退出的线程:signal。
3. 信号管理器之初始化
信号管理器的初始化是在 run_master 函数中进行的。
int run_master()
{
...
/* 初始化信号管理器 */
if ((ret = _srs_server->initialize_signal()) != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
return ret;
}
...
}
3.1 SrsServer::initialize_signal
int SrsServer::initialize_signal()
{
return signal_manager->initialize();
}
该函数接着又调用信号管理器 SrsSignalManager 类的初始化函数 initialize.
3.2 SrsSignalManager::initialize
int SrsSignalManager::initialize()
{
int ret = ERROR_SUCCESS;
/* Create signal pipe */
if (pipe(sig_pipe) < 0) {
ret = ERROR_SYSTEM_CREATE_PIPE;
srs_error("create signal manager pipe failed. ret=%d", ret);
return ret;
}
/* 根据给定的文件描述符sig_pipe[0](读管道)创建一个 _st_netfd_t 类型的结构体 */
if ((signal_read_stfd = st_netfd_open(sig_pipe[0])) == NULL) {
ret = ERROR_SYSTEM_CREATE_PIPE;
srs_error("create signal manage st pipe failed. ret=%d", ret);
return ret;
}
return ret;
}
3.2.1 st_netfd_open
_st_netfd_t *st_netfd_open(int osfd)
{
/* 这里构建一个 _st_netfd_t 的结构体,同时设置 osfd 为非阻塞 */
return _st_netfd_new(osfd, 1, 0);
}
3.2.2 _st_netfd_new
static _st_netfd_t *_st_netfd_new(int osfd, int nonblock, int is_socket)
{
_st_netfd_t *fd;
int flags = 1;
/* 这里调用到 epoll 的 _st_epoll_fd_new 函数,
* 该函数中主要是检测 osfd 文件描述符的大小是否超过
* 当前允许打开的文件描述符最大值,若是,则扩大当前支持
* 的文件描述符个数,否则直接返回 0 */
if ((*_st_eventsys->fd_new)(osfd) < 0) {
return NULL;
}
/* 若 _st_netfd_freelist 列表中有空闲的 _st_netfd_t 结构体,
* 则从其中取出一个使用 */
if (_st_netfd_freelist) {
fd = _st_netfd_freelist;
_st_netfd_freelist = _st_netfd_freelist->next;
} else {
/* 否则,新分配一个 _st_netfd_t */
fd = calloc(1, sizeof(_st_netfd_t));
if (!fd) {
return NULL;
}
}
fd->osfd = osfd;
fd->inuse = 1;
fd->next = NULL;
if (nonblock) {
/* Use just one system call */
if (is_socket && ioctl(osfd, FIONBIO, &flags) != -1) {
return fd;
}
/* Do it the Posix way */
if ((flags = fcntl(osfd, F_GETFL, 0)) < 0 ||
fcntl(osfd, F_SETFL, flags | O_NONBLOCK) < 0) {
st_netfd_free(fd);
return NULL;
}
}
return fd;
}
3.2.3 _st_epoll_fd_new
ST_HIDDEN int _st_epoll_fd_new(int osfd)
{
if (osfd >= _st_epoll_data->fd_data_size &&
_st_epoll_fd_data_expand(osfd) < 0)
return -1;
return 0;
}
该函数中仅检测当前打开的文件描述符 osfd 是否已超过当前 ST 所支持的文件描述符个数的最大值,若是,则扩大为原先的两倍.
3.2.4 _st_epoll_fd_data_expand
ST_HIDDEN int _st_epoll_fd_data_expand(int msxfd)
{
_epoll_fd_data_t *ptr;
int n = _st_epoll_data->fd_data_size;
/* 若大于当前 ST 中 epoll 所分配好的监听个数最大值,
* 则扩大两倍 */
while (maxfd >= n)
n <<= 1;
/* 重新分配 */
ptr = (_epoll_fd_data_t *)realloc(_st_epoll_data->fd_data,
n * sizeof(_epoll_fd_data_t));
if (!ptr)
return -1;
/* 将新增的内存置为 0 */
memset(ptr + _st_epoll_data->fd_data_size, 0,
(n - _st_epoll_data->fd_data_size) * sizeof(_epoll_fd_data_t));
_st_epoll_data->fd_data = ptr;
_st_epoll_data->fd_data_size = n;
return 0;
}
4. 信号管理器之注册信号
初始化好信号管理器后,接着向该信号管理器中注册信号。
int run_master()
{
...
if ((ret = _srs_server->register_signal()) != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
return ret;
}
...
}
4.1 SrsServer::register_signal
int SrsServer::register_signal()
{
// start signal process thread.
return signal_manager->start();
}
该函数中直接调用信号管理器的启动函数。
4.2 SrsSignalManager::start
// signal defines.
#define SIGNAL_RELOAD SIGHUP
int SrsSignalManager::start()
{
/**
* Note that if multiple processes are used (see below),
* the signal pipe should be initialized after the fork(2) call
* so that each process has its own private pipe.
*/
struct sigaction sa;
/* Install sig_catcher() as a signal handler */
sa.sa_handler = SrsSignalManager::sig_catcher;
sigemptyset(&sa.sa_mask);
sa.sa_flags = 0;
sigaction(SIGNAL_RELOAD, &sa, NULL);
sa.sa_handler = SrsSignalManager::sig_catcher;
sigemptyset(&sa.sa_mask);
sa.sa_flags = 0;
sigaction(SIGTERM, &sa, NULL);
sa.sa_handler = SrsSignalManager::sig_catcher;
sigemptyset(&sa.sa_mask);
sa.sa_flags = 0;
sigaction(SIGINT, &sa, NULL);
sa.sa_handler = SrsSignalManager::sig_catcher;
sigemptyset(&sa.sa_mask);
sa.sa_flags = 0;
sigaction(SIGUSR2, &sa, NULL);
srs_trace("signal installed");
/* 这里一层层调用下去,最后会调用 st_thread_create 函数创建一个新的线程 */
return pthread->start();
}
该函数中,为信号 SIGHUP、SIGTERM、SIGINT、SIGUSR2 等信号注册了同一个信号处理函数:sig_catcher。最后调用 pthread->start() 函数创建一个线程。从前面可知,该线程名为 signal,是一个无线循环且永不退出的线程。
4.2.1 SrsEndlessThread::start
int SrsEndlessThread::start()
{
return pthread->start();
}
4.2.2 SrsThread::start
该函数位于 srs_app_thread.cpp 文件中。
int SrsThread::start()
{
int ret = ERROR_SUCCESS;
if (tid) {
srs_info("thread %s already running.", _name);
return ret;
}
/* 创建一个线程,线程函数为 thread_fun,由前面可知创建的线程是
* 一个无线循环且从不退出的线程,因此 joinable 为 0,即不可被其他线程终止 */
if ((tid = st_thread_create(thread_fun, this, (_joinable ? 1 : 0), 0)) == NULL) {
ret = ERROR_ST_CREATE_CYCLE_THREAD;
srs_error("st_thread_create failed. ret=%d", ret);
return ret;
}
disposed = false;
// we set to loop to true for thread to run.
loop = true;
// wait for cid to ready, for parent thread to get the cid.
while (_cid < 0) {
/* 当 _cid 小于 0 时,调用 st_usleep 函数将当前线程添加到 sleep 队列中,
* 即表示当前线程进入休眠,然后保存当前线程的上下文环境,以便当前线程的
* 休眠时间到达时,从休眠状态中唤醒过来,即再次回到当前位置继续往下执行,
* 直到 _cid 不为 0. 当调度其他线程运行时,有可能会调度到上面的新建的线程
* signal,该线程的线程函数为 thread_fun,在该函数中会构建一个 context id,
* 即 _cid */
st_usleep(10 * 1000);
}
/* 当该线程从休眠中唤醒,且 _cid 准备好时,会设置 can_run 标志位,
* 表示 thread_fun 线程函数中的循环可以开始了 */
// now, cycle thread can run.
can_run = true;
return ret;
}
4.2.3 st_usleep
int st_usleep(st_utime_ usecs)
{
_st_thread_t *me = _ST_CURRENT_THREAD();
if (me->flags & _ST_FL_INTERRUPT) {
me->flags &= ~_ST_FL_INTERRUPT;
errno = EINTR;
return -1;
}
if (usecs != _ST_UTIME_NO_TIMEOUT) {
/* 将该线程添加到 sleep 队列中 */
me->state = _ST_ST_SLEEPING;
_ST_ADD_SLEEPQ(me, usecs);
} else {
me->state = _ST_ST_SUSPENDED;
}
/* 保存上下文环境,然后切换上下文环境,即调度其他线程执行 */
_ST_SWITCH_CONTEXT(me);
if (me->flags & _ST_FL_INTERRUPT) {
me->flags &= ~_ST_FL_INTERRUPT;
errno = EINTR;
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
该函数将该当前线程添加到 sleep 队列中,然后切换线程上下文。
注:线程超时的管理是在 idle 线程中进行的,在 idle 线程中会检测 sleep 队列中是否有线程的超时时间已经到达,若有,则唤醒该线程,即重新调度该线程从原先休眠的位置继续往下执行。
4.2.4 _ST_ADD_SLEEPQ
#define _ST_ADD_SLEEPQ(_thr, _timeout) _st_add_sleep_q(_thr, _timeout)
4.2.5 _st_add_sleep_q
void _st_add_sleep_q(_st_thread_t *trd, st_utime_t timeout)
{
/* 计算该线程超时的绝对时间 */
trd->due = _ST_LAST_CLOCK + timeout;
trd->flags |= _ST_FL_ON_SLEEPQ;
trd->heap_index = ++_ST_SLEEPQ_SIZE;
/* 将该线程插入到平衡二叉树中 */
heap_insert(trd);
}
ST 的超时管理是使用平衡二叉树实现的。
5. 信号的捕获
SRS 对于 SIGNAL_RELOAD(即 SIGHUP)、SIGTERM、SIGINT、SIGUSR2 等信号设置了同一个信号处理函数:sig_catcher。该信号处理函数主要是将发生的信号事件写入管道,转换为 I/O 事件。
void SrsSignalManager::sig_catcher(int signo)
{
int err;
/* Save errno to restore it after the write() */
err = errno;
/* write() is reentrant/async-safe */
int fd = SrsSignalManager::instance->sig_pipe[1];
write(fd, &signo, sizeof(int));
errno = err;
}
6. signal 线程
该 signal 线程是一个无限循环且永不退出的线程。该线程函数为 SrsThread::thread_fun,如下:
vid* SrsThread::thread_fun(void* arg)
{
SrsThread* obj = (SrsThread*)arg;
srs_assert(obj);
/* 进入线程循环 */
obj->thread_cycle();
// for valgrind to detect.
SrsThreadContext* ctx = dynamic_cast<SrsThreadContext*>(_srs_context);
if (ctx) {
ctx->clear_cid();
}
st_thread_exit(NULL);
return NULL;
}
6.1 线程循环:SrsThread::thread_cycle
void SrsThread::thread_cycle()
{
int ret = ERROR_SUCCESS;
_srs_context->generage_id();
srs_info("thread %s cycle start", _name);
_cid = _srs_context->get_id();
srs_assert(handler);
/* 多态:调用的是子类 SrsEndlessThread 的成员函数 on_thread_start */
handler->on_thread_start();
// thread is running now.
really_terminated = false;
/* 当 can_run 为 0 时,该线程进入休眠,将控制权让出去,调度其他线程运行,直到
* 其他线程将 can_run 置为 1,才会在唤醒后跳出该循环继续往下执行 */
// wait for cid to ready, for parent thread to get the cid.
while (!can_run && loop) {
st_usleep(10 * 1000);
}
/* 检测是否可以进入循环,该 loop 在 signal 线程创建后就已经置为 1 了 */
while (loop) {
/* 多态:调用子类 SrsEndlessThread 的成员函数 on_before_cycle */
if ((ret = handler->on_before_cycle()) != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
srs_warn("thread %s on before cycle failed, ignored and retry, ret=%d",
_name, ret);
goto failed;
}
srs_info("thread %s on before cycle success", _name);
if ((ret = handler->cycle()) != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
if (!srs_is_client_gracefully_close(ret) && !srs_is_system_control_error(ret))
{
srs_warn("thread %s cycle failed, ignored and retry, ret=%d", _name, ret);
}
goto failed;
}
srs_info("thread %s cycle success", _name);
if ((ret = handler->on_end_cycle()) != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
srs_warn("thread %s on end cycle failed, ignored and retry, ret=%d",
_name, ret);
goto failed;
}
srs_info("thread %s on end cycle success", _name);
failed:
if (!loop) {
break;
}
// to improve performance, donot sleep when interval is zero.
// @see: https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/237
if (cycle_interval_us != 0) {
st_usleep(cycle_interval_us);
}
}
// ready terminated now.
really_terminated = true;
handler->on_thread_stop();
srs_info("thread %s cycle finished", _name);
}
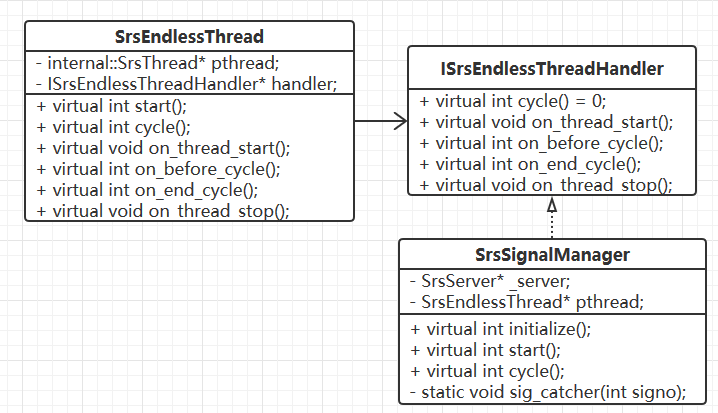
SrsThread、SrsEndlessThread 和 internal::ISrsThreadHandler 三者之间的关系

6.2 SrsEndlessThread::on_thread_start
位于 srs_app_thread.cpp:
void SrsEndlessThread::on_thread_start()
{
handler->on_thread_start();
}
由于 ISrsEndlessThreadHandler 的子类 SrsSignalManager 没有实现 on_thread_start 函数,因此还是调用父类的 on_thread_start 函数。
SrsEndlessThread、SrsSignalManager 和 ISrsEndlessThreadHandler 三者之间的关系
6.2.1 ISrsEndlessThreadHandler::on_thread_start
void ISrsEndlessThreadHandler::on_thread_start()
{
}
该函数为空。
6.3 SrsEndlessThread::on_before_cycle
int SrsEndlessThread::on_before_cycle()
{
return handler->on_before_cycle();
}
同理,参考上图,可知,ISrsEndlessThreadHandler 的子类 SrsSignalManager 没有实现 on_before_cycle 函数,因此还是调用父类的 on_before_cycle 函数。
int ISrsEndlessThreadHandler::on_before_cycle()
{
return ERROR_SUCCESS;
}
6.4 SrsEndlessThread::cycle
int SrsEndlessThread::cycle()
{
return handler->cycle();
}
这里,发生多态:ISrsEndlessThreadHandler 的子类 SrsSignalManager 实现了 cycle() 函数,因此调用子类的 cycle() 函数。
6.4.1 SrsSignalManager::cycle
位于 srs_app_server.cpp:
int SrsSignalManager::cycle()
{
int ret = ERROR_SUCCESS;
int signo;
/* Read the next signal from the pipe */
st_read(signal_read_stfd, &signo, sizeof(int), ST_UTIME_NO_TIMEOUT);
/* Process signal synchronously */
_server->on_signal(signo);
return ret;
}
该函数主要做两件事:
- 从管道中读取由信号事件状态而来的 I/O 事件,若本次没有读取到,则会对该管道进行监听,直到监听到事件才会将再次调度该线程
- 处理信号同步
6.4.2 st_read
这里调用 st_read 从管道中读取 I/O 事件,该 I/O 事件其实就是由 sig_catcher 函数将信号事件转换后的 I/O 事件。
ssize_t st_read(_st_netfd_t *fd, void *buf, size_t nbyte, st_utime_t timeout)
{
ssize_t n;
while ((n = read(fd->osfd, buf, nbyte)) < 0) {
if (errno == EINTR)
continue;
if (!_IO_NOT_READY_ERROR)
return -1;
/* Wait until the socket becomes readable */
if (st_netfd_poll(fd, POLLIN, timeout) < 0)
reurn -1;
}
return n;
}
该函数中直接调用 read 函数从管道中读取 nbyte 直接的数据到 buf 中,读取成功,直接返回;若失败,则调用 st_netfd_poll 函数轮询,超时时间为 timeout (由前面知,传入的超时时间为 -1)。
6.4.3 st_netfd_poll
/*
* Wait for I/O on a single descriptor.
*/
int st_netfd_poll(_st_netfd_t *fd, int how, st_utime_t timeou)
{
struct pollfd pd;
int n;
pd.fd = fd->osfd;
pd.events = (short)how;
pd.revents = 0;
/* 监听指定的 IO 事件 */
if ((n = st_poll(&pd, 1, timeout)) < 0)
return -1;
if (n == 0) {
/* Timed out */
errno = ETIME;
return -1;
}
if (pd.revents & POLLNVAL) {
errno = EBADF;
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
该函数中,又调用 st_poll 函数。
6.4.4 st_poll
int st_poll(struct pollfd *pds, int npds, st_utime_t timeout)
{
struct pollfd *pd;
struct pollfd *epd = pds + npds;
_st_pollq_t pq;
/*这里当前线程应为 signal 线程 */
_st_thread_t *me = _ST_CURRENT_THREAD();
int n;
/* 检测当前线程是否已被中断了 */
if (me->flags & _ST_FL_INTERRUPT) {
me->flags &= ~_ST_FL_INTERRUPT;
errno = EINTR;
return -1;
}
/* 这里调用的是 _st_epoll_pollset_add 函数向 epoll 中
* 添加或修改感兴趣的事件 */
if ((*_st_eventsys->pollset_add)(pds, npds) < 0)
return -1;
pq.pds = pds;
pq.npds = npds;
pq.thread = me;
pq.on_ioq = 1;
/* 向 io 队列中添加一个指向 _st_pollq_t 结构体的指针,该结构体代表正在监听的事件 */
_ST_ADD_IOQ(pq);
/* 若传入的超时时间 timeout 不为 -1,则将该线程休眠 timeout */
if (timeout != ST_UTIME_NO_TIMEOUT)
_ST_ADD_SLEEPQ(me, timeout);
/* 否则,该线程等待 I/O 事件的到达后才会再次调度,从下面继续运行 */
me->state = _ST_ST_IO_WAIT;
_ST_SWITCH_CONTEXT(me);
/* 若监听到所监听的 I/O 事件后,该线程再次被调度,从这里开始继续执行 */
n = 0;
/* 正常情况下,再次获得调度,pq.on_ioq 应为 0,若为 1,表示超时了,这里将其从 io 中删除 */
if (pq.on_ioq) {
/* If we timed out, the pollq might still be on the ioq. Remove it */
_ST_DEL_IOQ(pq);
/* 将该事件从 epoll 中移除 */
(*st_eventsys->pollset_del)(pds, npds);
} else {
/* Count the number of ready descriptors */
for (pd = pds; pd < epd; pd++) {
if (pd->revents)
n++;
}
}
if (me->flags & _ST_FL_INTERRUPT) {
me->flags &= ~_ST_FL_INTERRUPT;
errno = EINTR;
return -1;
}
/* 成功监听到事件,返回事件的个数 */
return n;
}
在该函数中:
- 首先是向 epoll中 添加或修改感兴趣的事件
- 构建一个 _st_pollq_t 结构体的指针变量,并将其添加到 io 队列中,表示正在监听该结构体上的事件
- 将当前线程的控制权让出,调度其他线程运行
- 当监听到 _st_pollq_t 中所要监听的事件后,该线程会再次获得调度,从切换线程处再次往下继续执行,最后也就是计算监听到的事件个数,然后返回该值
6.4.5 _st_epoll_pollset_add
位于 event.c:
#define _ST_EPOLL_READ_CNT(fd) (_st_epoll_data->fd_data[fd].rd_ref_cnt)
#define _ST_EPOLL_WRITE_CNT(fd) (_st_epoll_data->fd_data[fd].wr_ref_cnt)
#define _ST_EPOLL_EXCEP_CNT(fd) (_st_epoll_data->fd_data[fd].ex_ref_cnt)
#define _ST_EPOLL_READ_BIT(fd) (_ST_EPOLL_READ_CNT(fd) ? EPOLLIN : 0)
#define _ST_EPOLL_WRITE_BIT(fd) (_ST_EPOLL_WRITE_CNT(fd) ? EPOLLOUT : 0)
