1、sql 映射文件常见关键字
sql 映射文件中需要注意的一些关键字:
- parameterType: 指定要求输入参数的类型,可以指定为基本数据类型(如 int、float 等)、包装数据类型(如 String、Interger 等)以及用户自己编写的 JavaBean 封装类。不管参数是基本数据类型还是JavaBean,parameterType 都可以不填,mybatis 通过反射机制能够自动识别到调用 sql 语句的参数并进行填充。一般情况下可以不指定该关键字。
- resultType: 指定输出的结果类型。 resultType 就是用来指定数据库返回的信息对应的 Java 的数据类型。
- #{}:表示参数占位符,在大括号中书写参数名称来接受对应参数。#{} 实际上是通过 prepareStatement 对象来执行 sql 的,可以避免 SQL 注入问题。当传入的参数是java对象时,#{} 会自动根据参数名来获取对象的属性值。当 “#{}” 接受的是基本数据类型时可以用
value或者其他任意名称来获取,比如#{value}。 - ${}:${} 为字符串替换,是通过拼接字符串的方式来拼接成 sql 的。使用 “${}” 拼接符号拼接 SQL ,会引起 SQL 注入,所以一般不建议使用 “${}”。在 SQL 配置中,有时候需要拼接 sql 语句(例如模糊查询时),用 “#{}” 是无法达到目的的。
mybatis 的 sql 语句如果需要接收多个参数,我们可以通过以下方式来传递多个参数:
- 通过 java 对象进行传参。比如一个 java 类的对象
- 使用 @param 传递命名参数,sql 语句中通过 #{自定义参数名} 的形式来获取参数
- 可以使用 #{arg0} #{arg1} 的形式来根据参数的位置来获取参数。注意,mybatis 3.4之前的版本是通过 #{0}、#{1} 这种形式来使用的
- 通过 map 集合传递参数
2、关键字#{}和${}
#{}:表示参数占位符,在大括号中书写参数名称来接受对应参数。#{} 实际上是通过 prepareStatement 对象来执行 sql 的,可以避免 SQL 注入问题。当传入的参数是java对象时,#{} 会自动根据参数名来获取对象的属性值。当 “#{}” 接受的是基本数据类型时可以用 value 或者其他任意名称来获取,比如#{value}。
${}:${} 为字符串替换,是通过拼接字符串的方式来拼接成 sql 的。使用 “${}” 拼接符号拼接 SQL ,会引起 SQL 注入,所以一般不建议使用 “${}”。在 SQL 配置中,有时候需要拼接 sql 语句(例如模糊查询时),用 “#{}” 是无法达到目的的。
2.1、#{}和${}的区别
在MyBatis 的映射配置文件中,动态传递参数有两种方式:#{} 占位符、${} 拼接符。
两者的区别如下:
- #{} 为参数占位符 ?,即sql 预编译;${} 为字符串替换,即 sql 拼接
- #{} 为动态解析 -> 预编译 -> 执行;${} 为动态解析 -> 编译 -> 执行
- #{} 的变量替换是在DBMS 中;${} 的变量替换是在 DBMS 外
- 变量替换后,#{} 对应的变量自动加上单引号 ' ';变量替换后,${} 对应的变量不会加上单引号 ' '
- #{} 能防止sql 注入;${} 不能防止sql 注入
两者使用示例:
# 示例#{}的使用,
# 定义语法
select * from t_user where uid=#{uid}
# 然后
select * from t_user where uid= ?
