ECharts 基本概念
ECharts 基本概念: 系列
系列(series)是指:一组数值映射成对应的图 【一个系列对应一张图,series中的一个子项对应一张图。】

案例:多系列混合
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/echarts@4.7.0/dist/echarts.min.js"></script>
<style>
#chart {
800px;
height: 400px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="chart"></div>
<script>
const chartDom = document.getElementById('chart')
const chart = echarts.init(chartDom)
const option = {
xAxis: {
data: ['一季度', '二季度', '三季度', '四季度']
},
yAxis: {},
// 【一个系列对应一张图,series中的一个子项对应一张图。】
series: [{
type: 'pie',
// 第一个参数是字符串,不是数字
center: ['65%', 60],
radius: 35,
data: [{
// value:表示占比
name: '分类1', value: 50
}, {
name: '分类2', value: 60
}, {
name: '分类3', value: 55
}, {
name: '分类4', value: 70
}]
}, {
type: 'line',
// 每个数字对应xAxis.data中的每个柱状位置
// 【纵坐标的数字会以series中所有子项的data的最大值的这项为准,并成等差队列。】
data: [100, 112, 96, 123]
}, {
type: 'bar',
data: [79, 81, 88, 72]
}]
}
chart.setOption(option)
</script>
</body>
</html>
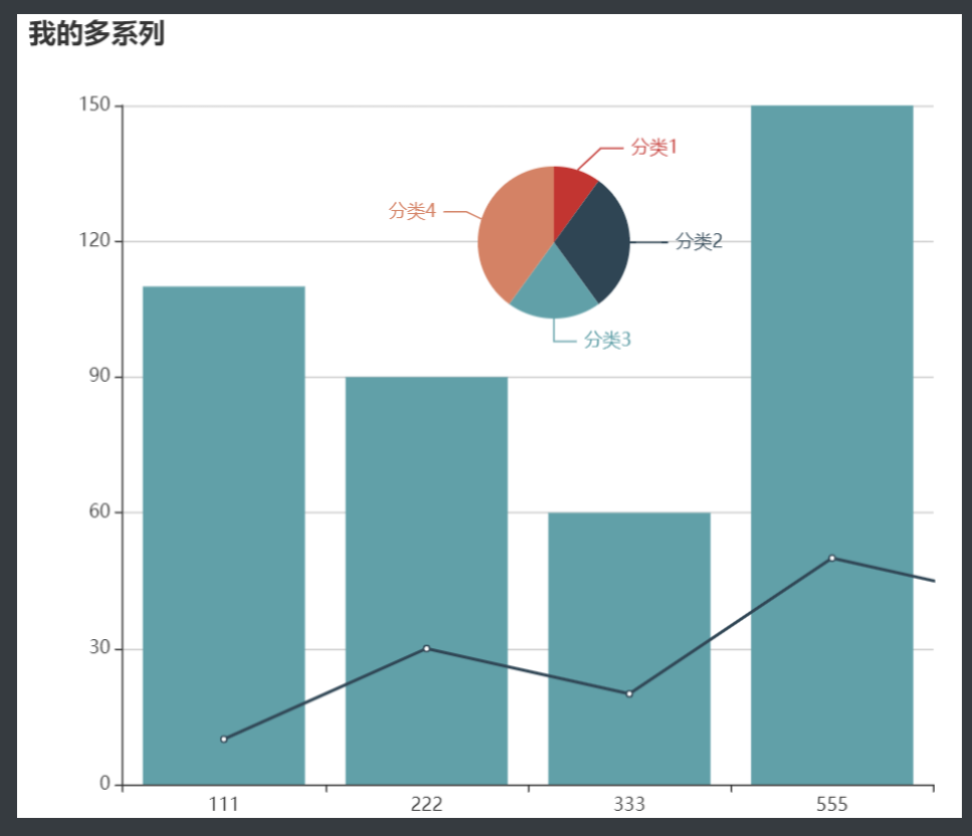
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/echarts@4.7.0/dist/echarts.js"></script>
<style>
#chart {
666px;
height: 566px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="chart"></div>
<script>
const chartDom = document.querySelector('#chart')
const chart = echarts.init(chartDom)
chart.setOption({
title: {
text: '我的多系列'
},
xAxis: {
data: [111, 222, 333, 555]
},
yAxis: {
},
series: [
{
name: '饼图',
type: 'pie',
center: [350, 150],
radius: 50,
data: [{
name: '分类1', value: 10
}, {
name: '分类2', value: 30
}, {
name: '分类3', value: 20
}, {
name: '分类4', value: 40
}]
},
{
name: '折线图',
type: 'line',
data: [10, 30, 20, 50, 40, 60, 80, 70]
},
{
name: '柱状图',
type: 'bar',
data: [110, 90, 60, 150, 66]
}
]
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
~
~
test-echarts.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/echarts@4.7.0/dist/echarts.js"></script>
<style>
#chart {
800px;
height: 400px;
}
</style>
<script>
// 路径:文档 --> 教程 --> ECharts 中的样式简介 --> 颜色主题(Theme --> 选择方案 --> 点击基本配置,修改配置 --> 下载主题 --> 点击复制,把js代码复制到<script><script>中 --> 在echarts.init添加第二个参数为刚刚生成的主题色 -->
(function (root, factory) {
if (typeof define === 'function' && define.amd) {
// AMD. Register as an anonymous module.
define(['exports', 'echarts'], factory);
} else if (typeof exports === 'object' && typeof exports.nodeName !== 'string') {
// CommonJS
factory(exports, require('echarts'));
} else {
// Browser globals
factory({}, root.echarts);
}
}(this, function (exports, echarts) {
var log = function (msg) {
if (typeof console !== 'undefined') {
