解决方案总结:
由于数据库层面的读写并发,引发的数据库与缓存数据不一致的问题(本质是后发生的读请求先返回了),可能通过两个小的改动解决:
1)修改服务Service连接池,id取模选取服务连接,能够保证同一个数据的读写都落在同一个后端服务上
“同一个数据的访问一定落到同一个服务上”
获取Service连接的CPool.GetServiceConnection()【返回任何一个可用Service连接】改为CPool.GetServiceConnection(longid)【返回id取模相关联的Service连接】这样的话,就能够保证同一个数据例如uid的请求落到同一个服务Service上
2)修改数据库DB连接池,id取模选取DB连接,能够保证同一个数据的读写在数据库层面是串行的
“让同一数据请求落到同一个数据库链接中“让同一个数据的访问能串行化”
“让同一个数据的访问通过同一条DB连接执行”
“在DB连接池层面稍微修改,按数据取连接即可”
获取DB连接的CPool.GetDBConnection()【返回任何一个可用DB连接】改为CPool.GetDBConnection(longid)【返回id取模相关联的DB连接】
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
redis系列之数据库与缓存数据一致性解决方案
数据库与缓存读写模式策略
写完数据库后是否需要马上更新缓存还是直接删除缓存?
(1)、如果写数据库的值与更新到缓存值是一样的,不需要经过任何的计算,可以马上更新缓存,但是如果对于那种写数据频繁而读数据少的场景并不合适这种解决方案,因为也许还没有查询就被删除或修改了,这样会浪费时间和资源
(2)、如果写数据库的值与更新缓存的值不一致,写入缓存中的数据需要经过几个表的关联计算后得到的结果插入缓存中,那就没有必要马上更新缓存,只有删除缓存即可,等到查询的时候在去把计算后得到的结果插入到缓存中即可。
数据库与缓存双写情况下导致数据不一致问题
场景一
当更新数据时,如更新某商品的库存,当前商品的库存是100,现在要更新为99,先更新数据库更改成99,然后删除缓存,发现删除缓存失败了,这意味着数据库存的是99,而缓存是100,这导致数据库和缓存不一致。
场景一解决方案
场景二
在高并发的情况下,如果当删除完缓存的时候,这时去更新数据库,但还没有更新完,另外一个请求来查询数据,发现缓存里没有,就去数据库里查,还是以上面商品库存为例,如果数据库中产品的库存是100,那么查询到的库存是100,然后插入缓存,插入完缓存后,原来那个更新数据库的线程把数据库更新为了99,导致数据库与缓存不一致的情况
场景二解决方案
遇到这种情况,可以用队列的去解决这个问,创建几个队列,如20个,根据商品的ID去做hash值,然后对队列个数取摸,当有数据更新请求时,先把它丢到队列里去,当更新完后在从队列里去除,如果在更新的过程中,遇到以上场景,先去缓存里看下有没有数据,如果没有,可以先去队列里看是否有相同商品ID在做更新,如果有也把查询的请求发送到队列里去,然后同步等待缓存更新完成。
这里有一个优化点,如果发现队列里有一个查询请求了,那么就不要放新的查询操作进去了,用一个while(true)循环去查询缓存,循环个200MS左右,如果缓存里还没有则直接取数据库的旧数据,一般情况下是可以取到的。
这里有一个优化点,如果发现队列里有一个查询请求了,那么就不要放新的查询操作进去了,用一个while(true)循环去查询缓存,循环个200MS左右,如果缓存里还没有则直接取数据库的旧数据,一般情况下是可以取到的。
在高并发下解决场景二要注意的问题
(1)读请求时长阻塞
由于读请求进行了非常轻度的异步化,所以一定要注意读超时的问题,每个读请求必须在超时间内返回,该解决方案最大的风险在于可能数据更新很频繁,导致队列中挤压了大量的更新操作在里面,然后读请求会发生大量的超时,最后导致大量的请求直接走数据库,像遇到这种情况,一般要做好足够的压力测试,如果压力过大,需要根据实际情况添加机器。
(2)请求并发量过高
这里还是要做好压力测试,多模拟真实场景,并发量在最高的时候QPS多少,扛不住就要多加机器,还有就是做好读写比例是多少
(3)多服务实例部署的请求路由
可能这个服务部署了多个实例,那么必须保证说,执行数据更新操作,以及执行缓存更新操作的请求,都通过nginx服务器路由到相同的服务实例上
(4)热点商品的路由问题,导致请求的倾斜
某些商品的读请求特别高,全部打到了相同的机器的相同丢列里了,可能造成某台服务器压力过大,因为只有在商品数据更新的时候才会清空缓存,然后才会导致读写并发,所以更新频率不是太高的话,这个问题的影响并不是很大,但是确实有可能某些服务器的负载会高一些。
(1)读请求时长阻塞
由于读请求进行了非常轻度的异步化,所以一定要注意读超时的问题,每个读请求必须在超时间内返回,该解决方案最大的风险在于可能数据更新很频繁,导致队列中挤压了大量的更新操作在里面,然后读请求会发生大量的超时,最后导致大量的请求直接走数据库,像遇到这种情况,一般要做好足够的压力测试,如果压力过大,需要根据实际情况添加机器。
(2)请求并发量过高
这里还是要做好压力测试,多模拟真实场景,并发量在最高的时候QPS多少,扛不住就要多加机器,还有就是做好读写比例是多少
(3)多服务实例部署的请求路由
可能这个服务部署了多个实例,那么必须保证说,执行数据更新操作,以及执行缓存更新操作的请求,都通过nginx服务器路由到相同的服务实例上
(4)热点商品的路由问题,导致请求的倾斜
某些商品的读请求特别高,全部打到了相同的机器的相同丢列里了,可能造成某台服务器压力过大,因为只有在商品数据更新的时候才会清空缓存,然后才会导致读写并发,所以更新频率不是太高的话,这个问题的影响并不是很大,但是确实有可能某些服务器的负载会高一些。
数据库与缓存数据一致性解决方案流程图
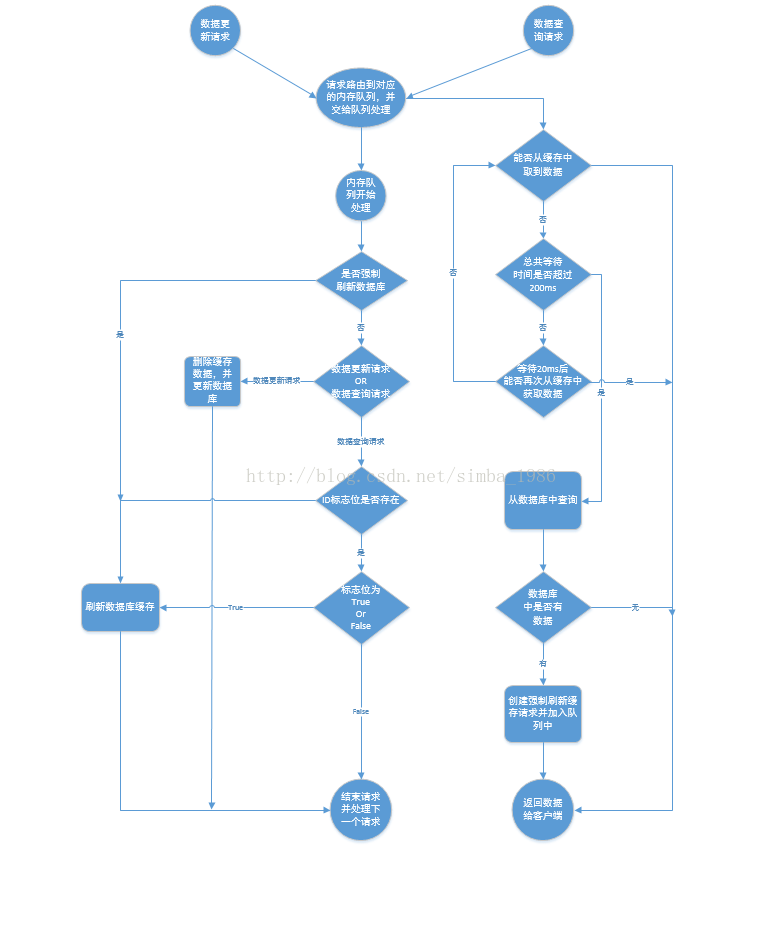
数据库与缓存数据一致性解决方案对应代码
商品库存实体
package com.shux.inventory.entity; public class InventoryProduct { private Integer productId; private Long InventoryCnt; public Integer getProductId() { return productId; } public void setProductId(Integer productId) { this.productId = productId; } public Long getInventoryCnt() { return InventoryCnt; } public void setInventoryCnt(Long inventoryCnt) { InventoryCnt = inventoryCnt; } }
