1.python库对应版本
其中collections是python自带的模块.
数据预处理
将诗句存放在列表里面,便于使用numpy进行下一步操作
poems_file ='poems.txt' poems = [] # 诗集 with open(poems_file, "r", encoding='utf-8') as f: for line in f: try: title, content = line.strip().split(':') content = content.replace(' ','') #避免诗词中存在多余字符 if '_' in content or '(' in content or '(' in content or '《' in content or '[' in content: continue if len(content) < 5 or len(content) > 79: continue content = '[' + content + ']' poems.append(content) except Exception as e: pass poems = sorted(poems,key=lambda line: len(line)) # 按诗的字数排序 for i in range(0,200): print(poems[i])

将诗句拆分成单个字,然后统计词频
# 词频 all_words = [] for poem in poems: all_words += [word for word in poem] counter = collections.Counter(all_words) count_pairs = sorted(counter.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1]) words, _ = zip(*count_pairs) # 取前多少个常用字 words = words[:len(words)] + (' ',) L = len(words) word_int_map = dict(zip(words, range(L))) # 把词和词出现的次数存成字典 poems_vector = [list(map(lambda word: word_int_map.get(word, L), poem)) for poem in poem] # 把每首诗的代表数字存成列表 # 输出词频列表 print(word_int_map)

生成词向量
# 每个字映射为一个数字ID word_num_map = dict(zip(words, range(len(words)))) # 把诗转换为向量形式 to_num = lambda word: word_num_map.get(word, len(words)) poems_vector = [ list(map(to_num, poem)) for poem in poems] for i in range(0,5): print(poems_vector[i])

生成特征值数组,并且预测目标值数组
batch_size = 1 n_chunk = len(poems_vector) // batch_size # 把诗词批量处理的数目 x_batches = [] #输入 y_batches = [] #标签 for i in range(n_chunk): #定义批量处理的两个索引,开始索引start_index和结束索引end_index start_index = i * batch_size end_index = start_index + batch_size #截取训练集样本 batches = poems_vector[start_index:end_index] length = max(map(len,batches)) #获取最长诗词长度 # 输入数据 按每块数据中诗句最大长度初始化数组,缺失数据补全 xdata = np.full((batch_size,length), word_num_map[' '], np.int32) #把x_data全都替换成诗词的数字代表数组 for row in range(batch_size): xdata[row,:len(batches[row])] = batches[row] # 标签数据 根据上一个字符预测下一个字符 所以这里y_batch数据应为x_batch数据向后移一位 ydata = np.copy(xdata) ydata[:,:-1] = xdata[:,1:] x_batches.append(xdata) y_batches.append(ydata) print(x_batches[0]) print(y_batches[0])
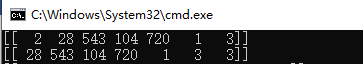
预测结果正确。
定义RNN-LSTM模型
#---------------------------------------------RNN训练模型--------------------------------------------# #batch_size代表每次训练时使用的诗词行数 input_data = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.int32, [batch_size, None]) #特征值,输入的数据长度不一致时,使用none自适应 output_targets = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.int32, [batch_size, None]) #目标值,输出为预测的某个字符,因此数据长度会不一致,也使用none自适应 # 定义RNN #模型是LSTM,rnn_size代表模型中的隐层数量,num_layers是神经网络深度 def neural_network(model='lstm', rnn_size=128, num_layers=2): #设置默认的LSTM模型单元 cell_fun = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell #初始化cell cell = cell_fun(rnn_size, state_is_tuple=True) #多层cell作为后一层cell的输出 cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell([cell] * num_layers, state_is_tuple=True) #生成初始状态,默认为0 initial_state = cell.zero_state(batch_size, tf.float32) with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope('rnnlm'): softmax_w = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("softmax_w", [rnn_size, len(words)+1]) softmax_b = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("softmax_b", [len(words)+1]) with tf.device("/cpu:0"): #cpu选择为embedding embedding = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("embedding", [len(words)+1, rnn_size]) # 根据inputs序列中每一个字符对应索引 在embedding中寻找对应向量,即字符转为连续向量:[字]==>[1]==>[0,1,0] inputs = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding, input_data) #因为句子长短不一致,所以使用dynamic_rnn自动进行时间维度的推进,并且可以使用不同长度的时间维度 outputs, last_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, inputs, initial_state=initial_state, scope='rnnlm') output = tf.reshape(outputs,[-1, rnn_size])#使用tf.reshape将outputs转换成一维向量 logits = tf.matmul(output, softmax_w) + softmax_b#使用tf_matmual将输出的output乘以权重softmax_w,再加上偏置softmax_b得到logits #softmax计算概率 probs = tf.nn.softmax(logits) return logits, last_state, probs, cell, initial_state
- 创建csv文件,收集训练过程中的数据集
#创建csv,将epoch,step,train_loss导入 f = open('loss.csv','w',encoding='UTF-8',newline='') #创建写入对象 csv_writer = csv.writer(f) #创建列表头 csv_writer.writerow(["epoch","step","train_loss"])
定义训练模型
#训练 def train_neural_network(): logits, last_state, _, _, _ = neural_network() targets = tf.reshape(output_targets, [-1])#一维向量 labels = tf.one_hot(tf.reshape(output_targets, [-1]), depth=(len(words) + 1)) #损失数 loss = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=labels, logits=logits)#交叉熵函数求损失数 cost = tf.reduce_mean(loss) #准确率 #accuracy = tf.equal(tf.argmax(labels, 1), tf.argmax(logits, 1)) #accuracy = tf.cast(accuracy, tf.float32) #accuracy_mean = tf.reduce_mean(accuracy) #使用gradient clippling的方式来防止梯度爆炸,learning_rate表示学习速率 learning_rate = tf.Variable(0.002, trainable=False) tvars = tf.compat.v1.trainable_variables() #使用tf.clip_by_global_norm设置tvars的梯度的最大范数为 grads, _ = tf.clip_by_global_norm(tf.gradients(cost, tvars), 5) #定义优化器 optimizer = tf.compat.v1.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate) #创建训练操作train_op,使用optimizer.apply_gradients将前面clip过的梯度应用到所有可训练的tvars上 train_op = optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, tvars)) #创建训练管理器 with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer()) saver = tf.compat.v1.train.Saver(tf.compat.v1.global_variables()) #开始训练 for epoch in range(10): step = 0 for batche in range(step_chunk): sess.run(train_op,feed_dict={input_data: x_batches[step], output_targets: y_batches[step]}) train_loss, _ = sess.run([cost, last_state], feed_dict={input_data: x_batches[step], output_targets: y_batches[step]}) #train_accuracy = sess.run(accuracy_mean, feed_dict={input_data: x_batches[step], output_targets: y_batches[step]}) csv_writer.writerow([epoch,step,train_loss])#数据写入csv文件 print("epoch:%3d step:%3d train_loss:%.6f" % (epoch,step,train_loss)) step += 1 if epoch % 10 == 0: saver.save(sess, 'save/poems.save') #模型存储到save目录下
样本的训练我是放在云服务器上训练,一共好像是6w还是8w数据,一共训练了大概3-4个小时。
不搭建FTP,即可实现云端文件的上传和下载,可以看我的另外一篇博客
随机写诗
随机生成特征数,将特征值转换成字,得到第一个字,再将该字转换成数字,预测下一个数,预测标准是基于词频,再将这个数转换成第二个字,以此类推即可。
