Spring认为所有的组件都应该放在Spring容器中,容器中的组件通过容器自动装配(DI)。控制反转是通过依赖注入实现的。所谓依赖注入指的是容器负责创建和维护对象之间的依赖关系,而不是通过对象本身负责自己的创建和解决自己的依赖。
依赖注入的主要目的是为了解耦,提现了一种“组合”的理念。而不是继承。
声明Bean的注解
- @Component组件:没有明确的角色。
- @Servcie:业务逻辑层使用
- @Repository:在数据访问层使用。
- @Controller:在展现成使用
注入Bean的注解,一般情况下通用。
- @Autowired:Spring提供的注解。
- @Inject:JSR-330提供的注解
- @ReSource:JSR-250提供的注解
@Configuration
- 导入jar组件
<dependency> <groupId>commons-logging</groupId> <artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId> <version>1.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>1.18.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency>
- 创建spring配置文件application.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <bean id="car" class="com.jdy.springannotation.bean.Car"> <property name="brand" value="五菱宏光"/> <property name="price" value="199999"/> </bean> </beans>
- 创建bean对象
@Setter @Getter @ToString public class Car { private String brand; private String price; }
- 测试
public class XML_Test { private ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = null; { context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml"); } @Test public void method_test01(){ for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) { System.out.println("BeanName = " + name); System.out.println(context.getBean(name)); } } }
-
创建配置类
/** * @Configuration:该注解表示该类是一个配置,该类功能和application,xml一样。 * @Bean:表示像IOC容器注册一个Bean,功能和application,xml里面的<bean>一样 */ @Configuration public class SpringAnnoConfig{ /** * 给容器中注册一个bean 类型为返回值类型,id默认是方法名字 * @return */ @Bean public Car car(){ Car car = new Car(); car.setBrand("MINI"); car.setPrice("100"); return car; } }
-
-
@Bean:相当于xml配置文件的<bean>标签。 @Bean所标注的方法的返回值相当于<bean>中的class属性值,方法名称相当于<bean>
测试
public class Test_00 { private AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = null; { context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringAnnoConfig.class); } @Test public void method_test01(){ for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) { System.out.println("BeanName = " + name); } } }
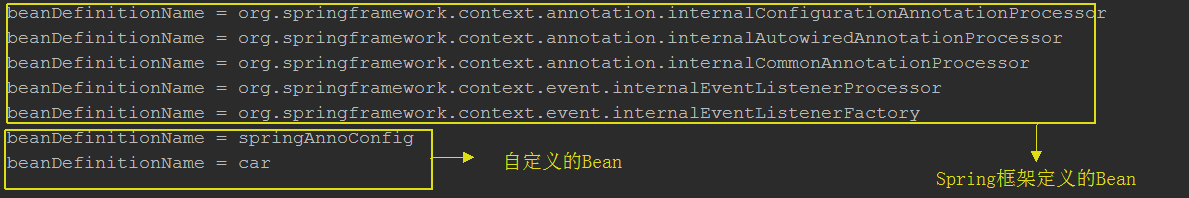
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:加载配置类。
二、组件扫描@ComponentScan
组件扫描的扫描规则很重。组件扫描过程中的过滤格则有两种
<!--扫描指定的组件添加到容器--> <context:include-filter type="" expression=""/> <!--扫描时过滤调指定的组件--> <context:exclude-filter type="" expression=""/>
- expression:表达式
- type:扫描规则
- annotation :按照注解的过滤
- assignable:按照类型过滤
- aspectJ:aspectJ扫描
- regex:按照正则表达式
- custom:自定义过滤规则
2.1、扫描规则xml方式
(1)、annotation
- 扫描时过滤指定组件
<!--包扫描--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.jdy.springannotation.controller, com.jdy.springannotation.service, com.jdy.springannotation.dao"> <!--按照注解类型的类型进行扫描排除 主要有@Controller @Service @Repository 这三个注解的任何一个都不扫描进Spring容器--> <context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Service"/> <context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/> <context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Repository"/> </context:component-scan>
以上三个过滤规则就是在扫描到含有@Controller 、@Service、 @Repository注解的组件不添加到IOC容器
<context:component-scan base-package="com.jdy.springannotation.controller, com.jdy.springannotation.service, com.jdy.springannotation.dao" use-default-filters="false"> <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Service"/> <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/> <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Repository"/> </context:component-scan>
以上三个过滤规则就是在扫描到含有@Controller 、@Service、 @Repository注解的组件添加到IOC容器,注意扫描指定包时关闭默认扫描规则use-default-filters="false"
@Test public void test02(){ String[] beanDefinitionNames = context.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for (String name : beanDefinitionNames) { System.out.println("name = " + name); } }
(2)、assignable按照类型排除
<context:component-scan base-package="com" > <!--type是给定类型 MyService类,以及其子类就不会被扫描进Spring容器--> <context:exclude-filter type="assignable" expression="com.service.Myservice"/> </context:component-scan>
(3)、custom自定义排除
- 自定义规则:(过滤含Service的)编写自定义的排除规则 实现TypeFilter接口,重写mach方法
- match方法返回值true:表示规则匹配成功 false:表示规则匹配失败
- match的两个参数:
- MetadataReader :当前正在扫描的类的信息
- MetadataReaderFactory :获取其他类(如超类和接口)的元数据读取器的工厂
