You are given n numbers a1, a2, ..., an. You can perform at most k operations. For each operation you can multiply one of the numbers by x. We want to make 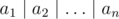 as large as possible, where
as large as possible, where  denotes the bitwise OR.
denotes the bitwise OR.
Find the maximum possible value of 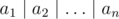 after performing at most k operations optimally.
after performing at most k operations optimally.
The first line contains three integers n, k and x (1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000, 1 ≤ k ≤ 10, 2 ≤ x ≤ 8).
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 109).
Output the maximum value of a bitwise OR of sequence elements after performing operations.
3 1 2
1 1 1
3
4 2 3
1 2 4 8
79
For the first sample, any possible choice of doing one operation will result the same three numbers 1, 1, 2 so the result is 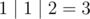 .
.
For the second sample if we multiply 8 by 3 two times we'll get 72. In this case the numbers will become 1, 2, 4, 72 so the OR value will be 79 and is the largest possible result.
题意:给你n个数,可以在任意位置乘以k次x;
求n个数最大的或值;
思路:首先显然尽量将最大的位置放1;所以尽量乘以大的数;
将全部拆分成二进制,复杂度N*60
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll __int64 #define mod 1000000007 #define esp 0.00000000001 const int N=2e5+10,M=1e6+10,inf=1e9; ll a[N]; ll flag[N]; ll quickmul(ll x,ll y) { ll ans=1; while(y) { if(y&1) ans*=x; x*=x; y>>=1; } return ans; } void update(ll x,ll gg) { int ji=0; while(x) { flag[ji++]+=(gg)*(x%2); x>>=1; } } ll getans() { ll base=1,sum=0; for(int i=0;i<=60;i++) { if(flag[i]) sum+=base; base*=2; } return sum; } int main() { ll x,y,z,i,t; scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d",&x,&y,&z); ll mul=quickmul(z,y); for(i=0;i<x;i++) scanf("%I64d",&a[i]),update(a[i],1); ll ans=0; for(i=0;i<x;i++) { update(a[i],-1); update(a[i]*mul,1); ans=max(ans,getans()); update(a[i]*mul,-1); update(a[i],1); } printf("%I64d ",ans); return 0; }
;