写在开篇
在项目的开发中,通常都会用到 Spring 来进行项目管理。在某些应用中,我们希望当Spring 容器将所有的 Bean 都初始化完成后,做一个操作(例如:将数据库中的字典,加载到内存中)。那么如何在 Spring IOC 容器初始化完成后,自动触发某个方法来完成某些业务逻辑配置相关的操作执行呢?一共能找到的介绍有如下7种,但是这7种还各自都有些不同之处。
解析8种实现方式
- 类实现ApplicationContextAware,重写setApplicationContext()方法
- 类实现InitializingBean,重写afterPropertiesSet()方法
- 在类中的方法上,添加@PostConstruct注解。(@PreDestroy注销时使用)
- 类实现BeanPostProcessor,重写postProcessBeforeInitialization()、postProcessAfterInitialization()方法
- 类实现 SmartLifecycle,重写相关方法
- 类实现ApplicationContextListener,重写onApplicationEvent()方法
- 类实现ApplicationRunner,重写run()方法
- 类实现CommandLineRunner,重写run()方法
说明:
第 1 、2 种方式,是在所有 bean 对象注册到 IOC 容器完成之后,通过 后置处理器 或者Spring 启动后的其他后置操作,来针对指定实现 ApplicationContextAware 或 InitializingBean 的一个bean类进行操作,达到配置全局的目的。比如说:将数据库中的字典,加载到内存中 这种,并不需要每一个bean都配置的功能。(提示:说到底第1、2种方式,和本文提及的 Spring IOC 初始化后。还是有一些出入的,本文也就一并都放到这里介绍了)
第 3 种方式,PostConstruct和 Spring 的启动流程无关,只和 Servlet 容器相关。(提示:Spring 项目在启动 Servlet(此处以 Tomcat 为例)时,已经完成了 IOC 的相关操作,满足本文题目在 Spring IOC 初始化后)
第 4 种方式,BeanPostProcessor是对 Spring IOC 容器中每个bean对象的前置、后置增强。(提示:也和本文要求 Spring IOC 容器初始化后有出入。本文也就一并都放到这里介绍了))
第 5 种方式,根据源码我们了解到 LifecycleProcessor 处理器是在Spring 容器启动最后一步 Last step: finishRefresh();这个方法中调用到的(提示:此时 Spring IOC 容器的初始化工作已经完成满足本文题目在 Spring IOC 初始化后)
第 6 种方式,使用 ApplicationListener 监听机制。监听 ApplicationContextListener<ContextRefreshedEvent>的方式,Spring IOC 容器在所有的bean都初始化完成并被成功装载后会触发该事件(提示:监听器方式 也可以满足本文题目在 Spring IOC 初始化后,执行部分逻辑操作)
第 7、8 种方式,实现 ApplicationRunner、CommandLineRunner 接口的方式。都是在容器启动完成的时执行。(提示:这种方式也可以满足本文题目在 Spring IOC 初始化后,执行部分逻辑操作)
综合来说: 只有3、5、6、7、8 这五种方式,是彻底在 Spring IOC容器初始化后,执行一些逻辑操作。其它三种方式只能说是变相满足本文要求吧
使用介绍
1.实现ApplicationContextAware,重写setApplicationContext()方法
实现ApplicationContextAware接口并重写setApplicationContext()方法获取ApplicationContext实例,这个要追溯到ApplicationContextAwareProcessor类。首先我们来看一下 ApplicationContextAwareProcessor 这个类,它是BeanPostProcessor(后置处理器)的一个实现类,此处附 Spring 启动源码来了解这个后置处理器。
此处源码分析, 你可参考:Spring IOC 源码解析一文学习更清晰。根据代码,重点:在注册后置处理器时,Spring IOC 容器已经初始化完成,所以我们可以通过这种方式,在 IOC 容器初始化后,执行一些逻辑操作。