- MetadataReader :当前正在扫描的类的信息
/** * @author Mr.jdy * @create 2020-07-05 22:05 * 自定义规则 */ public class MyRule implements TypeFilter { /** * @param metadataReader:读取到当前正在扫描的类的信息 * @param metadataReaderFactory:获取其他类(如超类和接口)的元数据读取器的工厂 * @return match方法返回值true:表示规则匹配成功 false:表示规则匹配失败 * @throws IOException */ @Override public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException { //获取当前正在扫描的类的类信息 ClassMetadata classMetadata = metadataReader.getClassMetadata(); //获取类名 String className = classMetadata.getClassName(); //获取当前类的注解信息 AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata(); //获取当前类型资源信息(路径信息) Resource resource = metadataReader.getResource(); // if(className.contains("Service")){ return true; } return false; } }
- 编写xml
<context:component-scan base-package="com">
<context:exclude-filter type="custom" expression="rule.MyRule"/>
</context:component-scan>
- 测试
@Test public void test02(){ ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml"); String[] beanDefinitionNames = ac.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for (String beanDefinitionName : beanDefinitionNames) { System.out.println("beanDefinitionName = " + beanDefinitionName); } }
2.2、扫描规则注解方式
(1)、开启组件扫描
@Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages="com") public class Config_01 { }
(2)、过滤指定组件
@ComponentScan(basePackages="com",excludeFilters ={ @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,value = {Controller.class}) } ) public class Config_01 { }
(3)、扫描指定的组件
@Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages="com",includeFilters ={ @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,value = {Controller.class}) },useDefaultFilters = false) public class MainConfig { }
(4)、自定义排除
@Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages="com.jdy",includeFilters ={ @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM,value = {MyRule.class}) },useDefaultFilters = false) public class MainConfig {}
三、Bean作用域@Scope
- singleton:单实例对象,创建IOC容器时就会创建单实例对象。
- prototype:多实例对象,并不会在创建IOC容器时就创建对象,是在调用获取对象的方法时,创建对象。
/**
* String SCOPE_SINGLETON = "singleton";
* singleton:单实例对象,创建IOC容器时就会创建单实例对象,
* String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = "prototype";
* prototype:多实例对象,并不会在创建IOC容器时就创建对象,是在调用获取对象的方法时,创建对象
*/
//@Scope(value = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON)
@Scope(value = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
@Bean(name = "person")
public Person person1(){
return new Person("jdy",18);
}
- 单实例对象,创建IOC容器时就会创建单实例对象
- 多实例对象,并不会在创建IOC容器时就创建对象,是在每次调用获取对象的方法时,创建对象
四、单例组件懒加载——@Lazy
- 单实例bean,默认在容器启动的时候创建对象;
- 懒加载:针对单实例bean,容器启动先不创建对象,第一次使用(获取)创建对象,并进行初始化。
@Scope(value = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON) @Lazy(value = true)//默认是true,开启懒加载 @Bean(name = "person") public Person person1(){ return new Person("jdy",18); }
xml配置方式
<bean id="car" class="com.jdy.bean.Car" scope="singleton" lazy-init="true"> <property name="brand" value="五菱宏光"/> <property name="price" value="199999"/> </bean>
Conditional:按照一定的条件进行判断,满足条件给容器注册bean,@Conditional注解放到类 上时,表示满足当前条件,这个类中的配置的所有bean注册才能生效(类中组件统一设置)。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD}) public @interface Conditional { Class<? extends Condition>[] value(); }
由Class<? extends Condition>[] value();可以看出需要编写自己定义的判断条件
需求场景,如果是windows运行环境,初始化bill,如果是linux环境初始化linus
5.1、编写自定义条件
public class LinuxCondition implements Condition { /** * @param context:判断条件,能使用的上下文(环境) * @param metadata:注释信息 * @return */ @Override public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { //1、能获取当前IOC使用的beanfactory ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory(); ClassLoader classLoader = context.getClassLoader(); //能获取当前环境信息 Environment environment = context.getEnvironment(); //能获取bean定义的注册类 BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = context.getRegistry(); //registry:可以判断容器中bean的注册情况,也可以给容器中注册bean,移除、获取。。 String property = environment.getProperty("os.name"); if(property.toLowerCase().contains("linux")){ return true; } return false; } }