# 不管传入的数值为数字类型或者字符串类型,最后都会自动给加上单引号
# 假设传入参数为10或者你好的中文,最后结果为:
select * from t_user where uid= '1'
select * from t_user where uid= '你好'
# 示例${}的使用,假设传入参数为1
# 定义语法,如果最后结果需要有单引号,我们需要主动加上单引号:
select * from t_user where uid= '${uid}'
# 最终结果
select * from t_user where uid= '1'
2.2、关键字#{}自动给变量加单引号的问题
使用 #{} 占位符时,MyBatis 为了防止SQL注入会为变量值自动加单引号。
示例:
# 定义语句
select * from table_a where name=#{name}
# 假设变量name="abc",则实际执行的SQL语句为:
select * from table_a where name='abc'
正常情况下,加上单引号可以避免 sql 注入问题,但是在有些情况下加入单引号会导致 sql 语句直接报错,比如如果变量名是表名或者列名时。
示例:
create table if not exists #{tableName}
# 如果变量tableName="abc",则实际执行的SQL如下,该SQL将无法执行
create table if not exists 'abc'
# 此时我们可以使用${}来替代#{}:
create table if not exists ${tableName}
# 则实际执行SQL为
create table if not exists abc
在变量是表名或者列名时,我们可以使用 ${},在使用 ${} 时需注意传入的变量值一定需保证是可靠的。
3、resultType
resultType指定输出的结果类型,就是用来指定数据库返回的信息对应的 Java 的数据类型。该 java 数据类型可以是任意的数据类型,不一定是一个实体类。如果 resultType 指定的是一个实体类,mybatis 执行 sql 语句后,会调用指定数据类型的类的无参构造函数来创建对象,将指定的列值赋值给同名的类属性。
mybatis 中 resultType 可选类型有如下几种:
- java 的基础类型及其包装类 int(java.lang.Integer)、string(java.lang.String)、double(java.lang.Double)等。
- 实体类,自己定义的实体类。
- map类型,如果使用resultMap这里可以使用自定义map。
- 集合,即返回的时一个List集合,其中该集合的类型可以为1,2,3中提到的类型。
注意如果是集合情形,那应该是集合可以包含的类型,而不能是集合本身。使用 resultType 或 resultMap,但不能同时使用。
3.1、返回基本数据类型
如果是基本数据类型,则 resultType 的值可以是基本数据类型的类的全限定名称,或者也可以直接写别名即可。比如:java.lang.Integer 的别名是 int。
基本数据类型的类的别名映射关系如下:
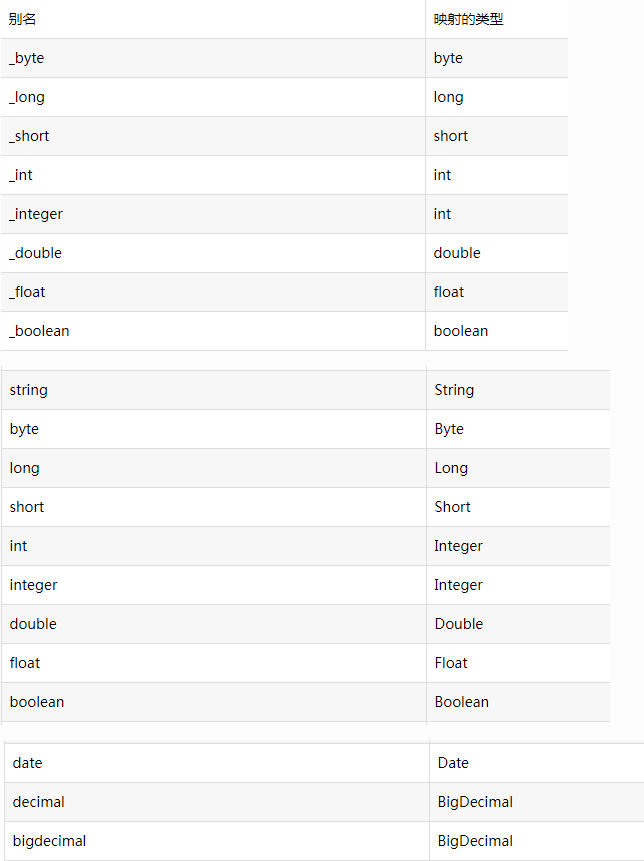
示例:
<mapper namespace="user"> <!-- 返回值为int,resultType可以写成int或者java.lang.Integer--> <select id="countUser" resultType="int"> select count(*) from user </select> </mapper>
3.2、返回一个 JavaBean
当返回一个 JavaBean 时,数据库中的列名需跟 JavaBean 的属性名一一对应,否则该属性将无法赋值成功。
比如根据某个字段获得数据库中的信息,把查询的结果信息封装成某个 JavaBean 类型的数据。
示例:
<mapper namespace="dao.StudentDao"> <select id="findStudentById" parameterType="int" resultType="entity.Student"> select * from student where id = #{id} </select> </mapper>
测试代码:
//mapper接口类 public interface StudentDao { public Student findStudentById(int id); } //测试代码 Student student = studentDao.findStudentById(2); System.out.println(student);
mybatis 执行 sql 语句后,会调用指定数据类型的类的无参构造函数来创建对象,将指定的列值赋值给同名的类属性,即自动将查询的结果映射成 JavaBean 中的属性。
3.2.2、自定义别名
当返回一个自定义的 JavaBean 对象时,我们可以在 mybatis 的配置文件中为该 JavaBean 定义一个别名,然后就可以在 resultType 中使用该别名了。
先在 mybatis 配置文件中定义别名:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> ... <typeAliases> <!--可以为多个类定义别名--> <typeAlias type="entity.Student" alias="myStu"></typeAlias> <!--或者也可以使用package来为该包中的所有类定义别名,类名就是别名(不区分大小写)--> <package name="entity"/> </typeAliases> ... </configuration>
使用 package 标签定义别名比较方便,但如果为多个包都定义了别名,而不同包中有相同类名,则可能在 sql 映射文件中使用别名可能会报错,因为 mybatis 不知道你这个别名指定的是哪个类。
定义别名后就可以在sql mapper 文件中使用了。可以使用 typeAlias 中指定的别名,如果是通过 package 标签定义的别名,则可以直接使用类名的全小写作为作为别名:
<mapper namespace="dao.StudentDao"> <select id="findStudentById" parameterType="int" resultType="myStu"> select * from student where id = #{id} </select> <select id="findStudentById" parameterType="int" resultType="student"> select * from student where id = #{id} </select> </mapper>
后面使用该 sql 跟使用普通 sql 一样。
