Uncle Tom's Inherited Land*
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3339 Accepted Submission(s): 1394
Special Judge
Problem Description
Your
old uncle Tom inherited a piece of land from his great-great-uncle.
Originally, the property had been in the shape of a rectangle. A long
time ago, however, his great-great-uncle decided to divide the land into
a grid of small squares. He turned some of the squares into ponds, for
he loved to hunt ducks and wanted to attract them to his property. (You
cannot be sure, for you have not been to the place, but he may have made
so many ponds that the land may now consist of several disconnected
islands.)
Your uncle Tom wants to sell the inherited land, but local rules now regulate property sales. Your uncle has been informed that, at his great-great-uncle's request, a law has been passed which establishes that property can only be sold in rectangular lots the size of two squares of your uncle's property. Furthermore, ponds are not salable property.
Your uncle asked your help to determine the largest number of properties he could sell (the remaining squares will become recreational parks).
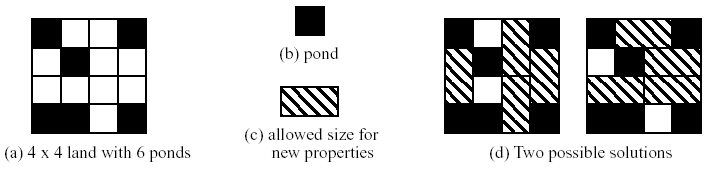
Your uncle Tom wants to sell the inherited land, but local rules now regulate property sales. Your uncle has been informed that, at his great-great-uncle's request, a law has been passed which establishes that property can only be sold in rectangular lots the size of two squares of your uncle's property. Furthermore, ponds are not salable property.
Your uncle asked your help to determine the largest number of properties he could sell (the remaining squares will become recreational parks).

Input
Input
will include several test cases. The first line of a test case contains
two integers N and M, representing, respectively, the number of rows
and columns of the land (1 <= N, M <= 100). The second line will
contain an integer K indicating the number of squares that have been
turned into ponds ( (N x M) - K <= 50). Each of the next K lines
contains two integers X and Y describing the position of a square which
was turned into a pond (1 <= X <= N and 1 <= Y <= M). The
end of input is indicated by N = M = 0.
Output
For
each test case in the input your program should first output one line,
containing an integer p representing the maximum number of properties
which can be sold. The next p lines specify each pair of squares which
can be sold simultaneity. If there are more than one solution, anyone is
acceptable. there is a blank line after each test case. See sample
below for clarification of the output format.
Sample Input
4 4
6
1 1
1 4
2 2
4 1
4 2
4 4
4 3
4
4 2
3 2
2 2
3 1
0 0
Sample Output
4
(1,2)--(1,3)
(2,1)--(3,1)
(2,3)--(3,3)
(2,4)--(3,4)
3
(1,1)--(2,1)
(1,2)--(1,3)
(2,3)--(3,3)
【分析】给出一个矩形图 将其中一些格子涂黑 问连续的两个白格子最多多少对。可以将每一个白色格子看成一 个点,然后分成两类 即每个点与他相邻的点分为两类,然后连边 二分图匹配
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <string> #include <map> #include <queue> #include <vector> #define inf 0x7fffffff #define met(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof a) typedef long long ll; using namespace std; const int N = 12005; const int M = 24005; int read() {int x=0,f=1;char c=getchar();while(c<'0'||c>'9') {if(c=='-')f=-1;c=getchar();}while(c>='0'&&c<='9') {x=x*10+c-'0';c=getchar();}return x*f;} int n,m,cnt; int dis[4][2]={{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}}; int tot,head[N]; int w[555][555],t[N],x[N],y[N]; struct man { int x,y,color,num; }; struct EDG { int to,next; }edg[M]; struct ANS { int x,y; }answ[N]; void add(int u,int v) { edg[cnt].to=v;edg[cnt].next=head[u];head[u]=cnt++; } void bfs(int u,int v) { queue<man>q; man s;s.color=0;s.num=++tot;s.x=u;s.y=v;q.push(s); w[u][v]=1;answ[tot].x=u;answ[tot].y=v; while(!q.empty()){ man t=q.front();q.pop(); for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int xx=t.x+dis[i][0];int yy=t.y+dis[i][1]; if(xx>=1&&xx<=n&&yy>=1&&yy<=m&&!w[xx][yy]){ man k;k.color=(t.color+1)%2;k.num=++tot;k.x=xx;k.y=yy; q.push(k);w[xx][yy]=1;answ[k.num].x=xx;answ[k.num].y=yy; if(!t.color)add(t.num,k.num); else add(k.num,t.num); } } } } bool dfs(int u) { for(int i=head[u];i!=-1;i=edg[i].next) { int v=edg[i].to; if(!t[v]) { t[v]=1; if(!y[v]||dfs(y[v])) { x[u]=v; y[v]=u; return true; } } } return false; } void MaxMatch() { int ans=0; for(int i=1; i<=tot; i++) { if(!x[i]) { met(t,0); if(dfs(i))ans++; } } printf("%d ",ans); for(int i=1;i<=tot;i++){ if(x[i]){ int v=x[i]; printf("(%d,%d)--(%d,%d) ",answ[i].x,answ[i].y,answ[v].x,answ[v].y); } } printf(" "); } int main() { while (~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)&&n&&m) { met(w,0);met(head,-1);met(x,0);met(y,0);met(edg,0);met(answ,0);cnt=0;tot=0; int k=read(); while(k--){ int x=read();int y=read(); w[x][y]=1; } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)if(!w[i][j])bfs(i,j); MaxMatch(); } return 0; }