官方文档:
https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html?highlight=built#ascii
一、数学运算类
| abs(x) | 求绝对值 1、参数可以是整型,也可以是复数 2、若参数是负数,则返回负数的模 |
| complex([real[, imag]]) | 创建一个复数 |
| divmod(a, b) | 分别取商和余数 注意:整型、浮点型都可以 |
| float([x]) | 将一个字符串或数转换为浮点数。如果无参数将返回0.0 |
| int([x[, base]]) | 将一个字符转换为int类型,base表示进制 |
| long([x[, base]]) | 将一个字符转换为long类型 |
| pow(x, y[, z]) | 返回x的y次幂 |
| range([start], stop[, step]) | 产生一个序列,默认从0开始 |
| round(x[, n]) | 四舍五入 |
| sum(iterable[, start]) | 对集合求和 |
| oct(x) | 将一个数字转化为8进制 |
| hex(x) | 将整数x转换为16进制字符串 |
| chr(i) | 返回整数i对应的ASCII字符 |
| bin(x) | 将整数x转换为二进制字符串 |
| bool([x]) | 将x转换为Boolean类型 |
二、集合类操作
| basestring() | str和unicode的超类 不能直接调用,可以用作isinstance判断 |
| format(value [, format_spec]) | 格式化输出字符串 格式化的参数顺序从0开始,如“I am {0},I like {1}” |
| unichr(i) | 返回给定int类型的unicode |
| enumerate(sequence [, start = 0]) | 返回一个可枚举的对象,该对象的next()方法将返回一个tuple |
| iter(o[, sentinel]) | 生成一个对象的迭代器,第二个参数表示分隔符 |
| max(iterable[, args...][key]) | 返回集合中的最大值 |
| min(iterable[, args...][key]) | 返回集合中的最小值 |
| dict([arg]) | 创建数据字典 |
| list([iterable]) | 将一个集合类转换为另外一个集合类 |
| set() | set对象实例化 |
| frozenset([iterable]) | 产生一个不可变的set |
| str([object]) | 转换为string类型 |
| sorted(iterable[, cmp[, key[, reverse]]]) | 队集合排序 |
| tuple([iterable]) | 生成一个tuple类型 |
| xrange([start], stop[, step]) | xrange()函数与range()类似,但xrnage()并不创建列表,而是返回一个xrange对象,它的行为与列表相似,但是只在需要时才计算列表值,当列表很大时,这个特性能为我们节省内存 |
三、逻辑判断
| all(iterable) | 1、集合中的元素都为真的时候为真 2、特别的,若为空串返回为True |
| any(iterable) | 1、集合中的元素有一个为真的时候为真 2、特别的,若为空串返回为False |
| cmp(x, y) | 如果x < y ,返回负数;x == y, 返回0;x > y,返回正数 |
四、反射
| callable(object) | 检查对象object是否可调用 1、类是可以被调用的 2、实例是不可以被调用的,除非类中声明了__call__方法 |
| classmethod() | 1、注解,用来说明这个方式是个类方法 2、类方法即可被类调用,也可以被实例调用 3、类方法类似于Java中的static方法 4、类方法中不需要有self参数 |
| compile(source, filename, mode[, flags[, dont_inherit]]) | 将source编译为代码或者AST对象。代码对象能够通过exec语句来执行或者eval()进行求值。 1、参数source:字符串或者AST(Abstract Syntax Trees)对象。 2、参数 filename:代码文件名称,如果不是从文件读取代码则传递一些可辨认的值。 3、参数model:指定编译代码的种类。可以指定为 ‘exec’,’eval’,’single’。 4、参数flag和dont_inherit:这两个参数暂不介绍 |
| dir([object]) | 1、不带参数时,返回当前范围内的变量、方法和定义的类型列表; 2、带参数时,返回参数的属性、方法列表。 3、如果参数包含方法__dir__(),该方法将被调用。当参数为实例时。 4、如果参数不包含__dir__(),该方法将最大限度地收集参数信息 |
| delattr(object, name) | 删除object对象名为name的属性 |
| eval(expression [, globals [, locals]]) | 计算表达式expression的值 |
| execfile(filename [, globals [, locals]]) | 用法类似exec(),不同的是execfile的参数filename为文件名,而exec的参数为字符串。 |
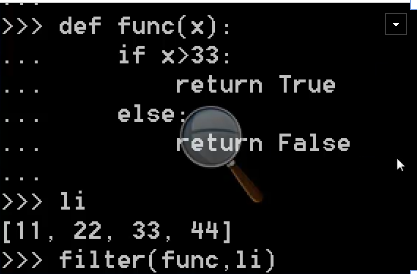
| filter(function, iterable) | 构造一个序列,等价于[ item for item in iterable if function(item)] 1、参数function:返回值为True或False的函数,可以为None 2、参数iterable:序列或可迭代对象 |
| getattr(object, name [, defalut]) | 获取一个类的属性 |
| globals() | 返回一个描述当前全局符号表的字典 |
| hasattr(object, name) | 判断对象object是否包含名为name的特性 |
| hash(object) | 如果对象object为哈希表类型,返回对象object的哈希值 |
| id(object) | 返回对象的唯一标识 |
