一般来说springBoot初始运行的类上面会加SpringBootApplication注解,但是我们发现不加注解也可以成功运行,示例如下:
pom.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.edu.spring</groupId> <artifactId>springboot</artifactId> <version>1.0.0</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>springboot</name> <!-- FIXME change it to the project's website --> <url>http://www.example.com</url> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId> <version>2.1.6.RELEASE</version> <scope>import</scope> <type>pom</type> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
App.java

package com.edu.spring.springboot; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; public class App { @Bean Runnable createRunnable(){ return () -> {System.out.println("spring boot is run");}; } public static void main( String[] args ) { ConfigurableApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(App.class, args); context.getBean(Runnable.class).run(); } }
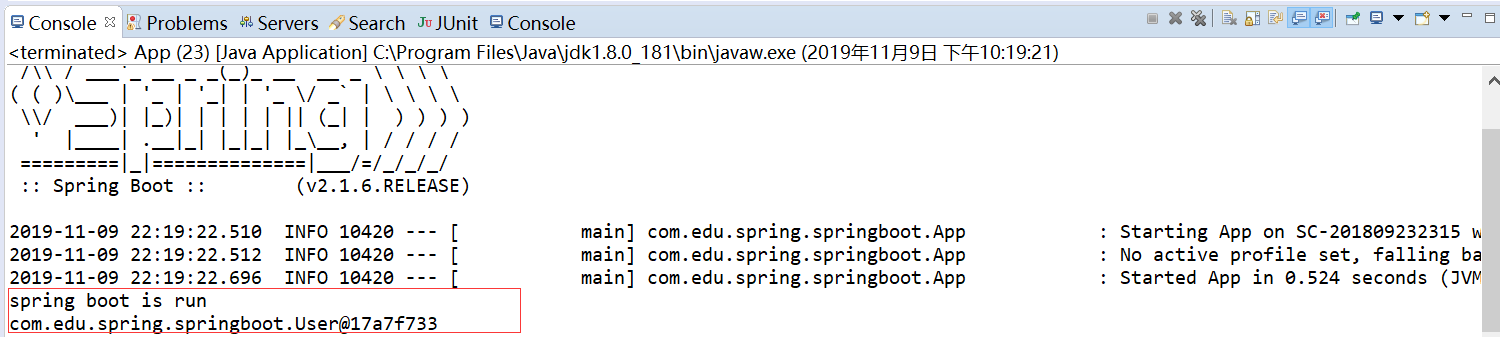
运行结果如下 :
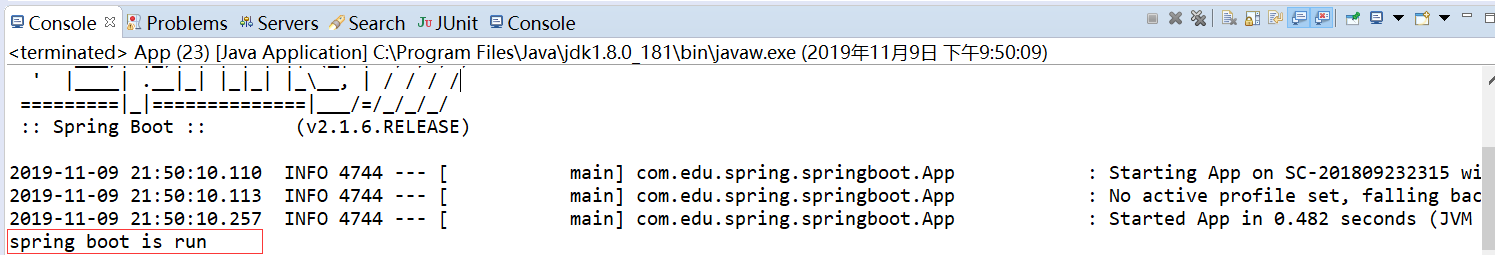
可以看到,springboot正常运行,并且可以创建bean,这是因为SpringApplication类中run方法,最终会调用SpringApplication的构造方法,其中传进去的参数(传的一个类)会作为源,被spring容器管理,部分源码如下:
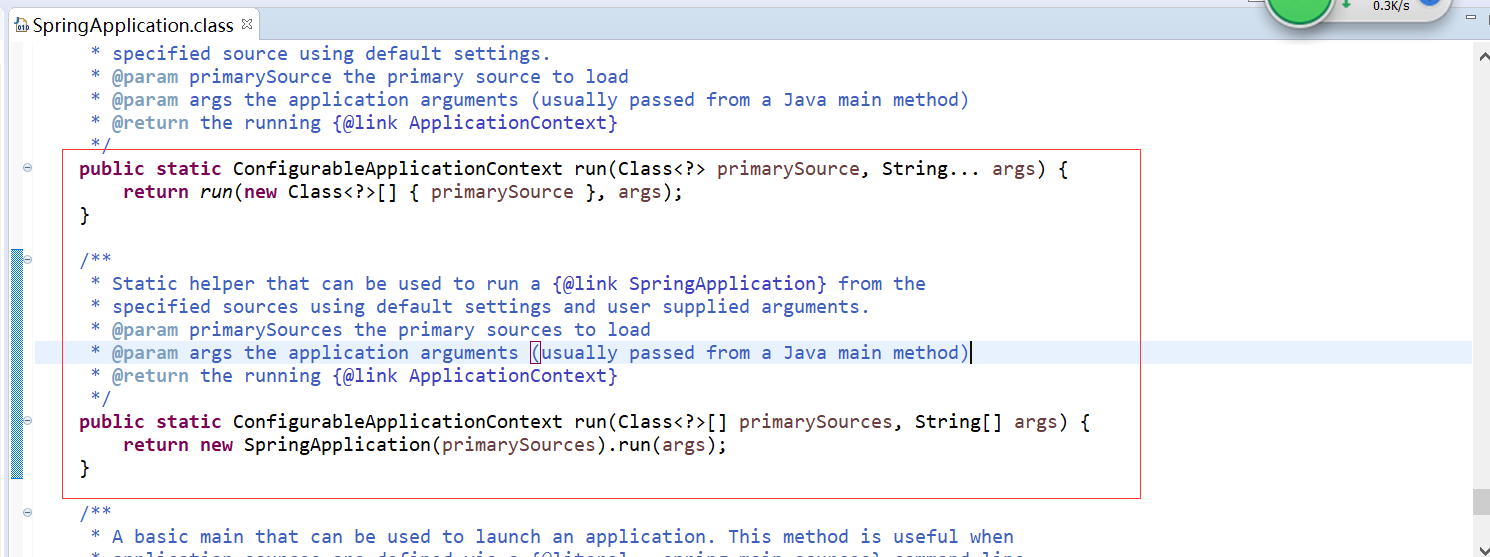
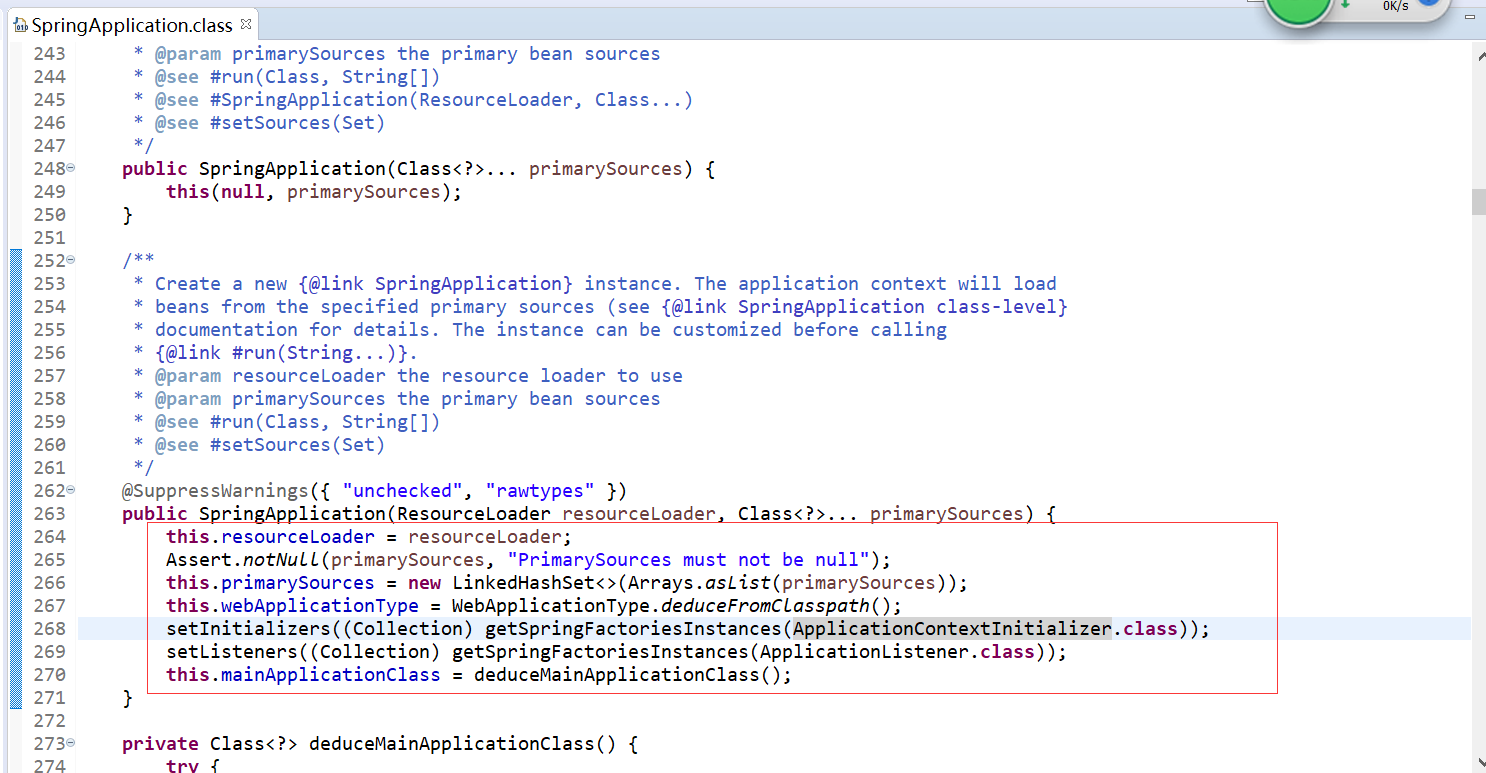
那么为什么我们通常还是会加SpringBootApplication注解呢?这是因为该注解包含了ComponentScan注解,以及其他注解,ComponentScan注解可以配置spring扫描的路径。所以在App.java中不加注解可以正常运行,并且创建bean,但是不会扫描到其他bean,测试如下:
添加 User.java

package com.edu.spring.springboot; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class User { }
App.java

package com.edu.spring.springboot; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; public class App { @Bean Runnable createRunnable(){ return () -> {System.out.println("spring