3.3、返回 List 集合
有时候我们要查询的数据不止一条,比如:模糊查询,全表查询等,这时候返回的数据可能不止是一条数据,对于多数据的处理可以存放在List集合中。
返回 list 集合时,resultType 返回值类型是集合内元素的数据类型,而不是 list。
示例:
<mapper namespace="dao.StudentDao"> <select id="findStudentAll" resultType="entity.Student"> select * from Student </select> <select id="selectMultiStudent" resultType="entity.Student"> select * from Student where id = #{myId} or name = #{myName} </select> </mapper>
测试代码:
//Mapper接口类 public interface StudentDao { public List<Student> findStudentAll(); public List selectMultiStudent(@Param("myId") Integer id, @Param("myName") String name); } //测试代码 List list = studentDao.selectMultiStudent(1, "李四"); List list2 = studentDao.findStudentAll();
3.4、返回Map类型
MyBatis 还支持将查询的数据封装成Map。
如果查询的结果是一条,mybatis 会将查询出来的结果以数据库列名作为 key,列值作为 value 存入到 Map 中。
示例:
<mapper namespace="dao.StudentDao"> <select id="getStuAsMap" resultType="map"> select * from Student where id = #{id} </select> </mapper>
测试代码:
//mapper接口类: public interface StudentDao { public Map<String, Object> getStuAsMap(int id); } //测试代码: Map<String, Object> map = studentDao.getStuAsMap(1); System.out.println(map); //输出结果:{name=wen, id=1, age=12}
如果查询的结果是多条数据,我们也可以把查询的数据以{表中某一字段名, JavaBean}方式来封装成Map。
示例:
<mapper namespace="dao.StudentDao"> <!--注意 resultType 返回值类型,不再是 'map',而是 Map 的 value 对应的 JavaBean 类型 --> <select id="getAllEmpsAsMap" resultType="employee"> select * from t_employee </select> </mapper>
测试代码:
// mapper接口类: // 查询所有员工的信息,把数据库中的id字段作为key,对应的 value 封装成 Employee 对象。@MapKey 中的值表示用数据库中的哪个字段名作 key @MapKey("id") Map<Integer, Employee> getAllEmpsAsMap();
4、resultMap
当数据库的列名和类的属性名能一一对应时,查询返回的数据能正确赋值给对应类的属性。但是当查询的返回的数据中列名和类的属性名不同时,此时类无法被正确赋值,此时我们可以使用 resultMap 属性。使用 resultMap 可以将指定的列名映射到特定的 java 类的属性。
示例:
<mapper namespace="dao.StudentDao">
<resultMap id="studentMap" type="entity.Student"> <!--column指定的是数据库的列名,property指定的是对应的实体类的属性。也就是希望将column指定的列名赋值给该实体类的property指定的属性--> <!--主键列使用id标签--> <id column="id" property="myid"></id> <!--非主键列使用result标签--> <result column="name" property="myname"></result> <result column="age" property="myage"></result> </resultMap>
<select id="findStudentAll" resultMap="studentMap"> select * from Student </select> </mapper>
测试代码:
//mapper接口类: public interface StudentDao { public Student findStudentById(int id); } //测试代码: System.out.println(studentDao.findStudentAll()); //输出结果:[Student{id=1, name='wen', age=12}, Student{id=2, name='李四', age=14}]
resultType 和 resultMap 不要一起用,二选一。
使用 resultMap 可以将指定的列名映射到特定的 java 类的属性。或者是我们也可以简单地在 sql 语句中使用 as 来为返回结果起个别名,以便对应上类的属性名。
比如:
<mapper namespace="dao.StudentDao"> <select id="findStudentById" parameterType="int" resultType="myStu"> select id, name as myname, age as myage from student where id = #{id} </select> </mapper>
5、给sql映射文件传递参数
5.1、通过 @param() 传递命名参数
在 sql 映射文件中,如果需要给 sql 语句传递多个参数,我们可以定义参数为一个 java 类,除以之外,我们也可以通过 @param("参数名") 的形式来传递多个参数。
下面以 mapper代理开发模式使用为例:
sql 映射文件内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="dao.StudentDao"> <!--通过#{}来获取自定义参数名--> <select id="selectMultiStudent" resultType="entity.Student"> select * from Student where id = #{myId} or name = #{myName} </select> </mapper>
接口类:
package dao; import entity.Student; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param; import java.util.List; public interface StudentDao { //通过@Param命名参数来传递多个参数,并且给参数命名 public List selectMultiStudent(@Param("myId") Integer id, @Param("myName") String name); }
使用:
public class Test02 { @Test public void test01() throws IOException { String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); SqlSession session = factory.openSession(); StudentDao studentDao = session.getMapper(StudentDao.class); List list = studentDao.selectMultiStudent(1, "李四"); System.out.println(list); session.close(); } }
5.2、通过 map 集合传递多个参数
我们可以通过一个 map 集合来给 sql 语句传递多个参数,在 sql 映射中通过 #{key} 的形式来获取参数。
下面以 mapper代理开发模式使用为例。sql 映射文件内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="dao.StudentDao"> <select id="selectByMap" resultType="entity.Student"> select * from Student where id = #{myId} or name = #{myName} </select> </mapper>
接口类:
package dao; import entity.Student; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; public interface StudentDao { public List selectByMap(Map map); }
使用:
public class Test02 { @Test public void test01() throws IOException { String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); SqlSession session = factory.openSession(); StudentDao studentDao = session.getMapper(StudentDao.class); Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("myId", 1); map.put("myName", "李四"); List list = studentDao.selectByMap(map); System.out.println(list); session.close(); } }
6、动态SQL
动态 SQL 是 MyBatis 的强大特性之一。在实际应用开发过程中,我们往往需要写复杂的 SQL 语句,需要拼接,而拼接SQL语句又稍微不注意,由于引号,空格等缺失可能都会导致错误。Mybatis提供了动态SQL,也就是可以根据用户提供的参数,动态决定查询语句依赖的查询条件或SQL语句的内容。
常见的动态SQL标签有:
- if
- where
- foreach
- choose (when, otherwise)
6.1、if 标签
语法:
<if test="条件">SQL语句</test> <!-- 示例--> <if test="age != null"> age > #{age} </if>
当 test 里面的条件为 true 时,会将该标签里面包含的 SQL 语句拼接到最终生成的 SQL 语句中。
示例:
<mapper namespace="dao.StudentDao"> <select id="selectByIf" resultType="entity.Student"> select * from Student where <if test="name != null and name != ''"> name = #{name} </if>
<if test="age != null"> and age > #{age} </if> </select> </mapper>
测试代码:
//接口类 public interface StudentDao { public Student selectByIf(Student Student); } //测试使用 Student student = new Student(); student.setName("wen"); student.setAge(10); studentDao.selectByIf(student);
上面的 sql 映射文件的写法,当 if 的判断为 true 时,才会将 if 标签里面的 SQL 语句拼接到最终的 SQL 语句当中。
6.1.1、if 标签的存在问题
使用 if 标签会有个问题,例如上面的判断当中,当第一个条件不满足,而第二个条件满足时,或者是都不满足时,此时语法变成了:
select * from Student where and age > ? select * from Student where
上面的两个 SQL 语句将直接报错。
此时我们可以在 where 条件后面加一个永远为真的判断以此来解决该问题,如下:
<mapper namespace="dao.StudentDao"> <select id="selectByIf" resultType="entity.Student"> select * from Student where 1=1 <if test="name != null and name != ''"> and name = #{name} </if> <if test="age != null"> and age > #{age} </if> </select> </mapper>
或者是使用 <where> 标签来解决也行。
6.2、where 标签
为了避免 if 标签存在的问题,我们可以将 where 标签和 if 标签配合使用。
