SpringBoot是为了简化Spring应用的创建、运行、调试、部署等一系列问题而诞生的产物,自动装配的特性让我们可以更好的关注业务本身而不是外部的XML配置,我们只需遵循规范,引入相关的依赖就可以轻易的搭建出一个 WEB 工程未接触
SpringBoot之前,搭建一个普通的WEB工程往往需要花费30分钟左右,如果遇到点奇葩的问题耽搁的时间会更长一点,但自从用了SpringBoot后,真正体会到什么叫分分钟搭建一个WEB,让我拥有更多的时间跟我的小伙伴们唠嗑了。使用SpringBoot后发现一切是如此的简单(还记得读书那会被JAR包,xml支配的恐惧吗,如今都可以说 good bye)设计的目标
- 为所有使用
Spring的开发者提供一个更简单,快速的入门体验- 提供一些常见的功能、如监控、WEB容器,健康,安全等功能
- 干掉XML,遵循规范,开箱即用
前提
SpringBoot为我们提供了一系列的依赖包,所以需要构建工具的支持:Maven或Gradle。由于本人更习惯使用Maven所以后续案例都是基于Maven与IntelliJ IDEA,同时这里是基于最新的SpringBoot2编写的哦...创建项目
初次接触,我们先来看看如何创建一个
Spring Boot项目,这里以IntelliJ IDEA为例,其他的IDE工具小伙伴们自行搜索创建方式。创建完项目后,各位小伙伴请认真、细心的对比下与传统的WEB工程有何区别(如:目录结构)。点击
File -> Project如果用过
Eclipse/IDEA等工具的,对创建项目肯定不会陌生,但为了照顾第一次使用的我贴上了图文选择
Spring Initializr到这一步选择的时候,如图中选项的是
Spring Initializr(官方的构建插件,需要联网),第二个是自己选择Maven构建,为了更好的适合初学者,我们将在本章用插件构建填写项目基本信息
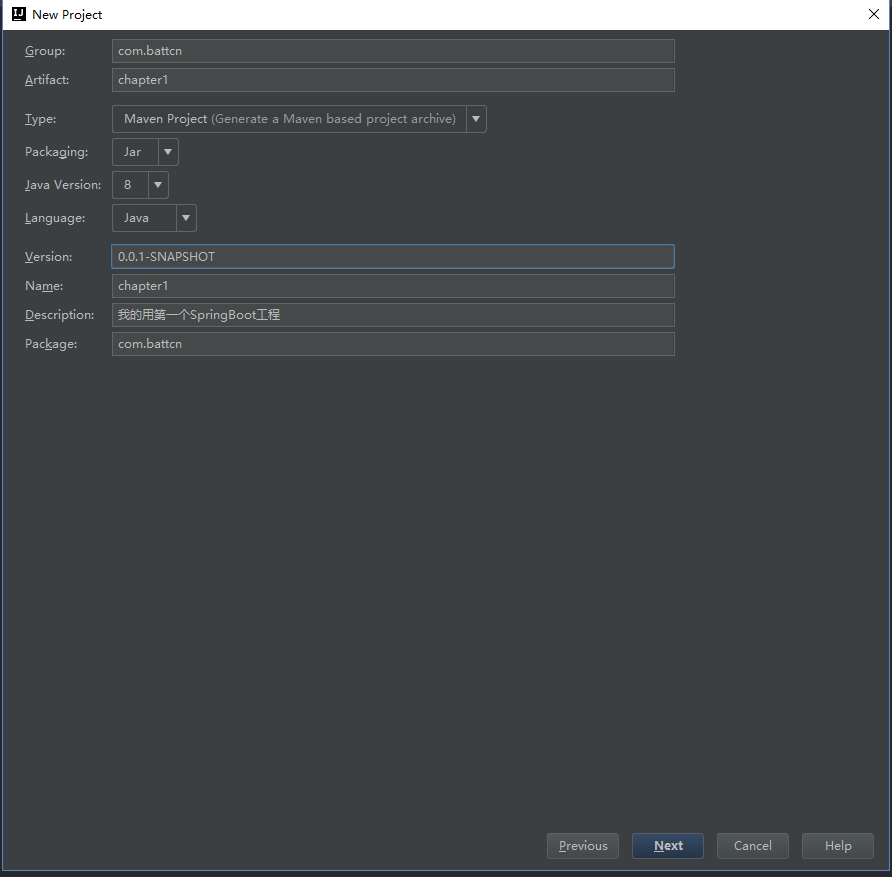
Group:组织ID,一般分为多个段,这里我只说两段,第一段为域,第二段为公司名称。域又分为org、com、cn等等,其中org为非营利组织,com为商业组织。如阿里、淘宝(com.alibaba/com.taobao)Artifact:唯一标识符,一般是项目名称选择包
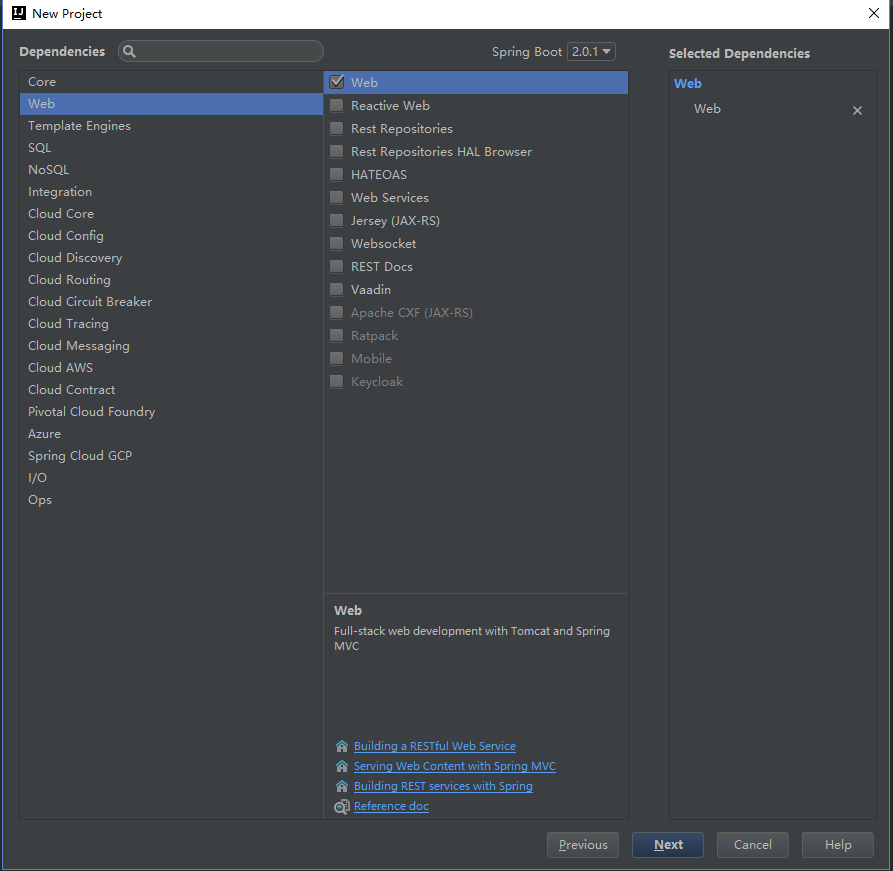
Spring Initializr为我们提供了很多的选项,不同的选项有不同的作用,在初期我们只需要依赖Web -> Web就可以了,选择好依赖包之后点击Next->Finish目录结果
目录结果 - src -main -java -package #主函数,启动类,运行它如果运行了 Tomcat、Jetty、Undertow 等容器 -SpringbootApplication -resouces #存放静态资源 js/css/images 等 - statics #存放 html 模板文件 - templates #主要的配置文件,SpringBoot启动时候会自动加载application.yml/application.properties - application.yml #测试文件存放目录 -test # pom.xml 文件是Maven构建的基础,里面包含了我们所依赖JAR和Plugin的信息 - pompom.xml 依赖
因为使用了
