今日内容:
1.迭代器(****)
2.生成器(***)
3.生成器表达式(*****)
4.面向过程编程(*****)
5.包的使用(***)
6.常用模块
logging (*****)
re (*****)
一.迭代器
迭代器就是迭代取值的工具
迭代是一个重复的过程,但是每一次重复都是基于上一次的结果而进行的
2.为何要用迭代器
针对没有索引的数据类型,如:字典,集合,文件,要想迭代取出其中包含的一个个的值
python解释器必须提供一种能够不依赖于索引的迭代取值工具
3.如何用迭代器
x=1
y=1.3
#以下都是可迭代对象
str1='hello'
list1=['a','b','c']
t1=('a','b','c')
dic={'x':1,'y':2}
set1={'m','n'}
f=open('a.txt',mode='rt',encoding='utf-8')
#对于可迭代对象来说,调用可迭代对象.__iter__()方法,得到的就是其迭代器对象
1.内置有__iter__方法,调用迭代器对象__iter__方法得到的仍然是迭代器本身
ps:文件对象本身就是一个迭代器对象,即同时也内置有__next__方法
2.内置有__next__方法
迭代器优点:
1.提供一种能够不依赖索引的、通用的迭代取值方式
补充:for循环可以称之为迭代器循环
for item in list1:
print(item)
a.调用in后面那个对象的__iter__方法,拿到一个迭代器对象
b.调用迭代器对象的__next__方法,拿到一个返回值赋值给变量item
c.循环往复,直到抛出异常,for循环会自动捕捉异常结束循环
迭代器的缺点:
1.针对同一个迭代器对象只能取完一次,不如按照索引或key取值方式灵活
2.无法预测迭代器对象所包含值的个数
1 l=['alex','andy','lily'] 2 count=0 3 while count<len(l): 4 print(l[count]) 5 count+=1
输出:
alex
andy
lily
1 #对于可迭代对象来说,调用可迭代对象.__iter__()方法,得到的就是其迭代器对象 2 dic={'x':1,'y':2} 3 iter_dic=dic.__iter__() #iter_dic=iter(dic) 作用相同 4 print(iter_dic) 5 k1=iter_dic.__next__() #k1=next(iter_dic) 作用相同 6 print(k1,type(k1)) 7 k2=iter_dic.__next__() #k2=next(iter_dic) 作用相同 8 print(k2,type(k2)) 9 try: 10 next(iter_dic) 11 except StopIteration: 12 print('==========>')
输出:
<dict_keyiterator object at 0x0000021B9D9370E8>
x <class 'str'>
y <class 'str'>
==========>
1 dic={'x':1,'y':2} 2 iter_dic=iter(dic) 3 while True: 4 try: 5 k=next(iter_dic) 6 print(k) 7 except StopIteration: 8 break
输出:
x
y
1 list1=['a','b','c'] 2 iter_list=iter(list1) 3 while True: 4 try: 5 k=next(iter_list) 6 print(k) 7 except StopIteration: 8 break
输出:
a
b
c
二.生成器
1.什么是生成器在函数内但凡出现yield关键字,再调用函数就不会触发函数体代码的执行了
会得到一个返回值,该返回就是一个生成器对象
而生成器本身就是一个迭代器
2.为何要用生成器
生成器是自定义的迭代器
3.如何用生成器
1.提供一种自定义迭代器的方式
2.可以用于返回值
yield与return区别
相同点:都可以用于返回值,个数以及类型都没有限制
不同点:yield可以返回多次值,return只能返回一次值
3.函数暂停及继续执行的状态是由yield保存的
1 def foo(): 2 print ('first') 3 yield 1 4 print ('second') 5 yield 2 6 print ('third') 7 yield 3 8 print ('fourth') 9 g=foo() #g是生成器=》就是迭代器 10 print (g.__next__()) #会触发g对应函数的函数体代码执行,直到碰到一个yield就暂停住,就该yield后的值当作本地__next__()的返回值 11 print (g.__next__()) 12 print (g.__next__())
输出:
first
1
second
2
third
3
1 def my_range(start,stop,step=1): 2 while start < stop: 3 yield start 4 start+=step 5 for i in my_range(1,10,2): 6 print (i)
输出:
1
3
5
7
9
1 #yield关键字表达式形式的应用 2 #x=yield 3 def dog(name): 4 print('dog[%s]准备开吃' %name) 5 while True: 6 food=yield 7 print('dog[%s]吃了:%s' %(name,food)) 8 dg1=dog('haha') 9 #强调:针对表达式形式的yield,在使用生成器时必先send(None),相当于先完成一个初始化操作 10 next(dg1) 11 #send有两个功能 12 #1.为当前暂停位置的yield赋值 13 #2.与next的效果一样,不传值默认传None 14 res=dg1.send('骨头') 15 print(res)
输出:
dog[haha]准备开吃
dog[haha]吃了:骨头
None