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); //1.此处 obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法,来完成Spring IOC容器的 定位、加载、注册 等操作 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. //2.此处用来注册配置后置处理器(说明在配置后置处理器时,IOC容器已经创建完成) registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); //省略部分源码 } catch (BeansException ex) { // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); } finally { resetCommonCaches(); } } }
示例:(本例使用 Spring Boot框架)
@Component public class AfterIocInitialConfig implements ApplicationContextAware { @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { //在此处执行逻辑操作 System.out.println("--ApplicationContextAware-------在此执行一些逻辑操作"); } }
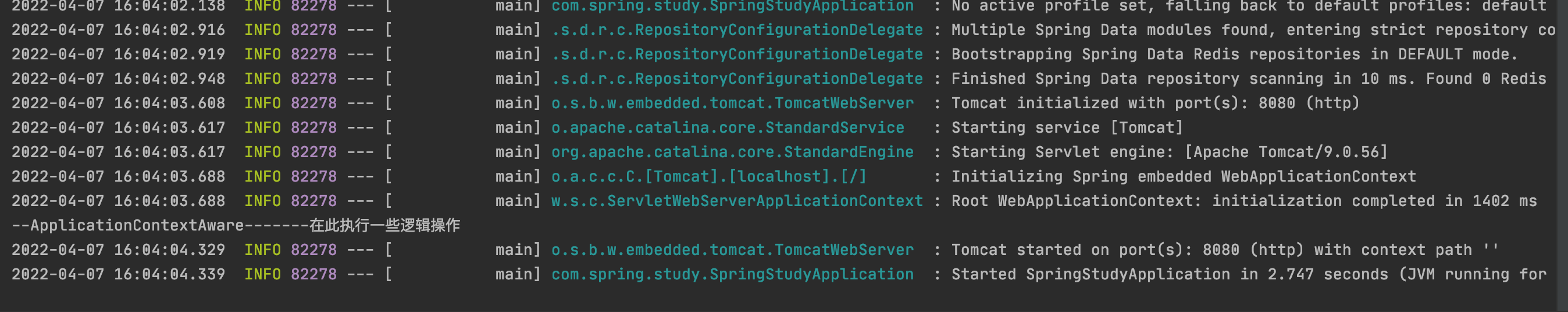
2.实现InitializingBean,重写afterPropertiesSet()方法
(bean 配置文件属性 init-method 用于在bean初始化时指定执行方法,可以用来替代继承 InitializingBean接口)
InitializingBean接口为bean提供了初始化方法的方式,它只包括afterPropertiesSet()方法,凡是继承该接口的类,在初始化 bean 的时候都会执行该方法。(注意:重写了InitializingBean的 bean 在初始化时才会执行,没重写的 bean 是不会被执行的)
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); //1.此处 obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法,来完成Spring IOC容器的 定位、加载、注册 等操作 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // 省略部分代码 // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. //2.初始化所有的单例 bean(实现InitializingBean,重写afterPropertiesSet()方法,在此处执行) finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); //省略部分源码 } catch (BeansException ex) { // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); } finally { resetCommonCaches(); } } }
示例:(本例使用 Spring Boot框架)
@Component public class InitializingBeanAfterIocInitialConfig implements InitializingBean { @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { //在此处执行逻辑操作 System.out.println("--InitializingBean------在此执行一些逻辑操作"); } }

3. 在类中的方法上,添加@PostConstruct注解。(@PreDestroy注销时使用)
@PostConstruct 说明:
被 @PostConstruct 修饰的方法会在服务器加载 Servlet 的时候运行,并且只会被服务器调用一次,类似于 Servlet 的 init() 方法。被@PostConstruct 修饰的方法会在构造函数之后,init() 方法之前运行。
@PostConstruct 注释用于在依赖关系注入完成之后需要执行的方法上,以执行任何初始化。此方法必须在将类放入服务之前调用。支持依赖关系注入的所有类都必须支持此注释。即使类没有请求注入任何资源,用@PostConstruct 注释的方法也必须被调用。注意:只有一个方法可以用此注释进行注释。