public class LinuxCondition implements Condition { /** * @param context:判断条件,能使用的上下文(环境) * @param metadata:注释信息 * @return */ @Override public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { //1、能获取当前IOC使用的beanfactory ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory(); ClassLoader classLoader = context.getClassLoader(); //能获取当前环境信息 Environment environment = context.getEnvironment(); //能获取bean定义的注册类 BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = context.getRegistry(); //registry:可以判断容器中bean的注册情况,也可以给容器中注册bean,移除、获取。。 String property = environment.getProperty("os.name"); if(property.toLowerCase().contains("linux")){ return true; } return false; } }
5.2、配置类
@Configuration public class MyConfig3 { @Bean(name = "bill") @Conditional({WindowsCondition.class}) public Person person01(){ Person person = new Person(); person.setName("bill"); return person; } @Conditional({ LinuxCondition.class}) @Bean(name = "linus") public Person person02(){ Person person = new Person(); person.setName("linus"); return person; } }
5.3、测试
@Test public void test04(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfig3.class); Person bean = context.getBean(Person.class); System.out.println("bean = " + bean); //获取环境变量的值 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = context.getEnvironment(); //获取操作系统 String property = environment.getProperty("os.name"); System.out.println("property = " + property); }
六、快速导入组件@Import
给容器中注册组件的方法:
-
-
包扫描+组件标注注解@Service/@Controller/@Component/@Repository.
-
使用@Bean,导入第三方包里面的组件
-
使用@Import,导入一个简单的组件每次都使用创建对象+@Bean注解,比较麻烦,所以Spring提供了@Import注解快速导入一个组件。
-
@Import(要导入到容器中的组件),容器中就会自动注册这个组件,id默认是全类名
-
ImportSelector:返回需要导入组件的全类名数组。
-
ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar:手动注册bean到容器中。
-
-
使用Spring提供的FactoryBean(工厂Bean):
-
默认获取到的工厂bean调用getObject创建的对象。
-
要获取工厂bean本身,需要在id前面加&。
-
-
@Bean(name = "linus") public Person person02(){return new Person(); }
6.3、@Import快速给容器中导入组件
(1)、@Import快速导入组件
@Configuration //快速导入的组件,id默认是全类名 @Import(value = {Student.class,Person.class,Car.class}) public class MyConfig3 { }
//自定义逻辑返回需要导入的组件 public class MySelect implements ImportSelector { /** * @param importingClassMetadata:当前标注@Import注解的类的所有注解信息。 * @return 返回值就是导入到容器的组件全类名 */ @Override public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) { //注意Car Dog类要用@Repository注解修饰,否则报错 return new String[]{"com.jdy.bean.Car","com.jdy.bean.Dog"}; } }
- 配置类
@Configuration @Import({MySelect.class}) public class MyConfig4 { }
(3)、ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
-
自定义BeanDefinitionRegistrar
public class MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar { /** * * @param importingClassMetadata:当前类注解信息 * @param registry:BeanDefinition注册类 * 把所有需要添加到容器中的bean通过 * BeanDefinitionRegistrar.registerBeanDefinition方法手动注册 * */ @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { //判断IOC容器中是否有 bean的id 时dog 的bean //指定Bean的定义信息 boolean student = registry.containsBeanDefinition("student"); if(!student){ //shu RootBeanDefinition rootBeanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(Student.class); registry.registerBeanDefinition("student",rootBeanDefinition); } } }
- 配置类
@Configuration @Import({MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class}) public class MyConfig5 { }
/** * @author Mr.jdy * @create 2020-07-09 22:25 */ public class AnimalFactory implements FactoryBean<Dog> { /** * 返回Bean对象,这个对象会添加到IOC容器中 * @return * @throws Exception */ @Override public Dog getObject() throws Exception { return new Dog(); } @Override public Class<?> getObjectType() { return Dog.class; } /** * 返回值true:单实例对象在IOC容器质保留一份;false:多实例 * @return */ @Override public boolean isSingleton() { return true; } }
- 主配置类
@Configuration public class MyConfig6 { @Bean public AnimalFactory getAnimalFactory(){ return new AnimalFactory(); } }
- 测试类
public void test07(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfig6.class); for (String beanDefinitionName : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) { System.out.println(beanDefinitionName); } //animalFactory实际返回是getObject方法的返回值 Object animalFactory = context.getBean("getAnimalFactory"); //加上&前缀就能回去工厂bean本身 Object animalFactory = context.getBean("&getAnimalFactory"); System.out.println("animalFactory = " + animalFactory); }