请求接口
public interface Request { public void process(); public Integer getProductId(); public boolean isForceFefresh(); }
数据更新请求
package com.shux.inventory.request; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import com.shux.inventory.biz.InventoryProductBiz; import com.shux.inventory.entity.InventoryProduct; /** ********************************************** * 描述:更新库存信息 * 1、先删除缓存中的数据 * 2、更新数据库中的数据 ********************************************** **/ public class InventoryUpdateDBRequest implements Request{ private InventoryProductBiz inventoryProductBiz; private InventoryProduct inventoryProduct; public InventoryUpdateDBRequest(InventoryProduct inventoryProduct,InventoryProductBiz inventoryProductBiz){ this.inventoryProduct = inventoryProduct; this.inventoryProductBiz = inventoryProductBiz; } @Override @Transactional public void process() { inventoryProductBiz.removeInventoryProductCache(inventoryProduct.getProductId()); inventoryProductBiz.updateInventoryProduct(inventoryProduct); } @Override public Integer getProductId() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return inventoryProduct.getProductId(); } @Override public boolean isForceFefresh() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return false; } }
查询请求
package com.shux.inventory.request; import com.shux.inventory.biz.InventoryProductBiz; import com.shux.inventory.entity.InventoryProduct; /** ********************************************** * 描述:查询缓存数据 * 1、从数据库中查询 * 2、从数据库中查询后插入到缓存中 ********************************************** **/ public class InventoryQueryCacheRequest implements Request { private InventoryProductBiz inventoryProductBiz; private Integer productId; private boolean isForceFefresh; public InventoryQueryCacheRequest(Integer productId,InventoryProductBiz inventoryProductBiz,boolean isForceFefresh) { this.productId = productId; this.inventoryProductBiz = inventoryProductBiz; this.isForceFefresh = isForceFefresh; } @Override public void process() { InventoryProduct inventoryProduct = inventoryProductBiz.loadInventoryProductByProductId(productId); inventoryProductBiz.setInventoryProductCache(inventoryProduct); } @Override public Integer getProductId() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return productId; } public boolean isForceFefresh() { return isForceFefresh; } public void setForceFefresh(boolean isForceFefresh) { this.isForceFefresh = isForceFefresh; } }
spring启动时初始化队列线程池
package com.shux.inventory.thread; import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import com.shux.inventory.request.Request; import com.shux.inventory.request.RequestQueue; import com.shux.utils.other.SysConfigUtil; /** ********************************************** * 描述:请求处理线程池,初始化队列数及每个队列最多能处理的数量 ********************************************** **/ public class RequestProcessorThreadPool { private static final int blockingQueueNum = SysConfigUtil.get("request.blockingqueue.number")==null?10:Integer.valueOf(SysConfigUtil.get("request.blockingqueue.number").toString()); private static final int queueDataNum = SysConfigUtil.get("request.everyqueue.data.length")==null?100:Integer.valueOf(SysConfigUtil.get("request.everyqueue.data.length").toString()); private ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(blockingQueueNum); private RequestProcessorThreadPool(){ for(int i=0;i<blockingQueueNum;i++){//初始化队列 ArrayBlockingQueue<Request> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Request>(queueDataNum);//每个队列中放100条数据 RequestQueue.getInstance().addQueue(queue); threadPool.submit(new RequestProcessorThread(queue));//把每个queue交个线程去处理,线程会处理每个queue中的数据 } } public static class Singleton{ private static RequestProcessorThreadPool instance; static{ instance = new RequestProcessorThreadPool(); } public static RequestProcessorThreadPool getInstance(){ return instance; } } public static RequestProcessorThreadPool getInstance(){ return Singleton.getInstance(); } /** * 初始化线程池 */ public static void init(){ getInstance(); } }
请求处理线程
package com.shux.inventory.thread; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import com.shux.inventory.request.InventoryUpdateDBRequest; import com.shux.inventory.request.Request; import com.shux.inventory.request.RequestQueue; /** ********************************************** * 描述:请求处理线程 ********************************************** **/ public class RequestProcessorThread implements Callable<Boolean>{ private ArrayBlockingQueue<Request> queue; public RequestProcessorThread(ArrayBlockingQueue<Request> queue){ this.queue = queue; } @Override public Boolean call() throws Exception { Request request = queue.take(); Map<Integer,Boolean> flagMap = RequestQueue.getInstance().getFlagMap(); //不需要强制刷新的时候,查询请求去重处理 if (!request.isForceFefresh()){ if (request instanceof InventoryUpdateDBRequest) {//如果是更新请求,那就置为false flagMap.put(request.getProductId(), true); } else { Boolean flag = flagMap.get(request.getProductId()); /** * 标志位为空,有三种情况 * 1、没有过更新请求 * 2、没有查询请求 * 3、数据库中根本没有数据 * 在最初情况,一旦库存了插入了数据,那就好会在缓存中也会放一份数据, * 但这种情况下有可能由于redis中内存满了,redis通过LRU算法把这个商品给清除了,导致缓存中没有数据 * 所以当标志位为空的时候,需要从数据库重查询一次,并且把标志位置为false,以便后面的请求能够从缓存中取 */ if ( flag == null) { flagMap.put(request.getProductId(), false); } /** * 如果不为空,并且flag为true,说明之前有一次更新请求,说明缓存中没有数据了(更新缓存会先删除缓存), * 这个时候就要去刷新缓存,即从数据库中查询一次,并把标志位设置为false */ if ( flag != null && flag) { flagMap.put(request.getProductId(), false); } /** * 这种情况说明之前有一个查询请求,并且把数据刷新到了缓存中,所以这时候就不用去刷新缓存了,直接返回就可以了 */ if (flag != null && !flag) { flagMap.put(request.getProductId(), false); return true; } } } request.process(); return true; } }
请求队列
package com.shux.inventory.request; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; /** ********************************************** * 描述:请求队列 ********************************************** **/ public class RequestQueue { private List<ArrayBlockingQueue<Request>> queues = new ArrayList<>(); private Map<Integer,Boolean> flagMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); private RequestQueue(){ } private static class Singleton{ private static RequestQueue queue; static{ queue = new RequestQueue(); } public static RequestQueue getInstance() { return queue; } } public static RequestQueue getInstance(){ return Singleton.getInstance(); } public void addQueue(ArrayBlockingQueue<Request> queue) { queues.add(queue); } public int getQueueSize(){ return queues.size(); } public ArrayBlockingQueue<Request> getQueueByIndex(int index) { return queues.get(index); } public Map<Integer,Boolean> getFlagMap() { return this.flagMap; } }
spring 启动初始化线程池类
package com.shux.inventory.listener; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; import org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent; import com.shux.inventory.thread.RequestProcessorThreadPool; /** ********************************************** * 描述:spring 启动初始化线程池类 ********************************************** **/ public class InitListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent>{ @Override public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(event.getApplicationContext().getParent() != null){ return; } RequestProcessorThreadPool.init(); } }
异步处理请求接口
package com.shux.inventory.biz; import com.shux.inventory.request.Request; /** ********************************************** * 描述:请求异步处理接口,用于路由队列并把请求加入到队列中 ********************************************** **/ public interface IRequestAsyncProcessBiz { void process(Request request); }
异步处理请求接口实现
package com.shux.inventory.biz.impl; import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import com.shux.inventory.biz.IRequestAsyncProcessBiz; import com.shux.inventory.request.Request; import com.shux.inventory.request.RequestQueue; /** ********************************************** * 描述:异步处理请求,用于路由队列并把请求加入到队列中 ********************************************** **/ @Service("requestAsyncProcessService") public class RequestAsyncProcessBizImpl implements IRequestAsyncProcessBiz { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass()); @Override public void process(Request request) { // 做请求的路由,根据productId路由到对应的队列 ArrayBlockingQueue<Request> queue = getQueueByProductId(request.getProductId()); try { queue.put(request); } catch (InterruptedException e) { logger.error("产品ID{}加入队列失败",request.getProductId(),e); } } private ArrayBlockingQueue<Request> getQueueByProductId(Integer productId) { RequestQueue requestQueue = RequestQueue.getInstance(); String key = String.valueOf(productId); int hashcode; int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : (hashcode = key.hashCode())^(hashcode >>> 16); //对hashcode取摸 int index = (requestQueue.getQueueSize()-1) & hash; return requestQueue.getQueueByIndex(index); } }
数据更新请求controller
package com.shux.inventory.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import com.shux.inventory.biz.IRequestAsyncProcessBiz; import com.shux.inventory.biz.InventoryProductBiz; import com.shux.inventory.entity.InventoryProduct; import com.shux.inventory.request.InventoryUpdateDBRequest; import com.shux.inventory.request.Request; import com.shux.utils.other.Response; /** ********************************************** * 描述:提交更新请求 ********************************************** **/ @Controller("/inventory") public class InventoryUpdateDBController { private @Autowired InventoryProductBiz inventoryProductBiz; private @Autowired IRequestAsyncProcessBiz requestAsyncProcessBiz; @RequestMapping("/updateDBInventoryProduct") @ResponseBody public Response updateDBInventoryProduct(InventoryProduct inventoryProduct){ Request request = new InventoryUpdateDBRequest(inventoryProduct,inventoryProductBiz); requestAsyncProcessBiz.process(request); return new Response(Response.SUCCESS,"更新成功"); } }
数据查询请求controller
package com.shux.inventory.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import com.shux.inventory.biz.IRequestAsyncProcessBiz; import com.shux.inventory.biz.InventoryProductBiz; import com.shux.inventory.entity.InventoryProduct; import com.shux.inventory.request.InventoryQueryCacheRequest; import com.shux.inventory.request.Request; /** ********************************************** * 描述:提交查询请求 * 1、先从缓存中取数据 * 2、如果能从缓存中取到数据,则返回 * 3、如果不能从缓存取到数据,则等待20毫秒,然后再次去数据,直到200毫秒,如果超过200毫秒还不能取到数据,则从数据库中取,并强制刷新缓存数据 ********************************************** **/ @Controller("/inventory") public class InventoryQueryCacheController { private @Autowired InventoryProductBiz inventoryProductBiz; private @Autowired IRequestAsyncProcessBiz requestAsyncProcessBiz; @RequestMapping("/queryInventoryProduct") public InventoryProduct queryInventoryProduct(Integer productId) { Request request = new InventoryQueryCacheRequest(productId,inventoryProductBiz,false); requestAsyncProcessBiz.process(request);//加入到队列中 long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); long allTime = 0L; long endTime = 0L; InventoryProduct inventoryProduct = null; while (true) { if (allTime > 200){//如果超过了200ms,那就直接退出,然后从数据库中查询 break; } try { inventoryProduct = inventoryProductBiz.loadInventoryProductCache(productId); if (inventoryProduct != null) { return inventoryProduct; } else { Thread.sleep(20);//如果查询不到就等20毫秒 } endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); allTime = endTime - startTime; } catch (Exception e) { } } /** * 代码执行到这来,只有以下三种情况 * 1、缓存中本来有数据,由于redis内存满了,redis通过LRU算法清除了缓存,导致数据没有了 * 2、由于之前数据库查询比较慢或者内存太小处理不过来队列中的数据,导致队列里挤压了很多的数据,所以一直没有从数据库中获取数据然后插入到缓存中 * 3、数据库中根本没有这样的数据,这种情况叫数据穿透,一旦别人知道这个商品没有,如果一直执行查询,就会一直查询数据库,如果过多,那么有可能会导致数据库瘫痪 */ inventoryProduct = inventoryProductBiz.loadInventoryProductByProductId(productId); if (inventoryProduct != null) { Request forcRrequest = new InventoryQueryCacheRequest(productId,inventoryProductBiz,true); requestAsyncProcessBiz.process(forcRrequest);//这个时候需要强制刷新数据库,使缓存中有数据 return inventoryProduct; } return null; } }