console && console.error && console.error(msg);
}
};
if (!echarts) {
log('ECharts is not Loaded');
return;
}
echarts.registerTheme('westeros', {
"color": [
"#516b91",
"#59c4e6",
"#edafda",
"#93b7e3",
"#a5e7f0",
"#cbb0e3"
],
"backgroundColor": "rgba(0,0,0,0)",
"textStyle": {},
"title": {
"textStyle": {
"color": "#516b91"
},
"subtextStyle": {
"color": "#93b7e3"
}
},
"line": {
"itemStyle": {
"normal": {
"borderWidth": "2"
}
},
"lineStyle": {
"normal": {
"width": "2"
}
},
"symbolSize": "6",
"symbol": "emptyCircle",
"smooth": true
},
"radar": {
"itemStyle": {
"normal": {
"borderWidth": "2"
}
},
"lineStyle": {
"normal": {
"width": "2"
}
},
"symbolSize": "6",
"symbol": "emptyCircle",
"smooth": true
},
"bar": {
"itemStyle": {
"normal": {
"barBorderWidth": 0,
"barBorderColor": "#ccc"
},
"emphasis": {
"barBorderWidth": 0,
"barBorderColor": "#ccc"
}
}
},
"pie": {
"itemStyle": {
"normal": {
"borderWidth": 0,
"borderColor": "#ccc"
},
"emphasis": {
"borderWidth": 0,
"borderColor": "#ccc"
}
}
},
"scatter": {
"itemStyle": {
"normal": {
"borderWidth": 0,
"borderColor": "#ccc"
},
"emphasis": {
"borderWidth": 0,
"borderColor": "#ccc"
}
}
},
"boxplot": {
"itemStyle": {
"normal": {
"borderWidth": 0,
"borderColor": "#ccc"
},
"emphasis": {
"borderWidth": 0,
"borderColor": "#ccc"
}
}
},
"parallel": {
"itemStyle": {
"normal": {
"borderWidth": 0,
"borderColor": "#ccc"
},
"emphasis": {
"borderWidth": 0,
"borderColor": "#ccc"
}
}
},
"sankey": {
"itemStyle": {
"normal": {
"borderWidth": 0,
"borderColor": "#ccc"
},
"emphasis": {
"borderWidth": 0,
"borderColor": "#ccc"
}
}
},
"funnel": {
"itemStyle": {
"normal": {
"borderWidth": 0,
"borderColor": "#ccc"
},
"emphasis": {
"borderWidth": 0,
"borderColor": "#ccc"
}
}
},
"gauge": {
"itemStyle": {
"normal": {
"borderWidth": 0,
"borderColor": "#ccc"
},
"emphasis": {
"borderWidth": 0,
"borderColor": "#ccc"
}
}
},
"candlestick": {
"itemStyle": {
"normal": {
"color": "#edafda",
"color0": "transparent",
"borderColor": "#d680bc",
"borderColor0": "#8fd3e8",
"borderWidth": "2"
}
}
},
"graph": {
"itemStyle": {
"normal": {
"borderWidth": 0,
"borderColor": "#ccc"
}
},
"lineStyle": {
"normal": {
"width": 1,
"color": "#aaaaaa"
}
},
"symbolSize": "6",
"symbol": "emptyCircle",
"smooth": true,
"color": [
"#516b91",
"#59c4e6",
"#edafda",
"#93b7e3",
"#a5e7f0",
"#cbb0e3"
],
"label": {
"normal": {
"textStyle": {
"color": "#eeeeee"
}
}
}
},
"map": {
"itemStyle": {
"normal": {
"areaColor": "#f3f3f3",
"borderColor": "#516b91",
"borderWidth": 0.5
},
"emphasis": {
"areaColor": "#a5e7f0",