boot is run");}; } public static void main( String[] args ) { ConfigurableApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(App.class, args); context.getBean(Runnable.class).run(); System.out.println(context.getBean(User.class)); } }
运行结果如下:
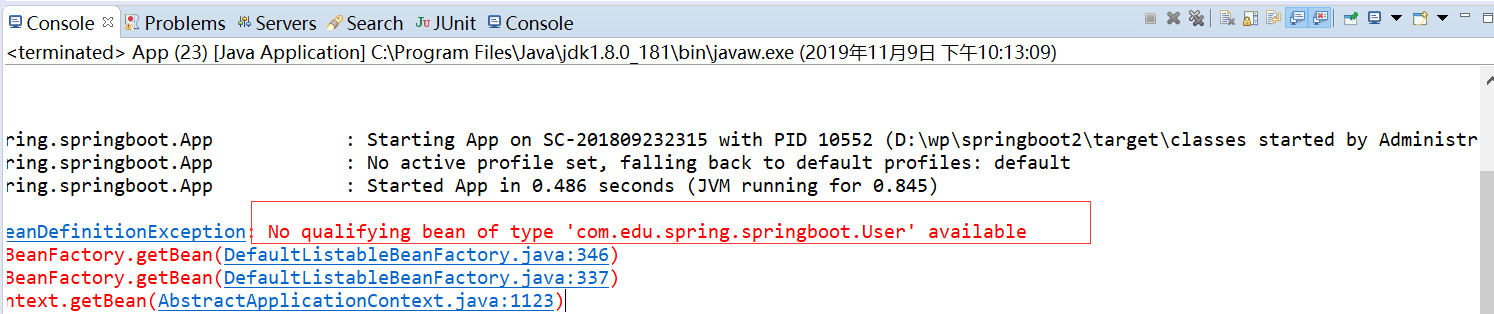
在App.java上面添加ComponentScan注解,可以扫描到User类

package com.edu.spring.springboot; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; @ComponentScan public class App { @Bean Runnable createRunnable(){ return () -> {System.out.println("spring boot is run");}; } public static void main( String[] args ) { ConfigurableApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(App.class, args); context.getBean(Runnable.class).run(); System.out.println(context.getBean(User.class)); } }
运行结果不会报错,如下:
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);中的App参数作为一个源,被spring容器初始化,该参数不一定是运行方法所在本身的类,可以是其他类,示例如下:
App.java

package com.edu.spring.springboot; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; public class App { public static void main( String[] args ) { ConfigurableApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(App2.class, args); context.getBean(Runnable.class).run(); System.out.println(context.getBean(User.class)); } }
App2.java

package com.edu.spring.springboot; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; @ComponentScan public class App2 { @Bean Runnable createRunnable(){ return () -> {System.out.println("spring boot is run");}; } }
同样可以获取Runnable和User的bean运行结果如下:
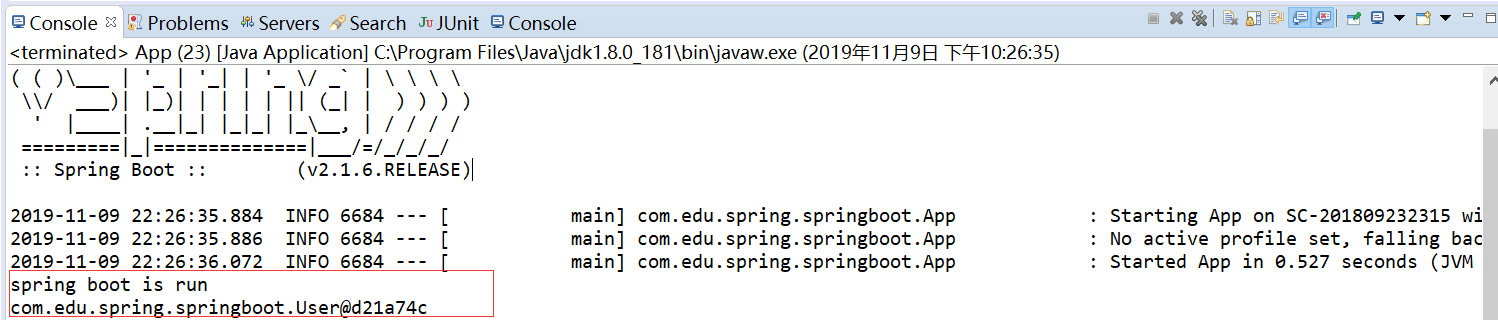
如果此时将创建Runnable的方法写在App.java中将不会获取该bean,程序报错。因为已经指定了源是App2.java。ComponentScan扫描同一级的包,或者子包,因此要将源放在最外层的包中。源可以添加注解SpringBootApplication或者ComponentScan。