@PreDestroy 说明:
被 @PreDestroy 修饰的方法会在服务器卸载 Servlet 的时候运行,并且只会被服务器调用一次,类似于 Servlet 的 destroy() 方法。被 @PreDestroy 修饰的方法会在 destroy() 方法之后运行,在 Servlet 被彻底卸载之前。
@PreDestroy 注释作为回调通知用于各方法,以表示该实例正处于被容器移除的过程中。用 @PreDestroy 注释的方法通常用于释放它已经持有的资源,所有支持 @PostConstruct 的容器管理对象都必须支持此注释
- 应用 @PostConstruct、@PreDestroy 注释的方法必须遵守以下所有标准:
- 该方法不得有任何参数,除非是在EJB 拦截器(interceptor)的情况下,它可以带有一个 InvocationContext 对象;
- 该方法的返回类型必须为 void;
- 该方法不得抛出已检查异常;
- 应用@PostConstruct 的方法可以使 pulbic、protected、package private 或 private;
- 除了应用程序客户端之外,该方法不能是 static;该方法可以是 final;
示例:(本例使用 Spring Boot框架)
@Component public class PostConstructConfig { //在服务器加载 Servlet 的时候执行 @PostConstruct public void doSomething() { //在此处执行逻辑操作 System.out.println("--PostConstruct------在此执行一些逻辑操作"); } //在服务器卸载 Servlet 的时候执行 @PreDestroy public void shutDownDoSomething() { System.out.println("--PostConstruct------卸载Servlet时执行"); } }
@PostConstruct 注解,显然和 Spring IOC容器的启动没有多大关系,它只和 Servlet 容器的加载有关系。加载 Servlet 时, IOC 容器其实已经初始化完成。所以使用 @PostConstruct 注解,可以满足 Spring IOC 容器初始化后,执行一些逻辑操作。
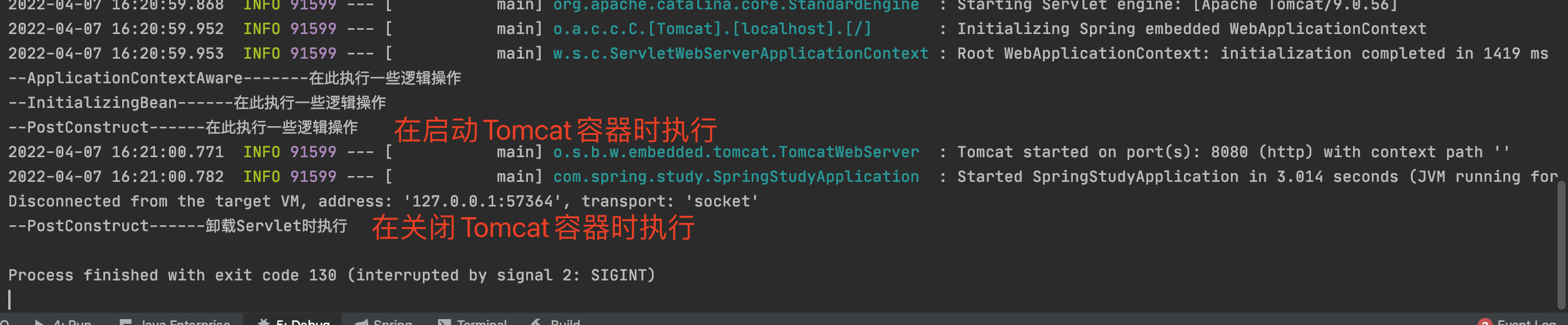
4.类实现BeanPostProcessor接口,重写postProcessBeforeInitialization()、postProcessAfterInitialization()方法
BeanPostProcessor是 Spring IOC 容器给我们提供的一个扩展接口。注意:该接口会在 Spring IOC 容器的每一个 bean 初始化前、后做一些相关操作,记住是每一个!!!。接口声明如下:
public interface BeanPostProcessor { //bean初始化方法调用前被调用 Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; //bean初始化方法调用后被调用 Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; }
比如说当前 IOC 容器,有200个bean对象。那么这200个bean对象都会在初始化前、后来调用被重写的postProcessBeforeInitialization()、postProcessAfterInitialization()方法,相当于是 bean 对象初始化的前置、后置增强。
@Component public class BeanPostProcessorConfig implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("--BeanPostProcessor--" + beanName + ":对象初始化前执行一些操作"); return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("--BeanPostProcessor--" + beanName +":对象初始化后执行一些操作"); return bean; } }
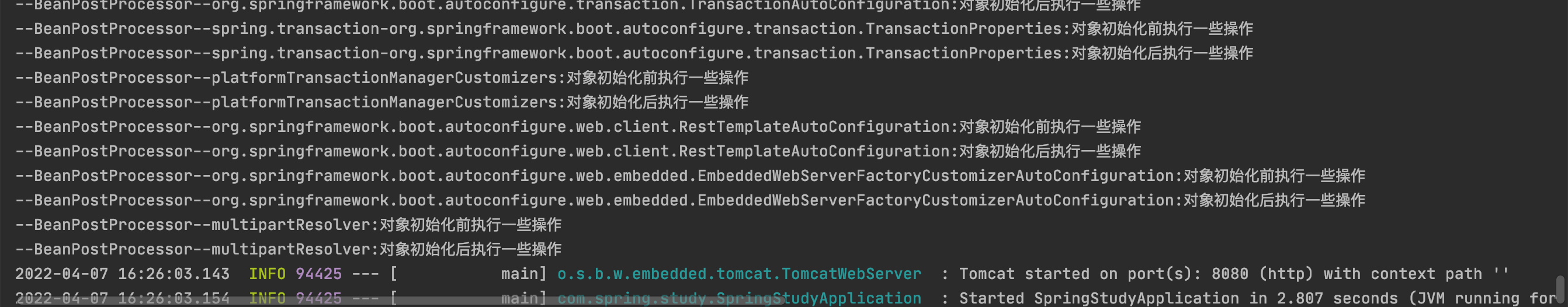
5.类实现 SmartLifecycle,重写相关方法