"borderColor": "#516b91",
"borderWidth": 1
}
},
"label": {
"normal": {
"textStyle": {
"color": "#000"
}
},
"emphasis": {
"textStyle": {
"color": "#516b91"
}
}
}
},
"geo": {
"itemStyle": {
"normal": {
"areaColor": "#f3f3f3",
"borderColor": "#516b91",
"borderWidth": 0.5
},
"emphasis": {
"areaColor": "#a5e7f0",
"borderColor": "#516b91",
"borderWidth": 1
}
},
"label": {
"normal": {
"textStyle": {
"color": "#000"
}
},
"emphasis": {
"textStyle": {
"color": "#516b91"
}
}
}
},
"categoryAxis": {
"axisLine": {
"show": true,
"lineStyle": {
"color": "#cccccc"
}
},
"axisTick": {
"show": false,
"lineStyle": {
"color": "#333"
}
},
"axisLabel": {
"show": true,
"textStyle": {
"color": "#999999"
}
},
"splitLine": {
"show": true,
"lineStyle": {
"color": [
"#eeeeee"
]
}
},
"splitArea": {
"show": false,
"areaStyle": {
"color": [
"rgba(250,250,250,0.05)",
"rgba(200,200,200,0.02)"
]
}
}
},
"valueAxis": {
"axisLine": {
"show": true,
"lineStyle": {
"color": "#cccccc"
}
},
"axisTick": {
"show": false,
"lineStyle": {
"color": "#333"
}
},
"axisLabel": {
"show": true,
"textStyle": {
"color": "#999999"
}
},
"splitLine": {
"show": true,
"lineStyle": {
"color": [
"#eeeeee"
]
}
},
"splitArea": {
"show": false,
"areaStyle": {
"color": [
"rgba(250,250,250,0.05)",
"rgba(200,200,200,0.02)"
]
}
}
},
"logAxis": {
"axisLine": {
"show": true,
"lineStyle": {
"color": "#cccccc"
}
},
"axisTick": {
"show": false,
"lineStyle": {
"color": "#333"
}
},
"axisLabel": {
"show": true,
"textStyle": {
"color": "#999999"
}
},
"splitLine": {
"show": true,
"lineStyle": {
"color": [
"#eeeeee"
]
}
},
"splitArea": {
"show": false,
"areaStyle": {
"color": [
"rgba(250,250,250,0.05)",
"rgba(200,200,200,0.02)"
]
}
}
},
"timeAxis": {
"axisLine": {
"show": true,
"lineStyle": {
"color": "#cccccc"
}
},
"axisTick": {
"show": false,
"lineStyle": {
"color": "#333"
}
},
"axisLabel": {
"show": true,
"textStyle": {
"color": "#999999"
}
},
"splitLine": {
"show": true,
"lineStyle": {
"color": [
"#eeeeee"
]
}
},
"splitArea": {
"show": false,
"areaStyle": {
"color": [
"rgba(250,250,250,0.05)",
"rgba(200,200,200,0.02)"
]
}
}
},
"toolbox": {
"iconStyle": {
"normal": {
"borderColor": "#999999"
},
"emphasis": {
"borderColor": "#666666"
}
}
},
"legend": {
"textStyle": {
"color": "#999999"
}
},
"tooltip": {
"axisPointer": {
"lineStyle": {
"color": "#cccccc",
"width": 1
},
"crossStyle": {
"color": "#cccccc",
"width": 1
}
}
},
"timeline": {
"lineStyle": {
"color": "#8fd3e8",
"width": 1
},
"itemStyle": {
"normal": {
"color": "#8fd3e8",
"borderWidth": 1
},
"emphasis": {
"color": "#8fd3e8"
}
},
"controlStyle": {
"normal": {
"color": "#8fd3e8",
"borderColor": "#8fd3e8",
"borderWidth": 0.5
},
"emphasis": {
"color": "#8fd3e8",
"borderColor": "#8fd3e8",
"borderWidth": 0.5
}
},
"checkpointStyle": {
"color": "#8fd3e8",
"borderColor": "rgba(138,124,168,0.37)"
},
"label": {
"normal": {
"textStyle": {
"color": "#8fd3e8"
}
},
"emphasis": {
"textStyle": {
"color": "#8fd3e8"
}
}
}
},
"visualMap": {
"color": [
"#516b91",
"#59c4e6",
"#a5e7f0"
]
},
"dataZoom": {
"backgroundColor": "rgba(0,0,0,0)",
"dataBackgroundColor": "rgba(255,255,255,0.3)",
"fillerColor": "rgba(167,183,204,0.4)",
"handleColor": "#a7b7cc",
"handleSize": "100%",
"textStyle": {
"color": "#333333"
}
},
"markPoint": {
"label": {
"normal": {
"textStyle": {
"color": "#eeeeee"
}
},
"emphasis": {
"textStyle": {
"color": "#eeeeee"
}
}
}
}
});
}));
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="chart"></div>
<script>
const chartDom = document.getElementById('chart');
// 1、引入echarts.js后,会生成全局的echarts类;2、参数二:主题的文本,参数三:渲染成svg
const chart = echarts.init(chartDom, 'westeros', { renderer: 'svg' });
// 不是setOptions,没有s
chart.setOption({
title: {
text: 'ECharts 入门案例'
},
// 渲染一个图表,至少需要添加3个元素
// x轴
xAxis: {
data: ['食品', '数码', '服饰', '箱包']
},
// y轴,没有数据,也要写上
yAxis: {},
// 数据、图表类型
series: {
type: 'bar', // 使用柱状图
data: [100, 120, 90, 150] // 一次对应xAxis.data的每一项
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
ECharts 4.0 新特性:dataset
ECharts 4 开始支持了 数据集(dataset)组件用于单独的数据集声明,从而数据可以单独管理,被多个组件复用,并且可以自由指定数据到视觉的映射。这一特性能将逻辑和数据分离,带来更好的复用,并易于理解。

案例:dataset 移植
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/echarts@4.7.0/dist/echarts.min.js"></script>
<style>
#chart {
800px;
height: 400px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="chart"></div>
<script>
const chartDom = document.getElementById('chart')
const chart = echarts.init(chartDom)
const option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'category'
},
yAxis: {},
dataset: {
source: [
['一季度', 79, 100, '分类1', 50],
['二季度', 81, 112, '分类2', 60],
['三季度', 88, 96, '分类3', 55],
['四季度', 72, 123, '分类4', 70],
]
},
series: [{
type: 'pie',
center: ['65%', 60],
radius: 35,
// encode里指定的数据,列要对得上,否则图标会错乱,有的不显示
encode: { itemName: 3, value: 4 }
}, {
type: 'line',
encode: { x: 0, y: 2 } // x指定的列会渲染到x轴上
}, {
type: 'bar',
encode: { x: 0, y: 1 }
}]
}
chart.setOption(option)
</script>
</body>
</html>
ECharts 基本概念: 组件
ECharts 中除了绘图之外其他部分,都可抽象为 「组件」。例如,ECharts 中至少有这些组件:xAxis(直角坐标系 X 轴)、yAxis(直角坐标系 Y 轴)、grid(直角坐标系底板)、angleAxis(极坐标系角度轴)...