| isinstance(object, classinfo) | 判断object是否是class的实例 |
| issubclass(class, classinfo) | 判断是否是子类 |
| len(s) | 返回集合长度 |
| locals() | 返回当前的变量列表 |
| map(function, iterable, ...) | 遍历每个元素,执行function操作 |
| memoryview(obj) | 返回一个内存镜像类型的对象 |
| next(iterator[, default]) | 类似于iterator.next() |
| object() | 基类 |
| property([fget[, fset[, fdel[, doc]]]]) | 属性访问的包装类,设置后可以通过c.x=value等来访问setter和getter |
| reduce(function, iterable[, initializer]) | 合并操作,从第一个开始是前两个参数,然后是前两个的结果与第三个合并进行处理,以此类推 |
| reload(module) | 重新加载模块 |
| setattr(object, name, value) | 设置属性值 |
| repr(object) | 将一个对象变幻为可打印的格式 |
| slice() | |
| staticmethod | 声明静态方法,是个注解 |
| super(type[, object-or-type]) | 引用父类 |
| type(object) | 返回该object的类型 |
| vars([object]) | 返回对象的变量,若无参数与dict()方法类似 |
| bytearray([source [, encoding [, errors]]]) | 返回一个byte数组 1、如果source为整数,则返回一个长度为source的初始化数组; 2、如果source为字符串,则按照指定的encoding将字符串转换为字节序列; 3、如果source为可迭代类型,则元素必须为[0 ,255]中的整数; 4、如果source为与buffer接口一致的对象,则此对象也可以被用于初始化bytearray. |
| zip([iterable, ...]) | 实在是没有看懂,只是看到了矩阵的变幻方面 |
五、IO操作
| file(filename [, mode [, bufsize]]) | file类型的构造函数,作用为打开一个文件,如果文件不存在且mode为写或追加时,文件将被创建。添加‘b’到mode参数中,将对文件以二进制形式操作。添加‘+’到mode参数中,将允许对文件同时进行读写操作 1、参数filename:文件名称。 2、参数mode:'r'(读)、'w'(写)、'a'(追加)。 3、参数bufsize:如果为0表示不进行缓冲,如果为1表示进行行缓冲,如果是一个大于1的数表示缓冲区的大小 。 |
| input([prompt]) | 获取用户输入 推荐使用raw_input,因为该函数将不会捕获用户的错误输入 |
| open(name[, mode[, buffering]]) | 打开文件 与file有什么不同?推荐使用open |
| 打印函数 | |
| raw_input([prompt]) | 设置输入,输入都是作为字符串处理 |
六、其他
help()--帮助信息
__import__()--没太看明白了,看到了那句“Direct use of __import__() is rare”之后就没心看下去了
apply()、buffer()、coerce()、intern()---这些是过期的内置函数,故不说明
abs():取绝对值

>>> abs(-1) 1 >>> abs(1) 1 >>> abs(-454) 454
all():全部为真是为真,有一个为假,则为假;返回布尔值
1、集合中的元素都为真的时候为真
2、特别的,若为空串返回为True

>>> l = [1,2,3] >>> all(l) True >>> li = [1,2,3,0,''] >>> all(li) False >>> >>> a = ' ' >>> any(a) True
any:只要有一个为真是为真,全部为假是为假;返回布尔值

>>> li = [1,2,3,0,''] >>> any(li) True >>> l3 = [0,''] >>> any(l3) False >>>
ascii:
1. 返回一个可打印的对象字符串方式表示,如果是非ascii字符就会输出x,u或U等字符来表示。

>>> ascii(1) '1' >>> ascii('&') "'&'" >>> ascii(9000000) '9000000' >>> ascii('中文') #非ascii字符 "'\u4e2d\u6587'"
bin :
把十进制转成二进制
>>> bin(512) '0b1000000000'
bool:
布尔值 :
空,None,0的布尔值为False,其余都为True
1 print(bool('')) #空字符串,返回值None 2 print(bool(None)) 3 print(bool(0))
执行结果:
1 False 2 False 3 False
bytes 把字符串转成字节
1 name='你好'
2 print(bytes(name,encoding='utf-8')) #手动把字符串编码,转成二进制
3 print(bytes(name,encoding='utf-8').decode('utf-8'))
#需要把字符串进行编码,再解码(用什么编码,就用什么解码)
执行结果:
1 b'xe4xbdxa0xe5xa5xbd' 2 你好
chr和ord:
ascll 码对应的编码,可以和ord制作一个简单的随机验证码
>>> chr(80) 'P' >>> ord('P') 80 >>>
dir:
显示函数内置属性和方法
>>> dir(str) ['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getnewargs__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill']
divmod:
取商得余数,用于做分页显示功能
>>> divmod(10,3)
(3, 1)
eval:
把字符串中的数据结构给提取出来
1.