在使用 Spring 开发时,我们都知道,所有 bean都交给 Spring IOC 容器来统一管理,其中包括每一个 bean 的加载和初始化。有时候,我们需要在 Spring 加载和初始化所有bean后,接着执行一些任务或者启动需要的异步服务,这样我们可以使用 SmartLifecycle 来做到。SmartLifecycle 是一个接口,继承自 Lifecycle(生命周期)、Phased(如果有多个实现 Liftcycle接口的类,通过getPhase()方法来确定执行先后顺序)两个接口。当 Spring 容器加载所有 bean 并完成初始化之后,会接着回调实现该接口的类中对应的方法(start()方法)。
LifecycleProcessor 处理器,在源码中的执行位置,如下所示:
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); //省略 // Last step: publish corresponding event. // 重点:LifecycleProcessor 在此处被调用(继续进入方法查看) finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { //省略 } finally { resetCommonCaches(); } } } protected void finishRefresh() { // Initialize lifecycle processor for this context. // 重点1:为当前context初始化 LifecycleProcessor() initLifecycleProcessor(); // Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first. // 重点2:调用 lifecycleProcessor 的 onRefresh() 方法(如果我们定义了一个类,实现了 lifecycle 相关接口,则会在此处调用自定义的 onRefresh() 方法) getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh(); // Publish the final event. // 事件机制发布(在下一种实现方式 ApplicationContextListener 中会涉及到) publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this)); // Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active. LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this); }
如果IOC容器没有 lifecycleProcessor,则会使用 DefaultLifecycleProcessor 类,此处附DefaultLifecycleProcessor 类源码(省略部分源码)
public class DefaultLifecycleProcessor implements LifecycleProcessor, BeanFactoryAware { private volatile long timeoutPerShutdownPhase = 30000; private volatile boolean running; /** * Specify the maximum time allotted in milliseconds for the shutdown of * any phase (group of SmartLifecycle beans with the same 'phase' value). * <p>The default value is 30 seconds. */ public void setTimeoutPerShutdownPhase(long timeoutPerShutdownPhase) { this.timeoutPerShutdownPhase = timeoutPerShutdownPhase; } /** * Start all registered beans that implement {@link Lifecycle} and are <i>not</i> * already running. Any bean that implements {@link SmartLifecycle} will be * started