Spring Initializr插件,所以如下的配置都不需要我们自己去写啦,需要注意的是版本要选择RELEASE,稳定版本BUG少<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.battcn</groupId> <artifactId>chapter1</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>chapter1</name> <description>我的用第一个SpringBoot工程</description> <!--版本采用的是最新的 2.0.1.RELEASE TODO 开发中请记得版本一定要选择 RELEASE 哦 --> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <!-- 默认就内嵌了Tomcat 容器,如需要更换容器也极其简单--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- 测试包,当我们使用 mvn package 的时候该包并不会被打入,因为它的生命周期只在 test 之内--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <!-- 编译插件 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>其它的依赖可以参考:官方文档
主函数入口
注意事项: 一个项目中切记不要出现多个
main函数,否在在打包的时候spring-boot-maven-plugin将找不到主函数(主动指定打包主函数入口除外…)/** * 我的第一个SpringBoot程序 * 其中 @RestController 等同于 (@Controller 与 @ResponseBody) * * @author Levin */ @RestController @SpringBootApplication public class Chapter1Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Chapter1Application.class, args); } @GetMapping("/demo1") public String demo1() { return "Hello battcn"; } @Bean public CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner(ApplicationContext ctx) { // 目的是 return args -> { System.out.println("来看看 SpringBoot 默认为我们提供的 Bean:"); String[] beanNames = ctx.getBeanDefinitionNames(); Arrays.sort(beanNames); Arrays.stream(beanNames).forEach(System.out::println); }; } }初窥配置文件
从启动日志中可以发现,
SpringBoot默认的端口是 8080 ,那么如果端口被占用了怎么办呢?不要慌,问题不大,配置文件分分钟解决你的困扰…2018-04-20 16:14:46.725 INFO 11184 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path ''修改默认配置
# 默认的 8080 我们将它改成 9090 server.port=9090 # 未定义上下文路径之前 地址是 http://localhost:8080 定义了后 http://localhost:9090 你能在tomcat做的事情,配置文件都可以 server.servlet.context-path=/chapter1在启动一次看看日志
2018-04-20 16:47:05.716 INFO 12108 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 9090 (http) with context path '/chapter1'测试