>>> dic={'name':'jam'}
>>> str(dic)
"{'name': 'jam'}"
>>> eval(str(dic))#字典类型转成字符串
{'name': 'jam'}
2.转换为python中的执行语句
>>> a = '1+2+3' >>> eval(a) 6
hash:
可hash的数据类型即不可变数据类型,不可hash的数据类型即可变数据类型
hash的作用:去网上下载软件,判断是否被人修改,通过比对hash值,就知道
>>> hash('12sdfdsaf3123123sdfasdfasdfasdfasdfasdfasdfasdfasfasfdasdf') 9045015416792321045 >>> hash('12sdfdsaf31231asdfasdfsadfsadfasdfasdf23') 6872701706427661775 >>>
help:
查看函数用法的说细信息
>>> help(all) Help on built-in function all in module builtins: all(iterable, /) Return True if bool(x) is True for all values x in the iterable. If the iterable is empty, return True.
bin、hex、oct:
进制转换
1 print(bin(10)) #10进制->2进制
执行结果:0b1010 #10进制->2进制
2 print(hex(12)) #10进制->16进制
执行结果:0xc #10进制->16进制
3 print(oct(12)) #10进制->8进制
执行结果:0o14 #10进制->8进制
isinstance 和 type:
判断类型
isinstance判断类型,返回布尔值
type 返回值的类型
>>> isinstance(1,int) True >>> isinstance('abc',str) True >>> isinstance({},list) False >>> type([]) <class 'list'> >>> type(1) <class 'int'>
globals 全局变量
globals()#打印全局变量
locals()#打印所有的局部变量变量
max 最大值 和 min最小值
1 l=[1,3,100,-1,2] 2 print(max(l)) 3 print(min(l))
执行结果:
1 100 #最大值 2 -1 #最小值
ps2: max 高级用法
说明:
1、max函数处理的是可迭代对象,相当于一个for循环取出每个元素进行比较
注意:不同类型之间不能进行比较
2、每个元素间进行比较,是从每个元素的第一位置依次比较,如果这一个位置分出大小,后
面的都不需要比较了,直接得出这俩元素的大小。
1 age_dic={'age1':18,'age2':20,'age3':100,'age4':30}
2 print(max(age_dic.values())) #取出最大年龄
3 print(max(age_dic)) #默认比较的是字典的key
执行结果:
1 100 2 age4
ps3: 取出年龄最大的key和values
1 age_dic={'alex_age':18,'wupei_age':20,'zsc_age':100,'lhf_age':30}
2 for item in zip(age_dic.values(),age_dic.keys()): #[(18,'alex_age') (20,'wupeiqi_age') () () ()]
3 print(item)
4
5 #取出年龄最大的key和values
6 print('=======>',list(max(zip(age_dic.values(),age_dic.keys())))) #max和zip联合使用
执行结果:
1 (100, 'zsc_age') 2 (30, 'lhf_age') 3 (18, 'alex_age') 4 (20, 'wupei_age') 5 6 7 =======> [100, 'zsc_age'] #取出年龄最大的key和values
ps4:
1 l=[
2 (5,'e'),
3 (1,'b'),
4 (3,'a'),
5 (4,'d'),
6 ]
7 l1=['a10','b12','c10',100] #不同类型之间不能进行比较
8 l1=['a10','a2','a10'] #不同类型之间不能进行比较
9 print(list(max(l)))
10
11 print('--->',list(max(l1)))
执行结果:
1 [5, 'e'] 2 ---> ['a', '2']
zip 将对象逐一配对
ps1:
1 print(list(zip(('a','n','c'),(1,2,3))))
2 print(list(zip(('a','n','c'),(1,2,3,4))))
3 print(list(zip(('a','n','c','d'),(1,2,3))))
执行结果:
1 [('a', 1), ('n', 2), ('c', 3)]
2 [('a', 1), ('n', 2), ('c', 3)]
3 [('a', 1), ('n', 2), ('c', 3)]
ps2:
1 p={'name':'alex','age':18,'gender':'none'}
2 print(list(zip(p.keys(),p.values())))
3 print(list(p.keys())) #取keys
4 print(list(p.values())) #values
5