<where> 标签里面可以包含多个 if 标签,当这些 if 标签中有一个为 true 时,则 where 会自动往 SQL 语句中增加 where 关键字,并且会自动剔除掉 if 标签返回的多余的 and、or 等关键字。否则的话,where 关键字不会增加到 SQL 语句当中。这样就能完美解决 if 标签可能存在的问题。
语法:
<where> <if test="条件"> SQL语句 </if> <if test="条件"> SQL语句 </if> </where>
示例:
<mapper namespace="dao.StudentDao"> <select id="selectByIfAndWhere" resultType="entity.Student"> select * from Student <where> <if test="name != null and name != ''"> name = #{name} </if> <if test="age != null"> or age > #{age} </if> </where> </select> </mapper>
测试代码:
//接口类 public interface StudentDao { public List selectByIfAndWhere(Student student); } //测试使用: Student student = new Student(); student.setAge(13); studentDao.selectByIfAndWhere(student)
<where> 标签会自动判断是否需要补全 where 关键字,并且会自动剔除多余的 and、or 等 sql 关键字,通过 where 标签就可以正常使用 if 标签了。
6.3、foreach 标签
mybatis 的 foreach 标签经常用于遍历集合,构建 in 条件语句或者批量操作语句。
<foreach> 标签的属性主要有 item,index,collection,open,separator,close。
- collection:表示迭代集合的名称。必选
- 如果 collection 类型是一个List的时候,则 collection 的值为 list;如果是一个 array 数组的时候,collection 的值为 array;如果collection类型为map,则 collection 的值可以是该 map 的某个 key 值,foreach 将该 key 的 value 值作为遍历对象进行遍历
- item:表示集合中的每一个元素。必选
- index:该元素的索引。可选
- open:该语句开始时的字符。可选
- separator:每个元素之间的分隔符。可选
- close:该语句结束时的字符。可选
使用示例:
参数为 list 类型:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="dao.StudentDao"> <!--下面代码最终实际会生成SQL语句:select * from Student where id in (1,2...)--> <select id="selectByForeach" resultType="entity.Student"> select * from Student where id in <foreach collection="list" index="index" item="myid" open="(" close=")" separator=","> #{myid} </foreach> </select> </mapper>
<foreach> 标签包含的语句,如果 item 的值是一个对象的话,则应该取对象的属性值,例如 #{itemObj.name}
测试代码:
//接口类 public interface StudentDao { public List selectByForeach(List list); } //测试代码 List list = new ArrayList(); list.add(1); list.add(2); System.out.println( studentDao.selectByForeach(list) );
参数为 map 类型:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="dao.StudentDao"> <!--下面代码最终实际会生成SQL语句:select * from Student where name like ... and id in (1,2...) --> <select id="selectByForeach2" resultType="entity.Student"> select * from Student where name like "%"#{myname}"%" and id in <foreach collection="idlist" index="index" item="myid" open="(" close=")" separator=","> #{myid} </foreach> </select> </mapper>
参数为 map 类型时,collection 的值是选定的需要用来遍历的 value 值的 key,即上面会将 map 的 idlist 的值来进行 foreach 遍历。
测试代码:
//接口类 public interface StudentDao { public List selectByForeach2(Map map); } //测试代码 List list = new ArrayList(); list.add(1); list.add(2); list.add(3); Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("idlist", list); map.put("myname", "wen"); System.out.println(studentDao.selectByForeach2(map));
6.4、代码片段(复用sql代码)
如果有一段 sql 代码在多个地方都会出现,我们可以将该段代码独立为 sql 代码片段,这样就可以在其他地方直接引用该片段而不用重复书写。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="dao.StudentDao"> <!-- 定义代码片段 --> <sql id="mysql"> select id,name,email,age from student </sql> <!-- 下面使用代码片段 --> <select id="findStudentById" parameterType="int" resultType="myStu"> <include refid="mysql" /> </select> </mapper>