#-----------随机五言和七言古诗生成------------# _, last_state, probs, cell, initial_state = neural_network()#声明对象 def gen_poem(poem_len,rows): def to_word(weights): t = np.cumsum(weights) s = np.sum(weights) sample = int(np.searchsorted(t, np.random.rand(1)*s)) while sample > 2000:#过滤生僻字 sample = int(np.searchsorted(t, np.random.rand(1)*s)) return words[sample] with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables()) saver.restore(sess, 'save/poems.save') #读取save目录下的模型 poem = '' i = 0 for i in range(rows): islen = True while islen: state_ = sess.run(cell.zero_state(1, tf.float32)) x = np.array([list(map(word_num_map.get, '['))]) [probs_, state_] = sess.run([probs, last_state], feed_dict={input_data: x, initial_state: state_}) sentence = '' while len(sentence) < poem_len: word = to_word(probs_) #将数字转换成字 if word != ',' and word != '。'and word != '['and word != ']'and word != '》'and word != '《'and word != '('and word != ')'and word != ' ': sentence += word #将字组合成句子 x = np.zeros((1,1)) x[0,0] = word_num_map[word] else: x = np.array([list(map(word_num_map.get, '['))])#词向量 #根据词向量,得到预测值 [probs_, state_] = sess.run([probs, last_state], feed_dict={input_data: x, initial_state: state_}) poem += sentence#将句子组合成诗 islen = False #i从0开始,生成第一句诗时(即五个字),i=4,此时添加逗号。 #生成第一句诗后,再生成一个句子时,poem的长度是11(10个字,1个逗号),此时i=9 ##abcde,i=4 fghij,i=9 if i % 2 == 0: poem += ',' else: poem += '。' i += 1 return poem
写藏头诗
根据已有的字去推测下一个字。
#-------------------------------生成藏头诗---------------------------------# def gen_poem_with_head(poem_len,heads): #利用数据生成字 def to_word(weights): t = np.cumsum(weights) s = np.sum(weights) sample = int(np.searchsorted(t, np.random.rand(1)*s))#随机选择 while sample > 2000:#过滤生僻字 sample = int(np.searchsorted(t, np.random.rand(1)*s)) return words[sample] with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer()) saver = tf.compat.v1.train.Saver(tf.compat.v1.global_variables()) saver.restore(sess, 'save/poems.save') #读取save目录下的模型 poem = '' i = 0 for head in heads: islen = True while islen: state_ = sess.run(cell.zero_state(1, tf.float32)) x = np.array([list(map(word_num_map.get, head))]) #x = np.array([list(map(word_num_map.get, '['))]) [probs_, state_] = sess.run([probs, last_state], feed_dict={input_data: x, initial_state: state_}) sentence = head #在所有字中随机选择数字 x = np.zeros((1,1)) x[0,0] = word_num_map[sentence] [probs_, state_] = sess.run([probs, last_state], feed_dict={input_data: x, initial_state: state_}) while len(sentence) < poem_len: word = to_word(probs_)#将数字转换成字 if word != ',' and word != '。'and word != '['and word != ']'and word != '》'and word != '《'and word != '('and word != ')'and word != ' ': sentence += word#将字组合成句子 x = np.zeros((1,1)) x[0,0] = word_num_map[word] #将字转换成词向量,预测下一个字 else: x = np.array([list(map(word_num_map.get, '['))])#词向量列表 #根据词向量,得到预测值 [probs_, state_] = sess.run([probs, last_state], feed_dict={input_data: x, initial_state: state_}) poem += sentence#将句子组合成诗 islen = False if i % 2 == 0: poem += ',' else: poem += '。' i += 1 return poem
完整代码如下:
poem_train.py
# coding=utf-8 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- #from __future__ import print_function import collections import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import csv #-------------------------------数据预处理---------------------------# poems_file ='poems.txt' #诗集 # 诗集 poems = [] with open(poems_file, "r", encoding='utf-8',) as f: for line in f: try: title, content = line.strip().split(':') content = content.replace(' ','') if '_' in content or '(' in content or '(' in content or '《' in content or '[' in content: continue if len(content) < 5 or len(content) > 79: continue content = '[' + content + ']' poems.append(content) except Exception as e: pass # 按诗的字数排序 print('训练样本:五言律诗和七言律诗') poems = sorted(poems,key=lambda line: len(line)) print('唐诗总数: ', len(poems)) # 统计每个字出现次数 all_words = [] for poem in poems: all_words += [word for word in poem] counter = collections.Counter(all_words) count_pairs = sorted(counter.