6 print(list(zip(['a','b'],'12345'))) #列表,只要是序列就可以打印出来
执行结果:
1 [('age', 18), ('name', 'alex'), ('gender', 'none')]
2 ['age', 'name', 'gender']
3 [18, 'alex', 'none']
4 [('a', '1'), ('b', '2')]
ps3:
max总结:
1 l=[1,3,100,-1,2]
2 print(max(l)) #比较出最大值
3
4
5 dic={'age1':18,'age2':10}
6 print(max(dic)) #比较的是key
7
8
9 print(max(dic.values())) #比较的是key,但是不知道是那个key对应的值
10
11
12 print(max(zip(dic.values(),dic.keys()))) #结合zip使用
执行结果:
1 100 #比较大小,得出最大值 2 3 age2 #比较的是key 4 5 18 #比较的是key,但是不知道是那个key对应的值 6 7 (18, 'age1') #结合zip拿用
ps4:
1 people=[
2 {'name':'alex','age':1000},
3 {'name':'wupei','age':10000},
4 {'name':'yuanhao','age':9000},
5 {'name':'linhaifeng','age':18},
6 ]
7 # max(people,key=lambda dic:dic['age'])
8 print('周绍陈取出来没有',max(people,key=lambda dic:dic['age'])) #提取年龄中的values,再进行比较
9
10 #上面题分解步骤,先取出ret的值,再给max进行比较
11 people=[
12 {'name':'alex','age':1000},
13 {'name':'wupei','age':10000},
14 {'name':'yuanhao','age':9000},
15 {'name':'linhaifeng','age':18},
16 ]
17
18 ret=[]
19 for item in people:
20 ret.append(item['age'])
21 print(ret)
22 max(ret)
执行结果:
1 #提取年龄中的values,再进行比较大小,得出age最大的
2
3 周绍陈取出来没有 {'name': 'wupei', 'age': 10000}
4
5
6 #上面题分解步骤,先取出ret的值,再给max进行比较,得出的值:
7
8 [1000, 10000, 9000, 18]
ps5:
chr : 返回一个字符串,其ASCII码是一个整型.比如chr(97)返回字符串'a'。参数i的范围在0- 255之间。
ord: 参数是一个ascii字符,返回值是对应的十进制整数
pow: 几的几次方
1 print(chr(97)) #ascll码应对的编码
2
3 print(ord('a')) #ascll码应对的数字
4
5 print(pow(3,3)) #3**3 几的几次方,相当于3的3次方
6
7 print(pow(3,3,2)) #3**3%2 3的3次方,取余
执行结果:
1 a #ascll码应对的编码 2 3 97 #ascll码应对的数字 4 5 27 #3**3 几的几次方,相当于3的3次方 6 7 1 #3**3%2 3的3次方,取余
18、reversed 反转
1 l=[1,2,3,4] 2 print(list(reversed(l))) 3 print(l)
执行结果:
1 [4, 3, 2, 1] #反转 2 [1, 2, 3, 4]
19、round 四舍五入
1 print(round(3.5)) #四舍五入
执行结果:
1 4
20、set 集合
1 print(set('hello')) #集合
执行结果:
1 {'l', 'e', 'o', 'h'}
21、slice 切片
1 l='hello' 2 s1=slice(3,5) #切片 取3到5的元素 3 s2=slice(1,4,2) #切片,指定步长为2 4 print(l[3:5]) 5 6 print(l[s1]) #切片 7 print(l[s2]) 8 9 print(s2.start) #开始 10 print(s2.stop) #结束 11 print(s2.step) 步长
执行结果:
1 lo 2 3 lo 4 5 el 6 7 1 8 9 4 10 11 2
22、sorted 排序
ps1:
1 l=[3,2,1,5,7] 2 l1=[3,2,'a',1,5,7] 3 print(sorted(l)) #排序 4 # print(sorted(l1)) #直接运行会报错,因为排序本质就是在比较大小,不同类型之间不可以比较大小
执行结果:
1 [1, 2, 3, 5, 7]
ps2:
1 people=[
2 {'name':'alex','age':1000},
3 {'name':'wupei','age':10000},
4 {'name':'yuanhao','age':9000},
5 {'name':'linhaifeng','age':18},
6 ]
7 print(sorted(people,key=lambda dic:dic['age'])) #按年龄进行排序
执行结果:
1 [{'age': 18, 'name': 'linhaifeng'}, {'age': 1000, 'name': 'alex'}, {'age': 9000, 'name': 'yuanhao'}, {'age': 10000, 'name': 'wupei'}]