within its 'phase', and all phases will be ordered from lowest to * highest value. All beans that do not implement {@link SmartLifecycle} will be * started in the default phase 0. A bean declared as a dependency of another bean * will be started before the dependent bean regardless of the declared phase. */ @Override public void start() { startBeans(false); this.running = true; } /** * Stop all registered beans that implement {@link Lifecycle} and <i>are</i> * currently running. Any bean that implements {@link SmartLifecycle} will be * stopped within its 'phase', and all phases will be ordered from highest to * lowest value. All beans that do not implement {@link SmartLifecycle} will be * stopped in the default phase 0. A bean declared as dependent on another bean * will be stopped before the dependency bean regardless of the declared phase. */ @Override public void stop() { stopBeans(); this.running = false; } @Override public void onRefresh() { startBeans(true); this.running = true; } @Override public void onClose() { stopBeans(); this.running = false; } @Override public boolean isRunning() { return this.running; } }
示例:(本例使用 Spring Boot框架)
@Component public class SmartLifecycleConfig implements SmartLifecycle, ApplicationContextAware { private boolean isRunning = false; private ApplicationContext context = null; @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { this.context = applicationContext; } /** * 1. 我们主要在该方法中启动任务或者其他异步服务,比如开启MQ接收消息 * 2. 当上下文被刷新(所有对象已被实例化和初始化之后)时,将调用该方法,默认生命周期处理器将检查每个SmartLifecycle对象的isAutoStartup()方法返回的布尔值。 * 如果为“true”,则该方法会被调用,而不是等待显式调用自己的start()方法。 */ @Override public void start() { System.out.println("---SmartLifecycle--执行start()方法"); // 执行完其他业务后,可以修改 isRunning = true isRunning = true; } /** * 如果工程中有多个实现接口SmartLifecycle的类,则这些类的start的执行顺序按getPhase方法返回值从小到大执行。 * 例如:1比2先执行,-1比0先执行。 stop方法的执行顺序则相反,getPhase返回值较大类的stop方法先被调用,小的后被调用。 */ @Override public int getPhase() { // 默认为0 System.out.println("---SmartLifecycle--执行getPhase方法"); return 0; } /** * 根据该方法的返回值决定是否执行start方法。 * 返回true时start方法会被自动执行,返回false则不会。 */ @Override public boolean isAutoStartup() { // return false; System.out.println("---SmartLifecycle--执行 isAutoStartup 方法"); return true; } /** * SmartLifecycle子类才有的方法,当isRunning方法返回true时,该方法才会被调用。 */ /*@Override public void stop(Runnable callback) { System.out.println("stop(Runnable)"); // 如果你让isRunning返回true,需要执行stop这个方法,那么就不要忘记调用callback.run()。 // 否则在你程序退出时,Spring的DefaultLifecycleProcessor会认为你这个TestSmartLifecycle没有stop完成,程序会一直卡着结束不了,等待一定时间(默认超时时间30秒)后才会自动结束。 // PS:如果你想修改这个默认超时时间,可以按下面思路做,当然下面代码是springmvc配置文件形式的参考,在SpringBoot中自然不是配置xml来完成,这里只是提供一种思路。 // <bean id="lifecycleProcessor" class="org.springframework.context.support.DefaultLifecycleProcessor"> // <!-- timeout value in milliseconds --> // <property name="timeoutPerShutdownPhase" value="10000"/> // </bean> callback.run(); isRunning = false; }*/ /** * 1. 只有该方法返回false时,start方法才会被执行。 * 2. 只有该方法返回true时,stop(Runnable callback)或stop()方法才会被执行。 */ @Override public boolean isRunning() { // 默认返回false System.out.println("---SmartLifecycle--执行 isRunning 方法"); return isRunning; } /** * 接口Lifecycle的子类的方法,只有非SmartLifecycle的子类才会执行该方法。<br/> * 1. 该方法只对直接实现接口Lifecycle的类才起作用,对实现SmartLifecycle接口的类无效。<br/> * 2. 方法stop()和方法stop(Runnable callback)的区别只在于,后者是SmartLifecycle子类的专属。 */ @Override public void stop() { System.out.println("---SmartLifecycle--执行 stop() 方法"); isRunning = false; } }
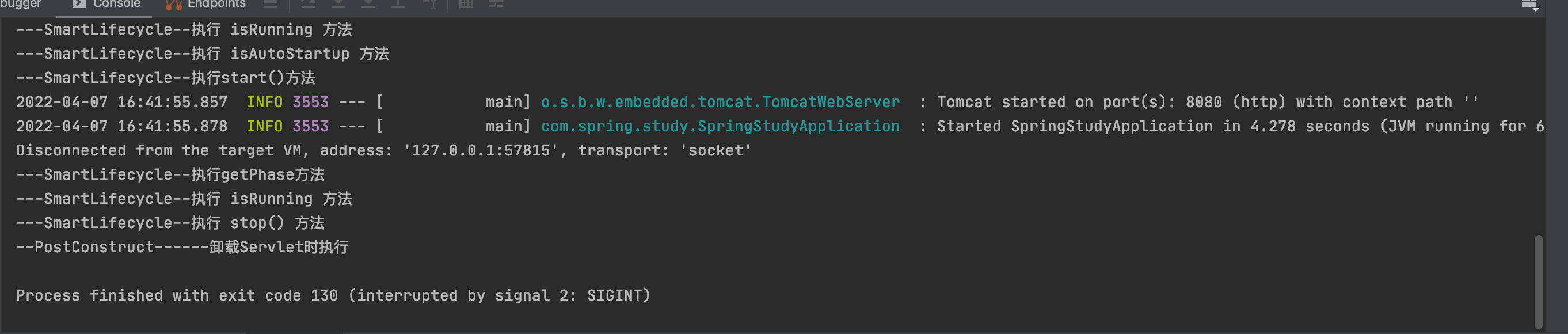
6.实现ApplicationContextListener<ContextRefreshedEvent>,重写onApplicationEvent()方法
ApplicationContextListener 事件机制是观察者设计模式的实现,通过ApplicationEvent类和ApplicationListener接口,可以实现ApplicationContext事件处理;如果容器中存在 ApplicationListener 的Bean,当 ApplicationContext 调用 publishEvent 方法时,对应的Bean会被触发。publishEvent() 方法,同刚刚介绍的 Lifecycle 类似,也是在 finishRefresh() 方法中调用的。如下所示:
protected void finishRefresh() { // Initialize lifecycle processor for this context. initLifecycleProcessor(); // Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first. getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh(); // Publish the final event. // 重点:事件机制发布(在下一种实现方式 ApplicationContextListener 中会涉及到) publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this)); // Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active. LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this); }
其中 Spring 有一些内置的事件,当完成某种操作时会发出某些事件动作。比如监听ContextRefreshedEvent事件,当所有的bean都初始化完成并被成功装载后会触发该事件,实现ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent>接口可以收到监听动作,然后可以写自己的逻辑。同样事件我们可以自定义、监听也可以自定义,完全根据自己的业务逻辑来处理。

示例:(本例使用 Spring Boot框架)
@Component public class ApplicationListenerConfig implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> { @Override public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) { System.out.println("--ApplicationListener--监听到所有的bean都已经初始化完成"); } }
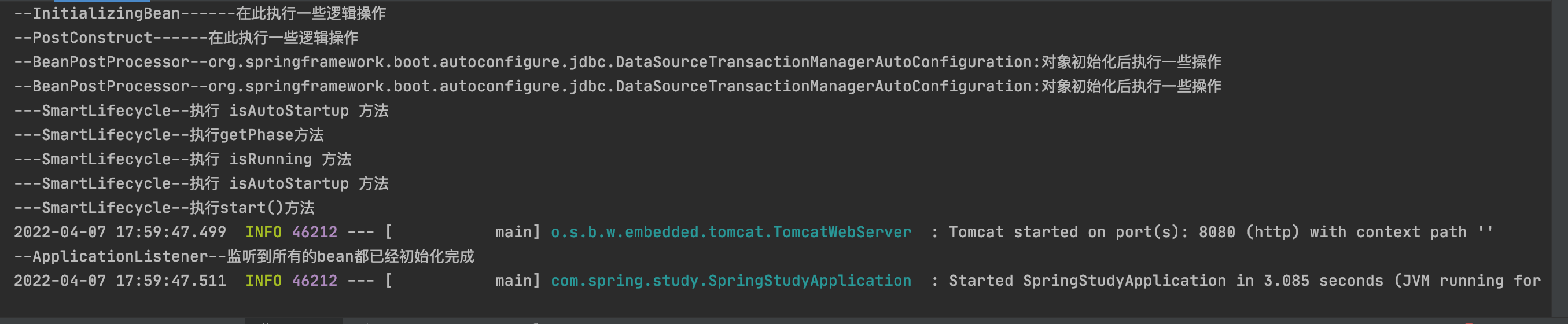
附录:
- 我们可以监听 ServletWebServerInitializedEvent 类,来监听 Servlet 是否初始化完成;
- 也可以监听 ApplicationReadyEvent 类,来监听应用(项目)是否启动完成。
7.类实现ApplicationRunner,重写run()方法
在开发中可能会有这样的情景。需要在容器启动的时候执行一些内容。比如读取配置文件,数据库连接之类的。Spring 项目中,我们可以通过实现 ApplicationRunner接口,重写run() 方法。它的执行时机为容器启动完成的时候。
示例:(本例使用 Spring Boot框架)
@Component public class ApplicationRunnerConfig implements ApplicationRunner { @Override public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception { System.out.println("--ApplicationRunner---当前项目已经启动完成"); } }

8.类实现CommandLineRunner,重写run()方法
SpringBoot 中额外给我们提供了一个接口,这个接口是 CommandLineRunner。它和 ApplicationRunner功能一样,也都需要重写run()方法。该接口也是在容器启动完成的时候执行。
它们的不同之处在于:(其它使用都相同)
ApplicationRunner 可以在 Spring、SpringBoot 项目中使用;CommandLineRunner 只能在 Spring Boot 中使用
ApplicationRunner 中 run() 方法的参数为 ApplicationArguments,而 CommandLineRunner 中 run() 方法的参数为 String数组。
示例:(本例使用 Spring Boot框架)
@Component public class CommandLineRunnerConfig implements CommandLineRunner { @Override public void run(String... args) throws Exception { System.out.println("--CommandLineRunner---当前项目已经启动完成"); } }
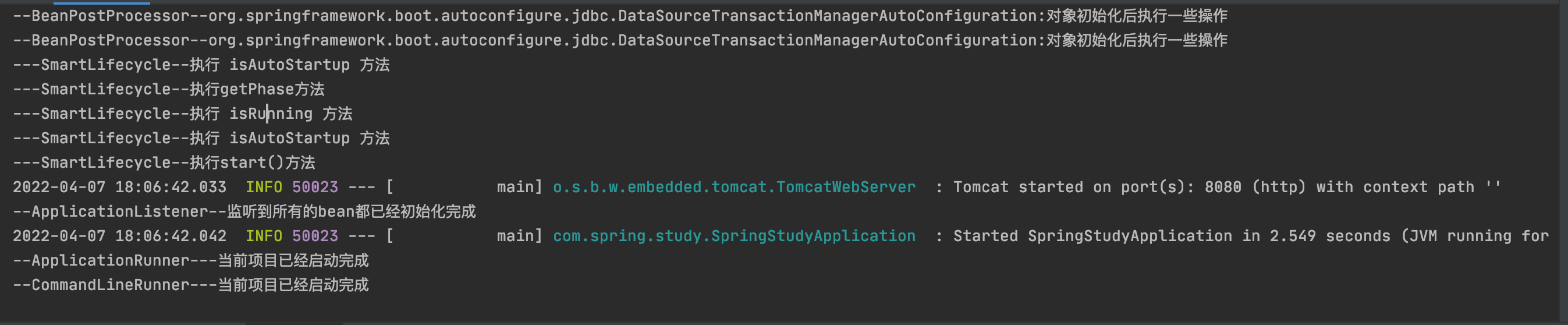
总结:执行顺序还是按照1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8的顺序进行加载的,每个实现都有不同的方式和不同的目的,同时需要了解每个实现的原理是什么,什么场景的时候使用。