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1]) words, _ = zip(*count_pairs) # 取前多少个常用字 words = words[:len(words)] + (' ',) # 每个字映射为一个数字ID word_num_map = dict(zip(words, range(len(words)))) # 把诗转换为向量形式 to_num = lambda word: word_num_map.get(word, len(words)) poems_vector = [ list(map(to_num, poem)) for poem in poems] # 每次取64首诗进行训练 batch_size = 64 step_chunk = len(poems_vector) // batch_size #把诗词批量处理的数目把诗词批量处理的数目 x_batches = [] #输入 y_batches = [] #预测 for i in range(step_chunk): #设置批量处理的两个索引 start_index = i * batch_size end_index = start_index + batch_size #截取训练集样本 batches = poems_vector[start_index:end_index] #获取最长诗词长度 length = max(map(len,batches)) # 输入数据 按每块数据中诗句最大长度初始化数组,缺失数据补全 xdata = np.full((batch_size,length), word_num_map[' '], np.int32) for row in range(batch_size): xdata[row,:len(batches[row])] = batches[row] # 标签数据 根据上一个字符预测下一个字符 所以这里y_batch数据应为x_batch数据向后移一位 ydata = np.copy(xdata) ydata[:,:-1] = xdata[:,1:] x_batches.append(xdata)#特征值数组 y_batches.append(ydata)#目标值数组 #----------------LSTM模型---------------# input_data = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.int32, [batch_size, None]) #特征值,输入的数据长度不一致时,使用none自适应 output_targets = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.int32, [batch_size, None]) #目标值,输出为预测的某个字符,因此数据长度会不一致,也使用none自适应 # 定义RNN模型为LSTM,rnn_size代表模型中的隐层数量,num_layers是神经网络深度 def neural_network(model='lstm', rnn_size=128, num_layers=2): cell_fun = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell#设置默认的LSTM模型单元 cell = cell_fun(rnn_size, state_is_tuple=True)#初始化cell #使用tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell创建2层lstm模型,作为后一层cell的输出,模型数量是[cell]*num_layers,得到的cell是RNNcell的子类 cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell([cell] * num_layers, state_is_tuple=True) #初始化cell,得到全0的初始状态 initial_state = cell.zero_state(batch_size, tf.float32) with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope('rnn'): softmax_w = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("softmax_w", [rnn_size, len(words)+1])#权重 softmax_b = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("softmax_b", [len(words)+1])#偏置 with tf.device("/cpu:0"):# 将计算限定在CPU中 embedding = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("embedding", [len(words)+1, rnn_size]) # 根据inputs序列中每一个字符对应索引 在embedding中寻找对应向量 inputs = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding, input_data) #使用tf.nn.dynamic_rnn调用多次call函数,outputs代表代表所有time_step的输出集合,last_state是最后一步的隐状态 #因为句子长短不一致,所以使用dynamic_rnn自动进行时间维度的推进,并且可以使用不同长度的时间维度 outputs, last_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, inputs, initial_state=initial_state, scope='rnn') #使用tf.reshape将outputs转换成一维向量 output = tf.reshape(outputs,[-1, rnn_size]) #使用tf_matmual将输出的output乘以权重softmax_w,再加上偏置softmax_b得到网络最后的输出logits logits = tf.matmul(output, softmax_w) + softmax_b probs = tf.nn.softmax(logits)#softmax计算概率 return logits, last_state, probs, cell, initial_state #创建csv,将epoch,step,train_loss导入 f = open('loss.csv','w',encoding='UTF-8',newline='') #创建写入对象 csv_writer = csv.writer(f) #创建列表头 csv_writer.writerow(["epoch","step","train_loss"]) #训练 def train_neural_network(): logits, last_state, _, _, _ = neural_network() targets = tf.reshape(output_targets, [-1])#一维向量 labels = tf.one_hot(tf.reshape(output_targets, [-1]), depth=(len(words) + 1)) #损失数 loss = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=labels, logits=logits)#交叉熵函数求损失数 cost = tf.reduce_mean(loss) #准确率 #accuracy = tf.equal(tf.argmax(labels, 1), tf.argmax(logits, 1)) #accuracy = tf.cast(accuracy, tf.float32) #accuracy_mean = tf.reduce_mean(accuracy) #使用gradient clippling的方式来防止梯度爆炸,learning_rate表示学习速率 learning_rate = tf.Variable(0.002, trainable=False) tvars = tf.compat.v1.trainable_variables() #使用tf.clip_by_global_norm设置tvars的梯度的最大范数为 grads, _ = tf.clip_by_global_norm(tf.gradients(cost, tvars), 5) #定义优化器 optimizer = tf.compat.v1.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate) #创建训练操作train_op,使用optimizer.apply_gradients将前面clip过的梯度应用到所有可训练的tvars上 train_op = optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, tvars)) #创建训练管理器 with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer()) saver = tf.compat.v1.train.Saver(tf.compat.v1.global_variables()) #开始训练 for epoch in range(10): step = 0 for batche in range(step_chunk): sess.run(train_op,feed_dict={input_data: x_batches[step], output_targets: y_batches[step]}) train_loss, _ = sess.run([cost, last_state], feed_dict={input_data: x_batches[step], output_targets: y_batches[step]}) #train_accuracy = sess.run(accuracy_mean, feed_dict={input_data: x_batches[step], output_targets: y_batches[step]}) csv_writer.writerow([epoch,step,train_loss])#数据写入csv文件 print("epoch:%3d step:%3d train_loss:%.6f" % (epoch,step,train_loss)) step += 1 if epoch % 10 == 0: saver.save(sess, 'save/poems.save') #模型存储到save目录下 print("--训练开始--") train_neural_network() print("--训练结束--")
poem_pro.py
# coding=utf-8 import collections import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf #------数据预处理----# poems_file ='poems.txt' poems = [] # 诗集 with open(poems_file, "r", encoding='utf-8') as f: for line in f: try: title, content = line.strip().split(':') content = content.replace(' ','') #避免诗词中存在多余字符 if '_' in content or '(' in content or '(' in content or '《' in content or '[' in content: continue if len(content) < 5 or len(content) > 79: continue content = '[' + content + ']' poems.append(content) except Exception as e: pass poems = sorted(poems,key=lambda line: len(line)) # 按诗的字数排序 ''' for i in range(0,200): print(poems[i]) ''' # 词频 all_words = [] for poem in poems: all_words += [word for word in poem] counter = collections.Counter(all_words) count_pairs = sorted(counter.