概述
前文「JDK源码分析-HashMap(1)」分析了 HashMap 主要方法的实现原理(其他问题以后分析),本文分析下 LinkedHashMap。
先看一下 LinkedHashMap 的类继承结构图:
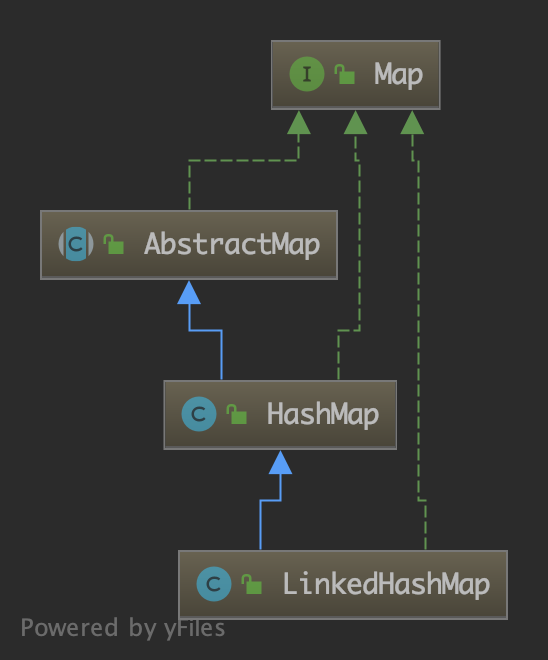
可以看到 LinkedHashMap 继承了 HashMap。
我们知道 HashMap 是无序的,即迭代器的顺序与插入顺序没什么关系。而 LinkedHashMap 在 HashMap 的基础上增加了顺序:分别为「插入顺序」和「访问顺序」。即遍历 LinkedHashMap 时,可以保持与插入顺序一致的顺序;或者与访问顺序一致的顺序。
LinkedHashMap 内部如何实现这两种顺序的呢?它是通过一个双链表来维持的。因此可以将 LinkedHashMap 理解为「双链表 + 散列表」,或者“有序的散列表”。
代码分析
节点类 Entry
LinkedHashMap 内部有一个嵌套类 Entry,它继承自 HashMap 中的 Node 类,如下:
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> { Entry<K,V> before, after; Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { super(hash, key, value, next); } }
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; V value; Node<K,V> next; Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { this.hash = hash; this.key = key; this.value = value; this.next = next; } // ... }
该 Entry 类就是 LinkedHashMap 中的节点类。可以看到,它在 Node 类的基础上又增加了 before 和 after 两个变量,它们保存的是节点的前驱和后继(从字面意思也可以进行推测),从而来维护 LinkedHashMap 的顺序。
成员变量
/** * The head (eldest) of the doubly linked list. */ transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head; /** * The tail (youngest) of the doubly linked list. */ transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail; /** * The iteration ordering method for this linked hash map: true * for access-order, false for insertion-order. * LinkedHashMap 的迭代顺序:true 为访问顺序;false 为插入顺序。 */ final boolean accessOrder;
构造器
构造器1:
/** * Constructs an empty insertion-ordered LinkedHashMap instance * with the default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75). */ public LinkedHashMap() { super(); accessOrder = false; }
这里的 super() 方法调用了 HashMap 的无参构造器。该构造器方法构造了一个容量为 16(默认初始容量)、负载因子为 0.75(默认负载因子)的空 LinkedHashMap,其顺序为插入顺序。
构造器 2、3、4、5:
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity) { super(initialCapacity); accessOrder = false; } public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { super(initialCapacity, loadFactor); accessOrder = false; } public LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { super(); accessOrder = false; putMapEntries(m, false); } public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean accessOrder) { super(initialCapacity, loadFactor); this.accessOrder = accessOrder; }
可以看到上面几个构造器都是通过调用父类(HashMap)的构造器方法初始化,对此不再进行分析。前面 4 个构造器的 accessOrder 变量默认值都为 false;最后一个稍微不一样,它的 accessOrder 可以在初始化时指定,即指定 LinkedHashMap 的顺序(插入或访问顺序)。
put 方法
LinkedHashMap 本身没有实现 put 方法,它通过调用父类(HashMap)的方法来进行读写操作。这里再贴下 HashMap 的 put 方法:
public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); } final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) // 新的 bin 节点 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { Node<K,V> e; K k; // key 已存在 if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p; // 散列冲突 else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else { // 遍历链表 for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { // 将新节点插入到链表末尾 if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }
这个方法哪个地方跟 LinkedHashMap 有联系呢?如何能保持 LinkedHashMap 的顺序呢?且看其中的 newNode() 方法,它在 HashMap 中的代码如下:Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { return new Node<>(hash, key, value, next); }
但是,LinkedHashMap 重写了该方法:
// 新建一个 LinkedHashMap.Entry 节点 Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) { LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p = new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e); // 将新节点连接到列表末尾 linkNodeLast(p); return p; }
// link at the end of list private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p) { LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last = tail; tail = p; // list 为空 if (last == null) head = p; else { // 将新节点插入到 list 末尾 p.before = last; last.after = p; } }
可以看到,每次插入新节点时,都会存到列表的末尾。原来如此,LinkedHashMap 的插入顺序就是在这里实现的。
此外,上文分析 HashMap 时提到两个回调方法:afterNodeAccess 和 afterNodeInsertion。它们在 HashMap 中是空的:
// Callbacks to allow LinkedHashMap post-actions void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> p) { } void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { }
同样,LinkedHashMap 对它们进行了重写。先来分析 afterNodeAccess 方法:
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last; // accessOrder 为 true 表示访问顺序 if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) { // p 为访问的节点,b 为其前驱,a 为其后继 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p = (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after; p.after = null; // p 是头节点 if (b == null) head = a; else b.after = a; if (a != null) a.before = b; else last = b; if (last == null) head = p; else { p.before = last; last.after = p; } tail = p; ++modCount; } }
为了便于分析和理解,这里画出了两个操作示意图:
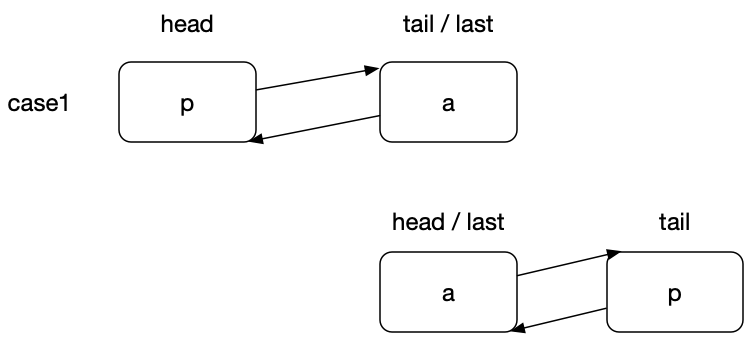

这里描述了进行该操作前后的两种情况。可以看到,该方法执行后,节点 p 被移到了 list 的末尾。
get 方法
LinkedHashMap 重写了 HashMap 的 get 方法,主要是为了维持访问顺序,代码如下:
public V get(Object key) { Node<K,V> e; if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null) return null; // 若为访问顺序,将访问的节点移到列表末尾 if (accessOrder) afterNodeAccess(e); return e.value; }
这里的 getNode 方法是父类的(HashMap)。若 accessOrder 为 true(即指定为访问顺序),则将访问的节点移到列表末尾。
LinkedHashMap 中重写的 afterNodeInsertion 方法:
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // possibly remove eldest LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> first; if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) { K key = first.key; removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true); } } // LinkedHashMap 中默认的返回值为 false,即这里的 removeNode 方法不执行 protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) { return false; }
removeNode 方法是父类 HashMap 中的。
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value, boolean matchValue, boolean movable ) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index; // table 不为空,且给的的 hash 值所在位置不为空 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v; // 给定 key 对应的节点,在数组中第一个位置 if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) node = p; // 给定的 key 所在位置为红黑树或链表 else if ((e = p.next) != null) { if (p instanceof TreeNode) node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key); else { do { if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) { node = e; break; } p = e; } while ((e = e.next) != null); } } // 删除节点 if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value || (value != null && value.equals(v)))) { if (node instanceof TreeNode) ((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable); else if (node == p) tab[index] = node.next; else p.next = node.next; ++modCount; --size; // 删除节点后的操作 afterNodeRemoval(node); return node; } } return null; }
afterNodeRemoval 方法在 HashMap 中的实现也是空的:
void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> p) { }
LinkedHashMap 重写了该方法:
void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> e) { // unlink LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p = (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after; p.before = p.after = null; if (b == null) head = a; else b.after = a; if (a == null) tail = b; else a.before = b; }
该方法就是双链表删除一个节点的操作。
代码演练
LinkedHashMap 用法
我们知道 HashMap 是无序的,例如:
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("bush", "a"); map.put("obama", "b"); map.put("trump", "c"); map.put("lincoln", "d"); System.out.println(map); // 输出结果(无序): // {obama=b, trump=c, lincoln=d, bush=a}
而若换成 LinkedHashMap,则可以保持插入的顺序:
Map<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(); map.put("bush", "a"); map.put("obama", "b"); map.put("trump", "c"); map.put("lincoln", "d"); System.out.println(map); // 输出结果(插入顺序): // {bush=a, obama=b, trump=c, lincoln=d}
指定 LinkedHashMap 的顺序为访问顺序:
Map<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(2, 0.75f, true); map.put("bush", "a"); map.put("obama", "b"); map.put("trump", "c"); map.put("lincoln", "d"); System.out.println(map); map.get("obama"); System.out.println(map); // 输出结果(插入顺序): // {bush=a, obama=b, trump=c, lincoln=d} // 访问 obama 后,obama 移到了末尾 // {bush=a, trump=c, lincoln=d, obama=b}
实现 LRU 缓存
private static class LRUCache<K, V> extends LinkedHashMap<K, V> { private int capacity; public LRUCache(int capacity) { super(16, 0.75f, true); this.capacity = capacity; } @Override protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) { return size() > capacity; } }
使用举例:
LRUCache<String, String> lruCache = new LRUCache<>(2); lruCache.put("bush", "a"); lruCache.put("obama", "b"); lruCache.put("trump", "c"); System.out.println(lruCache); // 输出结果: // {obama=b, trump=c}
这里定义的 LRUCache 类中,对 removeEldestEntry 方法进行了重写,当缓存中的容量大于 2,时会把最早插入的元素 "bush" 删除。因此只剩下两个值。
小结
1. LinkedHashMap 继承自 HashMap,其结构可以理解为「双链表 + 散列表」;
2. 可以维护两种顺序:插入顺序或访问顺序;
3. 可以方便的实现 LRU 缓存;
4. 线程不安全。
Stay hungry, stay foolish.

PS: 本文首发于微信公众号【WriteOnRead】。