#define _ST_EPOLL_EXCEP_BIT(fd) (_ST_EPOLL_EXCEP_CNT(fd) ? EPOLLPRI : 0)
#define _ST_EPOLL_EVENTS(fd)
(_ST_EPOLL_READ_BIT(fd)|_ST_EPOLL_WRITE_BIT(fd)|_ST_EPOLL_EXCEP_BIT(fd))
ST_HIDDEN int _st_epoll_pollset_add(struct pollfd *pds, int npds)
{
struct epoll_event ev;
int i, fd;
int old_events, events, op;
/* Do as many checks as possible up front */
for (i = 0; i < npds; i++) {
fd = pds[i].fd;
if (fd < 0 || !pds[i].events ||
(pds[i].events & ~(POLLIN | POLLOUT | POLLPRI))) {
errno = EINVAL;
return -1;
}
if (fd >= _st_epoll_data->fd_data_size &&
_st_epoll_fd_data_expand(fd) < 0)
return -1;
}
for (i = 0; i < npds; i++) {
fd = pds[i].fd;
/* 先保存该描述符旧的监听的事件 */
old_events = _ST_EPOLL_EVENTS(fd);
/* 根据本次该 fd 要监听的事件,将相应事件的引用值加 1 */
if (pds[i].events & POLLIN)
_ST_EPOLL_READ_CNT(fd)++;
if (pds[i].events & POLLOUT)
_ST_EPOLL_WRITE_CNT(fd)++;
if (pds[i].events & POLLPRI)
_ST_EPOLL_EXCEP_CNT(fd)++;
/* 再次获取该 fd 新的要监听的事件 */
events = _ST_EPOLL_EVENTS(fd);
/* 若旧监听事件与新的监听事件不等 */
if (events != old_events) {
/* 若旧监听事件不为0,则本次操作为修改该 fd 要监听的事件,
* 否则该 fd 新添加要监听的事件 */
op = old_events ? EPOLL_CTL_MOD : EPOLL_CTL_ADD;
ev.events = events;
ev.data.fd = fd;
/* 向 epoll 对象中添加或修改感兴趣的事件,返回 0 表示成功 */
if (epoll_ctl(_st_epoll_data->epfd, op, fd, &ev) < 0 &&
(op != EPOLL_CTL_ADD || errno != EEXIST))
break;
/* 若是向 epoll 中添加感兴趣的事件 */
if (op == EPOLL_CTL_ADD) {
/* epoll 的 epoll_event 类的数组元素个数加 1 */
_st_epoll_data->evtlist_cnt++;
if (_st_epoll_data->evtlist_cnt > _st_epoll_data->evtlist_size)
_st_epoll_evtlist_expand();
}
}
}
if (i < npds) {
/* Error */
int err = errno;
/* Unroll the state */
_st_epoll_pollset_del(pds, i + 1);
errno = err;
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
该函数主要是向 epoll 中添加或修改感兴趣的事件。
6.4.6 SrsServer::on_signal
void SrsServer::on_signal(int signo)
{
if (signo == SIGNAL_RELOAD) {
signal_reload = true;
return;
}
if (signo == SIGINT || signo == SIGUSR2) {
#ifdef SRS_AUTO_GPERF_MC
rs_trace("gmc is on, main cycle will terminate normally.");
signal_gmc_stop = true;
#else
srs_trace("user terminate program");
#ifdef SRS_AUTO_MEM_WATCH
srs_memory_report();
#endif
exit(0);
#endif
return;
}
if (signo == SIGTERM && !signal_gracefully_quit) {
srs_trace("user terminate program, gracefully quit.");
signal_gracefully_quit = true;
return;
}
}
在该函数中对捕获的信号进行相应的处理。
致此,以上就是 SRS 对信号的管理。