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1]) words, _ = zip(*count_pairs) # 取前多少个常用字 words = words[:len(words)] + (' ',) L = len(words) word_int_map = dict(zip(words, range(L))) # 把词和词出现的次数存成字典 poems_vector = [list(map(lambda word: word_int_map.get(word, L), poem)) for poem in poem] # 把每首诗的代表数字存成列表 # 输出词频列表 #print(word_int_map) # 每个字映射为一个数字ID word_num_map = dict(zip(words, range(len(words)))) # 把诗转换为向量形式 to_num = lambda word: word_num_map.get(word, len(words)) poems_vector = [ list(map(to_num, poem)) for poem in poems] ''' for i in range(0,5): print(poems_vector[i]) ''' batch_size = 1 n_chunk = len(poems_vector) // batch_size # 把诗词批量处理的数目 x_batches = [] #输入 y_batches = [] #标签 for i in range(n_chunk): #定义批量处理的两个索引,开始索引start_index和结束索引end_index start_index = i * batch_size end_index = start_index + batch_size #截取训练集样本 batches = poems_vector[start_index:end_index] length = max(map(len,batches)) #获取最长诗词长度 # 输入数据 按每块数据中诗句最大长度初始化数组,缺失数据补全 xdata = np.full((batch_size,length), word_num_map[' '], np.int32) #把x_data全都替换成诗词的数字代表数组 for row in range(batch_size): xdata[row,:len(batches[row])] = batches[row] # 标签数据 根据上一个字符预测下一个字符 所以这里y_batch数据应为x_batch数据向后移一位 ydata = np.copy(xdata) ydata[:,:-1] = xdata[:,1:] x_batches.append(xdata) y_batches.append(ydata) #print(x_batches[0]) #print(y_batches[0]) #---------------------------------------------RNN训练模型--------------------------------------------# #batch_size代表每次训练时使用的诗词行数 input_data = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.int32, [batch_size, None]) #特征值,输入的数据长度不一致时,使用none自适应 output_targets = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.int32, [batch_size, None]) #目标值,输出为预测的某个字符,因此数据长度会不一致,也使用none自适应 # 定义RNN #模型是LSTM,rnn_size代表模型中的隐层数量,num_layers是神经网络深度 def neural_network(model='lstm', rnn_size=128, num_layers=2): #设置默认的LSTM模型单元 cell_fun = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell #初始化cell cell = cell_fun(rnn_size, state_is_tuple=True) #多层cell作为后一层cell的输出 cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell([cell] * num_layers, state_is_tuple=True) #生成初始状态,默认为0 initial_state = cell.zero_state(batch_size, tf.float32) with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope('rnnlm'): softmax_w = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("softmax_w", [rnn_size, len(words)+1]) softmax_b = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("softmax_b", [len(words)+1]) with tf.device("/cpu:0"): #cpu选择为embedding embedding = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("embedding", [len(words)+1, rnn_size]) # 根据inputs序列中每一个字符对应索引 在embedding中寻找对应向量,即字符转为连续向量:[字]==>[1]==>[0,1,0] inputs = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding, input_data) #因为句子长短不一致,所以使用dynamic_rnn自动进行时间维度的推进,并且可以使用不同长度的时间维度 outputs, last_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, inputs, initial_state=initial_state, scope='rnnlm') output = tf.reshape(outputs,[-1, rnn_size])#使用tf.reshape将outputs转换成一维向量 logits = tf.matmul(output, softmax_w) + softmax_b#使用tf_matmual将输出的output乘以权重softmax_w,再加上偏置softmax_b得到logits #softmax计算概率 probs = tf.nn.softmax(logits) return logits, last_state, probs, cell, initial_state #-----------随机五言和七言古诗生成------------# _, last_state, probs, cell, initial_state = neural_network()#声明对象 def gen_poem(poem_len,rows): def to_word(weights): t = np.cumsum(weights) s = np.sum(weights) sample = int(np.searchsorted(t, np.random.rand(1)*s)) while sample > 2000:#过滤生僻字 sample = int(np.searchsorted(t, np.random.rand(1)*s)) return words[sample] with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables()) saver.restore(sess, 'save/poems.save') #读取save目录下的模型 poem = '' i = 0 for i in range(rows): islen = True while islen: state_ = sess.run(cell.zero_state(1, tf.float32)) x = np.array([list(map(word_num_map.get, '['))]) [probs_, state_] = sess.run([probs, last_state], feed_dict={input_data: x, initial_state: state_}) sentence = '' while len(sentence) < poem_len: word = to_word(probs_) #将数字转换成字 if word != ',' and word != '。'