案例:各种组件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/echarts@4.7.0/dist/echarts.min.js"></script>
<style>
#chart {
800px;
height: 400px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="chart"></div>
<script>
const chartDom = document.getElementById('chart')
const chart = echarts.init(chartDom)
const option = {
title: {
text: '数据可视化',
subtext: '哈哈哈数据可视化'
},
xAxis: {
type: 'category'
},
yAxis: {},
// 图例,要和series绑定,绑定方法:给series的子项添加name属性,属性名和data中的保持一致才会在图表中显示name文字
legend: {
data: [
{
name: '分类',
// 强制设置图形为圆。
icon: 'circle',
// 设置文本为红色
textStyle: {
color: 'red'
}
},
'折线图',
'柱状图'
],
left: 100
},
// 右上角功能区
toolbox: {
feature: {
saveAsImage: {}, // 改变按钮位置,把保存图片放到最前面
dataZoom: {
yAxisIndex: false // 设置为false,不控制任何y轴,缩放才会正常
},
restore: {} // 还原按钮,写了才会显示
}
},
dataZoom: [{
show: true,
// 分别从30%、70%的位置开始、结束
start: 30,
end: 70
}],
dataset: {
source: [
['一季度', 79, 100, '分类1', 50],
['二季度', 81, 112, '分类2', 60],
['三季度', 88, 96, '分类3', 55],
['四季度', 72, 123, '分类4', 70]
]
},
grid: [{
// 【表示图表距离左边、顶部的距离,有上右下左,只影响图表位置,不影响标题、图例等组件,因为图例组件本身有同样的属性控制位置。】
left: 50,
top: 70
}],
series: [{
name: '分类',
type: 'pie',
center: ['65%', 60],
radius: 35,
encode: { itemName: 3, value: 4 }
}, {
name: '折线图',
type: 'line',
encode: { x: 0, y: 2 }
}, {
name: '柱状图',
type: 'bar',
encode: { x: 0, y: 1 }
}]
}
chart.setOption(option)
</script>
</body>
</html>
test-echarts-series.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/echarts@4.7.0/dist/echarts.js"></script>
<style>
#chart {
800px;
height: 400px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="chart"></div>
<script>
const chartDom = document.getElementById('chart');
const chart = echarts.init(chartDom);
chart.setOption({
dataset: {
source: [
['一季度', 100, 79, '分类1', 50],
['二季度', 112, 81, '分类2', 60],
['三季度', 96, 88, '分类3', 55],
['四季度', 123, 72, '分类4', 70]
]
},
title: {
text: 'ECharts 多系列案例',
subtext: '哈哈数据可视化呵呵'
},
xAxis: {
data: ['一季度', '二季度', '三季度', '四季度']
},
yAxis: {},
// 图例,要和series绑定,绑定方法:给series的子项添加name属性
legend: {
data: [{
// 可以修改图例的样式
name: '分类',
icon: 'circle',
textStyle: {
color: 'red'
}
}, '折线图', '柱状图'],
left: 300 // 距离左侧位置
},
grid: {
top: 100,
left: '10%',
right: '10%',
bottom: 100
},
// 右上角功能区
toolbox: {
feature: {
saveAsImage: {}, // 改变按钮位置,把保存图片放到最前面
dataZoom: {
yAxisIndex: false // 设置为false,不控制任何y轴,缩放才会正常
},
restore: {}
}
},
// 【底部控制可视区的滚动条】
dataZoom: [
{
show: true,
start: 30,
end: 70
}
],
series: [{
name: '分类',
type: 'pie', // 饼图
center: ['65%', 60], // 饼图【圆心】的位置 【距离左侧65%,距离右侧60px(应该是上侧)】
radius: 35,
encode: { itemName: 3, value: 4 } // 第四列、第五列
}, {
name: '折线图',
type: 'line',
encode: { x: 0, y: 1 }
}, {
name: '柱状图',
type: 'bar',
encode: { x: 0, y: 2 }
}]
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
ECharts 基本概念:定位
大多数组件都提供了定位属性,我们可以采用类似 CSS absolute 的定位属性来控制组件的位置,下面这个案例可以通过修改 grid 组件定位来控制图表的位置

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/echarts@4.7.0/dist/echarts.min.js"></script>
<style>
#chart {
800px;
height: 400px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
top: <input type="text" id="top">
left: <input type="text" id="left">
right: <input type="text" id="right">
bottom: <input type="text" id="bottom">
</div>
<div id="chart"></div>
<script>
let _left = 0
let _top = 0
let _bottom = 0
let _right = 0
const topInput = document.getElementById('top')
const leftInput = document.getElementById('left')
const bottomInput = document.getElementById('bottom')
const rightInput = document.getElementById('right')
const chartDom = document.getElementById('chart')
const chart = echarts.init(chartDom)
function addInputEvent(dom, key) {
dom.addEventListener('input', function (e) {
value = e.target.value
switch (key) {
case 'top':
_top = value
break
case 'left':
_left = value
break
case 'bottom':
_bottom = value
break
case 'right':
_right = value
break
}
render()
})
}
function render() {
const option = {
title: {
text: '数据可视化',
subtext: '哈哈哈数据可视化哈哈哈'
},
xAxis: {
type: 'category'
},
yAxis: {},
dataset: {
source: [
['一季度', 79, 100, '分类1', 50],
['二季度', 81, 112, '分类2', 60],
['三季度', 88, 96, '分类3', 55],
['四季度', 72, 123, '分类4', 70],
]
},
grid: [{
left: _left,
top: _top,
right: _right,
bottom: _bottom
}],
series: [{
name: '折线图',
type: 'line',
encode: { x: 0, y: 2 }
}]
}
chart.setOption(option)
}
window.onload = function () {
topInput.value = _top
leftInput.value = _left
bottomInput.value = _bottom
rightInput.value = _right
addInputEvent(topInput, 'top')
addInputEvent(leftInput, 'left')
addInputEvent(bottomInput, 'bottom')
addInputEvent(rightInput, 'right')
render()
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
ECharts 基本概念:坐标系
很多系列,例如 line(折线图)、bar(柱状图)、scatter(散点图)、heatmap(热力图)等等,需要运行在 “坐标系” 上。坐标系用于布局这些图,以及显示数据的刻度等等。例如 ECharts 中至少支持这些坐标系:直角坐标系、极坐标系、地理坐标系(GEO)、单轴坐标系、日历坐标系 等。其他一些系列,例如 pie(饼图)、tree(树图)等等,并不依赖坐标系,能独立存在。还有一些图,例如 graph(关系图)等,既能独立存在,也能布局在坐标系中,依据用户的设定而来。
一个坐标系,可能由多个组件协作而成。我们以最常见的直角坐标系来举例。直角坐标系中,包括有 xAxis(直角坐标系 X 轴)、yAxis(直角坐标系 Y 轴)、grid(直角坐标系底板)三种组件。xAxis、yAxis 被 grid 自动引用并组织起来,共同工作。
案例:散点图
我们来看下图,这是最简单的使用直角坐标系的方式:只声明了 xAxis、yAxis 和一个 scatter(散点图系列),ECharts 会为它们创建 grid 并进行关联:

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/echarts@4.7.0/dist/echarts.min.js"></script>
<style>
#chart {
800px;
height: 400px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="chart"></div>
<script>
const chartDom = document.getElementById('chart')
const chart = echarts.init(chartDom)
const option = {
xAxis: {},
yAxis: {},
dataset: {
source: [
[13, 44],
[51, 51],
[51, 32],
[67, 19],
[19, 33]
]
},
series: [{
type: 'scatter', // 散点图的名称
encode: { x: 0, y: 1 }
}]
}
chart.setOption(option)
</script>
</body>
</html>
案例:双坐标系
双坐标系只能存在于一个坐标系中。
再来看下图,两个 yAxis,共享了一个 xAxis。两个 series,也共享了这个 xAxis,但是分别使用不同的 yAxis,使用 yAxisIndex 来指定它自己使用的是哪个 yAxis:

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/echarts@4.7.0/dist/echarts.min.js"></script>
<style>
#chart {
800px;
height: 400px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="chart"></div>
<script>
const chartDom = document.getElementById('chart')
const chart = echarts.init(chartDom)
const option = {
legend: {},
tooltip: {},
xAxis: {
// 多坐标系需要明确指定xAxis的type。这里xAxis是2012~2015这样的分类数据。
type: 'category'
},
yAxis: [{
// 纵坐标的线错位的另一种解决方案:自定义左右坐标系的刻度
min: 0,
max: 100
}, {
min: 0,
max: 100,
// 左右两边的纵坐标的线错位,把右边的线隐藏
// splitLine: {
// show: false
// }
}],
dataset: {
source: [
['product', '2012', '2013', '2014', '2015'],
['Matcha Latte', 41.1, 30.4, 65.1, 53.3],
['Milk Tea', 86.5, 92.1, 85.7, 83.1]
]
},
series: [
{
type: 'bar',
seriesLayoutBy: 'row', // 以行的方式进行取数据
yAxisIndex: 0 // 表示这个柱状图对应的是yAxis的第一个坐标系
},
{
type: 'line',
seriesLayoutBy: 'row',
yAxisIndex: 1
}
]
}
chart.setOption(option)
</script>
</body>
</html>
案例:多坐标系
多坐标系允许有多个直角坐标系。
再来看下图,一个 ECharts 实例中,有多个 grid,每个 grid 分别有 xAxis、yAxis,他们使用 xAxisIndex、yAxisIndex、gridIndex 来指定引用关系:

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/echarts@4.7.0/dist/echarts.min.js"></script>
<style>
#chart {
800px;
height: 400px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="chart"></div>
<script>
const chartDom = document.getElementById('chart')
const chart = echarts.init(chartDom)
const option = {
legend: {},
tooltip: {},
xAxis: [
{
type: 'category',
gridIndex: 0
},
{
type: 'category',
gridIndex: 1
}
],
yAxis: [
{
// y轴的坐标系也要指定gridIndex,和x轴保持一致
gridIndex: 0
},
{
gridIndex: 1
}
],
dataset: {
source: [
['product', '2012', '2013', '2014', '2015'],
['Matcha Latte', 41.1, 30.4, 65.1, 53.3],
['Milk Tea', 86.5, 92.1, 85.7, 83.1],
['Cheese Cocoa', 24.1, 67.2, 79.5, 86.4]
]
},
// 建2个,用来区分2个坐标系,通过间距区分,否则重叠在一起不好区分
grid: [
{
bottom: '55%'
},
{
top: '55%'
}
],
series: [
// 这几个系列会在第一个直角坐标系中,每个系列对应到 dataset 的每一行。
{
type: 'bar',
seriesLayoutBy: 'row'
},
{
type: 'bar',
seriesLayoutBy: 'row'
},
{
type: 'bar',
seriesLayoutBy: 'row'
},
// 这几个系列会在第二个直角坐标系中,每个系列对应到 dataset 的每一列。
{
type: 'bar',
xAxisIndex: 1,
yAxisIndex: 1
},
{
type: 'bar',
xAxisIndex: 1,
yAxisIndex: 1
},
{
type: 'bar',
xAxisIndex: 1, // 选择哪个x轴
yAxisIndex: 1
},
{
type: 'bar',
xAxisIndex: 1,
yAxisIndex: 1
}
]
}
chart.setOption(option)
</script>
</body>
</html>