1 def dog(name): 2 print('dog[%s]准备开吃' %name) 3 food_list=[] 4 while True: 5 food=yield food_list 6 food_list.append(food) 7 print('dog[%s]吃了:%s' %(name,food)) 8 dg1=dog('haha') 9 #强调:针对表达式形式的yield,在使用生成器时必先send(None),相当于先完成一个初始化操作 10 next(dg1) 11 #send有两个功能 12 #1.为当前暂停位置的yield赋值 13 #2.与next的效果一样,不传值默认传None 14 res=dg1.send('骨头') 15 print(res) 16 res=dg1.send('馒头') 17 print(res)
输出:
dog[haha]准备开吃
dog[haha]吃了:骨头
['骨头']
dog[haha]吃了:馒头
['骨头', '馒头']
查询/etc 下所有文中含‘python’的文件,迭代查询
grep -rl 'python' /etc
三.生成器表达式
1 #生成器表达式 2 l=[i**2 for i in range(1,11)] 3 print (l) 4 5 names=['alex','andy','tom'] 6 #l=[name.upper() for name in names if name != 'andy'] 7 l=(name.upper() for name in names if name != 'andy') 8 #print(l) 9 print(next(l))
输出:
[1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100]
ALEX
四.面向过程编程
1.核心是过程二字,过程指的是解决问题的步骤,即先干什么再干什么
基于该思想编程写程序就好比在设计一条流水线,是一种机械式的思维方式
优点:复杂的问题流程化,进而简单化
缺点:牵一发而动全身,扩展性差
1 def communicate(): 2 name=input('username>>').strip() 3 pwd=input('password>>').strip() 4 return (name,pwd) 5 def auth(name,pwd): 6 if name =='andy' and pwd =='123': 7 return True 8 else: 9 return False 10 def index(res): 11 if res: 12 print('welcome') 13 else: 14 print('login fail') 15 def main(): 16 user,pwd=communicate() 17 res=auth(user,pwd) 18 index(res)
五.包的使用
1.什么是包
包本质就是一个包含有__init__.py文件夹,文件夹是用来组织文件
强调,包以及包下所有的文件都是用来被导入使用的,没有一个文件时用来被直接运行
因为包其实时模块的一种形式而已
2.import p1
a.创建p1的名称空间
b.执行p1下的__init__.py文件的代码,将执行过程中产生的名字都丢到名称空间中
c.在当前执行文件中拿到一个名字p1, p1指向__init__.py的名称空间
3.包内模块的绝对导入与相对导入
绝对导入:每次导入都是以最顶级包为起始开始导入
相当导入:相对于当前所在的文件,.代表当前所在的文件,..代表上一级
强调:相对导入只能在被导入的模块中使用
在执行文件中不能用.或者..的导入方式
4.注意
但凡在点的左边必须时一个包
1 def f1(): 2 pass 3 def f2(): 4 pass 5 def f3(): 6 pass 7 def f4(): 8 pass 9 def f5(): 10 pass 11 def f6(): 12 pass
六.常用模块
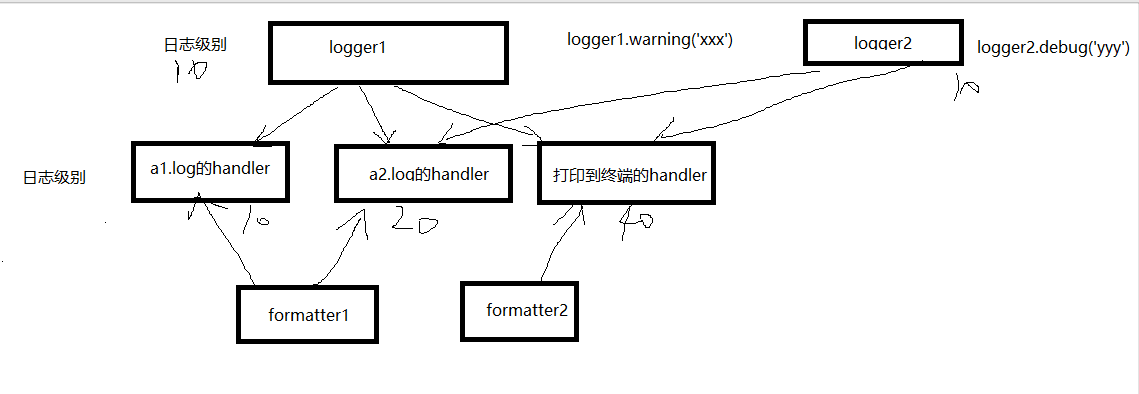
1.logging
logger1=logging.getLogger('交易日志')
2)filter过滤
3)handler对象需要与logger对绑定,用来接收logger对象传过来的日志,控制打印到不同的地方(不同的文件、终端)
fh1=logging.FileHandler(filename='a1.log',encoding='utf-8')
fh2=logging.FileHandler(filename='a2.log',encoding='utf-8')
sh=logging.StreamHandler()
4)formmter对象需要与handler对象绑定,用于控制handler对象的日志格式
formmater1=logging.Formatter(
fmt='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s -%(module)s: %(message)s',
datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %p'
)
formmater2=logging.Formatter(
fmt='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s : %(message)s',
datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %p'
)
# 设置日志级别:logger与handler两层关卡都放行,日志最终才放行
logger1.setLevel(10)
fh1.setLevel(10)
fh2.setLevel(40)
sh.setLevel(10)
# 建立logger对象与handler对象的绑定关系
logger1.addHandler(fh1)
logger1.addHandler(fh2)
logger1.addHandler(sh)
# 建立handler对象与formmater对象的绑定关系
fh1.setFormatter(formmater1)