and word != '['and word != ']'and word != '》'and word != '《'and word != '('and word != ')'and word != ' ': sentence += word #将字组合成句子 x = np.zeros((1,1)) x[0,0] = word_num_map[word] else: x = np.array([list(map(word_num_map.get, '['))])#词向量 #根据词向量,得到预测值 [probs_, state_] = sess.run([probs, last_state], feed_dict={input_data: x, initial_state: state_}) poem += sentence#将句子组合成诗 islen = False #i从0开始,生成第一句诗时(即五个字),i=4,此时添加逗号。 #生成第一句诗后,再生成一个句子时,poem的长度是11(10个字,1个逗号),此时i=9 ##abcde,i=4 fghij,i=9 if i % 2 == 0: poem += ',' else: poem += '。' i += 1 return poem #-------------------------------生成藏头诗---------------------------------# def gen_poem_with_head(poem_len,heads): #利用数据生成字 def to_word(weights): t = np.cumsum(weights) s = np.sum(weights) sample = int(np.searchsorted(t, np.random.rand(1)*s))#随机选择 while sample > 2000:#过滤生僻字 sample = int(np.searchsorted(t, np.random.rand(1)*s)) return words[sample] with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer()) saver = tf.compat.v1.train.Saver(tf.compat.v1.global_variables()) saver.restore(sess, 'save/poems.save') #读取save目录下的模型 poem = '' i = 0 for head in heads: islen = True while islen: state_ = sess.run(cell.zero_state(1, tf.float32)) x = np.array([list(map(word_num_map.get, head))]) #x = np.array([list(map(word_num_map.get, '['))]) [probs_, state_] = sess.run([probs, last_state], feed_dict={input_data: x, initial_state: state_}) sentence = head #在所有字中随机选择数字 x = np.zeros((1,1)) x[0,0] = word_num_map[sentence] [probs_, state_] = sess.run([probs, last_state], feed_dict={input_data: x, initial_state: state_}) while len(sentence) < poem_len: word = to_word(probs_)#将数字转换成字 if word != ',' and word != '。'and word != '['and word != ']'and word != '》'and word != '《'and word != '('and word != ')'and word != ' ': sentence += word#将字组合成句子 x = np.zeros((1,1)) x[0,0] = word_num_map[word] #将字转换成词向量,预测下一个字 else: x = np.array([list(map(word_num_map.get, '['))])#词向量列表 #根据词向量,得到预测值 [probs_, state_] = sess.run([probs, last_state], feed_dict={input_data: x, initial_state: state_}) poem += sentence#将句子组合成诗 islen = False if i % 2 == 0: poem += ',' else: poem += '。' i += 1 return poem print('开始') print('五言诗') print(gen_poem(5,4)) print('七言诗') print(gen_poem(7,4)) print('五言藏头诗') print(gen_poem_with_head(5,'春夏秋冬')) print('七言藏头诗') print(gen_poem_with_head(7,'春夏秋冬')) print('结束')
生成效果:
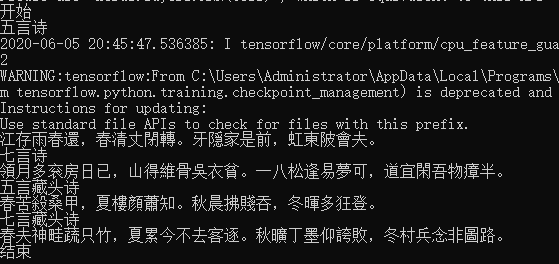
古诗可以生成。
本人猜测不押韵的原因是因为数据集样本中的古诗不是同一类型。在我读高中的时候,隐约记得,古诗的流派有很多种,比如有田园诗派,婉约派,山水诗,边塞诗等等。
另外藏头诗的效果也不太好,有时候藏头诗是不能生成的。本人猜测原因可能有以下两点:
1.训练集中可能没有出现过这几个字。
2.选取的高频字中,没有这几个字。
预测损失数
打开csv文件,然后使用数据选项卡中的预测工作表。
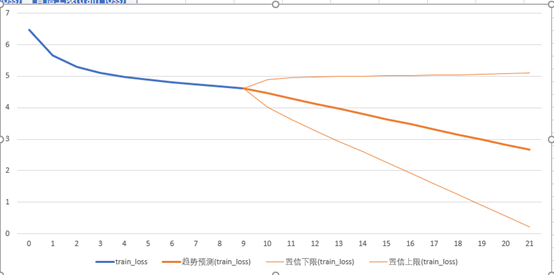
中间加粗的橙色线条即是我们的预测数据,可以看出损失数在不断降低。
左下和右上的线条组成的区间叫做误差区间。
参考书籍:
21个项目玩转深度学习。
tensorflow实战。
深度学习之tensorflow入门原理与进阶实战。
参考博客: