Little Mishka enjoys programming. Since her birthday has just passed, her friends decided to present her with array of non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an of n elements!
Mishka loved the array and she instantly decided to determine its beauty value, but she is too little and can't process large arrays. Right because of that she invited you to visit her and asked you to process m queries.
Each query is processed in the following way:
- Two integers l and r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n) are specified — bounds of query segment.
- Integers, presented in array segment [l, r] (in sequence of integers al, al + 1, ..., ar) even number of times, are written down.
- XOR-sum of written down integers is calculated, and this value is the answer for a query. Formally, if integers written down in point 2 are x1, x2, ..., xk, then Mishka wants to know the value
 , where
, where  — operator of exclusive bitwise OR.
— operator of exclusive bitwise OR.
Since only the little bears know the definition of array beauty, all you are to do is to answer each of queries presented.
The first line of the input contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1 000 000) — the number of elements in the array.
The second line of the input contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — array elements.
The third line of the input contains single integer m (1 ≤ m ≤ 1 000 000) — the number of queries.
Each of the next m lines describes corresponding query by a pair of integers l and r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n) — the bounds of query segment.
Print m non-negative integers — the answers for the queries in the order they appear in the input.
3
3 7 8
1
1 3
0
7
1 2 1 3 3 2 3
5
4 7
4 5
1 3
1 7
1 5
0
3
1
3
2
In the second sample:
There is no integers in the segment of the first query, presented even number of times in the segment — the answer is 0.
In the second query there is only integer 3 is presented even number of times — the answer is 3.
In the third query only integer 1 is written down — the answer is 1.
In the fourth query all array elements are considered. Only 1 and 2 are presented there even number of times. The answer is 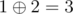 .
.
In the fifth query 1 and 3 are written down. The answer is 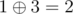 .
.
思路:利用离线求每个区间不同数的异或和,再求区间的异或和,区间的异或和相当与区间的奇数个数的异或和;
利用区间异或和 异或 区间不同数的异或和 == 区间偶数个数的异或和;
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long #define esp 1e-10 const int N=1e6+10,M=1e6+10,mod=1e9+7,inf=1e9+10; struct is { int l,r; int pos; }a[N]; int b[N]; int ans[N]; map<int,int>last; int cmp(is x,is y) { if(x.r!=y.r) return x.r<y.r; return x.l<y.l; } int treeunq[N]; int tree[N]; int lowbit(int x) { return x&-x; } int update(int x,int change,int n,int *tree) { while(x<=n) { tree[x]^=change; x+=lowbit(x); } } int query(int x,int *tree) { int sum=0; while(x) { sum^=tree[x]; x-=lowbit(x); } return sum; } int main() { int x,y,z,i,t; while(~scanf("%d",&x)) { memset(tree,0,sizeof(tree)); memset(treeunq,0,sizeof(treeunq)); for(i=1;i<=x;i++) { scanf("%d",&b[i]); tree[i]=b[i]; y=lowbit(i); for(t=1;t<y;t++) tree[i]^=b[i-y+t]; } scanf("%d",&y); for(i=1;i<=y;i++) scanf("%d%d",&a[i].l,&a[i].r),a[i].pos=i; sort(a+1,a+y+1,cmp); int st=1; for(i=1;i<=y;i++) { while(st<=a[i].r) { if(last[b[st]]!=0) update(last[b[st]],b[st],x,treeunq); last[b[st]]=st; update(st,b[st],x,treeunq); st++; } ans[a[i].pos]=query(a[i].r,tree)^query(a[i].l-1,tree)^query(a[i].r,treeunq)^query(a[i].l-1,treeunq); } for(i=1;i<=y;i++) printf("%d ",ans[i]); } return 0; }