本次测试采用
junit进行,当然也可以启动项目后直接访问http://localhost:9090/chapter/demo1进行测试import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.boot.test.web.client.TestRestTemplate; import org.springframework.boot.web.server.LocalServerPort; import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; import java.net.URL; import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals; @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT) public class Chapter1ApplicationTests { @LocalServerPort private int port; private URL base; @Autowired private TestRestTemplate template; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { // TODO 因为我们修改了 content-path 所以请求后面要带上 this.base = new URL("http://localhost:" + port + "/chapter1/demo1"); } @Test public void demo1() throws Exception { ResponseEntity<String> response = template.getForEntity(base.toString(), String.class); assertEquals(response.getBody(), "Hello battcn"); } }拓展知识
自定义Banner
SpringBoot启动的时候我们可以看到如下内容,这一块其实是可以自定义的哦,而且在 2.X 版本中,它支持的格式从文本扩展到banner.txt、banner.jpg、banner.gif、banner.jpeg等等,只需要在resouces目录下添加指定命名的文件即可. ____ _ __ _ _ /\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ ( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ / _` | \/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) ) ' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / / =========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/ :: Spring Boot :: (v2.0.1.RELEASE)总结
目前很多大佬都写过关于
SpringBoot的教程了,如有雷同,请多多包涵,本教程基于最新的spring-boot-starter-parent:2.0.1.RELEASE编写,包括新版本的特性都会一起介绍…