fh2.setFormatter(formmater1)
sh.setFormatter(formmater2)
# 使用logger1对象产生日志,打印到不同的位置
# logger1.debug('alex给egon转账1亿')
logger1.warning('alex可能要赔一个亿')
1 import logging 2 3 logging.debug('调试debug') 4 logging.info('消息info') 5 logging.warning('警告warn') 6 logging.error('错误error') 7 logging.critical('严重critical') 8 9 ''' 10 WARNING:root:警告warn 11 ERROR:root:错误error 12 CRITICAL:root:严重critical 13 '''
输出:
WARNING:root:警告warn
ERROR:root:错误error
CRITICAL:root:严重critical
完整的日志内容:
1.时间
2.级别
3.类型
2.re模块
1 import re 2 3 print(re.findall('w','hello123 -_*()')) #匹配字母数字下划线 4 print(re.findall('W','hello123 -_*()')) #匹配非字母数字下划线 5 print(re.findall('andy','helloandy123 -_andy*()')) #匹配andy 6 print(re.findall('^andy','helloandy123 -_andy*()')) #匹配andy开头 7 print(re.findall('andy$','helloandy123 -_andy')) #匹配andy结尾 8 print(re.findall('s','h ell lo')) #匹配任意空字符 9 print(re.findall(' ','h ell lo')) #匹配制表符 10 print(re.findall(' ','h ell lo')) #匹配换行符 11 print(re.findall('S','h ell lo')) #匹配任意非空字符 12 print(re.findall('d','hello123 -_*()'))#匹配数字 13 #.代表匹配除了换行符意外的任意单个字符 14 print(re.findall('a.c','abc a*c a1c a c aaaaac a c hello123 -_*()'))#.匹配除了换行符以外的任意单个字符 15 print(re.findall('a.c','abc a*c a1c a c aaaaac a c hello123 -_*()',re.DOTALL))#.匹配任意单个字符 16 #[]代表匹配我们自定范围的任意一个字符,[]减号必须放在最后 17 print(re.findall('d[+*/-]d','1+3 a1!3sdf 2*3 1/4 2-3 a c aaaaac a c hello123 -_*()'))#.匹配除了换行符以外的任意单个字符 18 print(re.findall('a[0-9]c','a1c a2c a11c abc a*c a9c hello123 -_*()'))#.匹配除了换行符以外的任意单个字符 19 print(re.findall('a[A-Za-z]c','a1c a2c a11c abc a*c a9c hello123 -_*()'))#.匹配除了换行符以外的任意单个字符
输出:
['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', '1', '2', '3', '_']
[' ', '-', '*', '(', ')']
['andy', 'andy']
[]
['andy']
[' ', ' ', '
']
[' ']
['
']
['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'l', 'o']
['1', '2', '3']
['abc', 'a*c', 'a1c', 'aac', 'a c']
['abc', 'a*c', 'a1c', 'a
c', 'aac', 'a c']
['1+3', '2*3', '1/4', '2-3']
['a1c', 'a2c', 'a9c']
['abc']
1 #重复匹配 2 #? :代表左边那一个字符出现0次或1次 3 print(re.findall('ab?','b ab abb abbb bbbba')) 4 print(re.findall('ab{0,1}','b ab abb abbb bbbba')) 5 6 7 #* :代表左边那一个自处出现0次或无穷次,如果没有可以凑活,但如果>1个,有多少就必须拿多少 8 print(re.findall('ab*','b ab abb abbb bbbba')) 9 print(re.findall('ab{0,}','b ab abb abbb bbbba')) 10 11 12 #+ :代表左边那一个字符出现1次或无穷次,至少要有一个,但如果有>1个,有多少就必须拿多少 13 print(re.findall('ab+','b ab abb abbb bbbba')) 14 print(re.findall('ab{1,}','b ab abb abbb bbbba')) 15 16 17 #{n,m}:代表左边那一个字符出现n次到m次,至少要有n个,但如果有>n个,就拿<=m个 18 print(re.findall('ab{2,5}','b ab abbbbbbbbbbb abb abbbbb bbbbbba')) 19 20 #.* :匹配任意0个或无穷个任意字符,默认贪是婪匹配,找离a最远的c 21 print(re.findall('a.*c','hello a123124cqweqwec+')) 22 23 #.*? :匹配任意0个或无穷个任意字符,默认是非贪婪匹配,找离a最近的c 24 print(re.findall('a.*?c','hello a123124cqweqwec+aasdasdc')) 25 26 print(re.findall('href="(.*?)"','<div class="div1"><a href="https://www.baidu.com">"点我啊"</a></dic><div class="div1"><a href="https://www.baidu.com">"点我啊"</a></dic><div class="div1"><a href="https://www.python.com">"点我啊"</a></dic>')) 27 # ?: 28 print(re.findall('compan(ies|y)','Too many companies have gone bankrupt, and the nnext one is my company')) 29 print(re.findall('compan(?:ies|y)','Too many companies have gone bankrupt, and the nnext one is my company')) 30 31 #[]内^代表取反 32 print(re.findall('a[^0-9]c','hello a1c abc a123124cqweqwec+')) 33 34 print(re.findall('a\c','ac a1c abc aac')) 35 print(re.findall(r'a\c','ac a1c abc aac'))
输出:
['ab', 'ab', 'ab', 'a']
['ab', 'ab', 'ab', 'a']
['ab', 'abb', 'abbb', 'a']
['ab', 'abb', 'abbb', 'a']
['ab', 'abb', 'abbb']
['ab', 'abb', 'abbb']
['abbbbb', 'abb', 'abbbbb']
['a123124cqweqwec']
['a123124c', 'aasdasdc']
['https://www.baidu.com', 'https://www.baidu.com', 'https://www.python.com']
['ies', 'y']
['companies', 'company']
['abc']
['a\c']
['a\c']
1 print(re.findall(r'andy','ac andy a1c abc aac andy ')) 2 #re.search从左往右匹配,成功一个就结束,不成功最后返回None 3 print(re.search(r'andy','ac andy a1c abc aac andy ')) 4 print(re.search(r'andy','ac andy a1c abc aac andy ').group()) 5 obj=re.search('href="(.*?)"','<div class="div1"><a href="https://www.baidu.com">"点我啊"</a></dic><div class="div1"><a href="https://www.baidu.com">"点我啊"</a></dic><div class="div1"><a href="https://www.python.com">"点我啊"</a></dic>') 6 print(obj.group()) 7 #以下同等作用 8 print(re.search(r'^andy','ac andy a1c abc aac andy ')) 9 print(re.match(r'andy','ac andy a1c abc aac andy ')) 10 #切分 11 msg='root:x:0:0::/root:/bin/bash' 12 print(re.split('[:/]',msg)) 13 #替换 14 print(re.sub('andy','haha','andy hello andy')) 15 print(re.sub('^andy','haha','andy hello andy')) 16 print(re.sub('andy$','haha','andy hello andy'))
输出:
['andy', 'andy']
<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(4, 8), match='andy'>
andy
href="https://www.baidu.com"
None
None
['root', 'x', '0', '0', '', '', 'root', '', 'bin', 'bash']
haha hello haha
haha hello andy
andy hello haha
1 obj=re.compile('href="(.*?)"') 2 3 msg1='<div class="div1"><a href="https://www.baidu.com">点我啊</a></div><div class="div1"><a href="https://www.python.org">点我啊</a></div>' 4 # print(re.findall('href="(.*?)"',msg1)) 5 print(obj.findall(msg1)) 6 7 msg2='<div class="div1"><a href="https://www.sina.com.cn">点我啊</a></div><div class="div1"><a href="https://www.tmall.com">点我啊</a></div>' 8 # print(re.search('href="(.*?)"',msg2).group(1)) 9 print(obj.search(msg2).group(1))
输出:
['https://www.baidu.com', 'https://www.python.org']
https://www.sina.com.cn