ps3:
1 name_dic={
2 'abyuanhao': 11900,
3 'alex':1200,
4 'wupei':300,
5 }
6 print(sorted(name_dic)) #按key排序
7
8 print(sorted(name_dic,key=lambda key:name_dic[key])) #取出字典的values
9
10 print(sorted(zip(name_dic.values(),name_dic.keys()))) #按价格从低到高排序
执行结果:
1 ['abyuanhao', 'alex', 'wupei'] 2 3 ['wupei', 'alex', 'abyuanhao'] 4 5 [(300, 'wupei'), (1200, 'alex'), (11900, 'abyuanhao')]
23、str , type
str 转换成字符型
type 查看某一个东西的数据类型
ps1:
1 print(str('1')) #str 转换成字符型
2 print(type(str({'a':1}))) #type 查看数据类型
3
4 dic_str=str({'a':1})
5 print(type(eval(dic_str))) #eval 转换数据类型
执行结果:
1 1 2 <class 'str'> 3 <class 'dict'>
ps2:
int类型加1
1 msg='123' 2 if type(msg) is str: 3 msg=int(msg) 4 res=msg+1 5 print(res)
执行结果:
1 124
24、vars 跟一个列表或多个字典
1 def test(): 2 msg='撒旦法阿萨德防撒旦浪费艾丝凡阿斯蒂芬' 3 print(locals()) #打印出上一层的值,如果上一层没有,再往上找 4 print(vars()) #如果没有参数,跟locals一样,如果有参数,查看某一个方法,显示成字典的方式 5 test() 6 print(vars(int))
执行结果:
1 {'msg': '撒旦法阿萨德防撒旦浪费艾丝凡阿斯蒂芬'}
2 {'msg': '撒旦法阿萨德防撒旦浪费艾丝凡阿斯蒂芬'}
3 {'denominator': <attribute 'denominator' of 'int' objects>, '__mod__': <slot wrapper '__mod__' of 'int' objects>, '__radd__': <slot wrapper '__radd__' of 'int' objects>, '__floordiv__': <slot wrapper '__floordiv__' of 'int' objects>, '__doc__': "int(x=0) -> integer
int(x, base=10) -> integer
Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments
are given. If x is a number, return x.__int__(). For floating point
numbers, this truncates towards zero.
If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string,
bytes, or bytearray instance representing an integer literal in the
given base. The literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded
by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36.
Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
>>> int('0b100', base=0)
4", '__ceil__': <method '__ceil__' of 'int' objects>, '__sizeof__': <method '__sizeof__' of 'int' objects>, '__pos__': <slot wrapper '__pos__' of 'int' objects>, '__gt__': <slot wrapper '__gt__' of 'int' objects>, '__rtruediv__': <slot wrapper '__rtruediv__' of 'int' objects>, '__sub__': <slot wrapper '__sub__' of 'int' objects>, '__rdivmod__': <slot wrapper '__rdivmod__' of 'int' objects>, '__new__': <built-in method __new__ of type object at 0x5D677028>, '__rshift__': <slot wrapper '__rshift__' of 'int' objects>, '__rmod__': <slot wrapper '__rmod__' of 'int' objects>, '__neg__': <slot wrapper '__neg__' of 'int' objects>, '__xor__': <slot wrapper '__xor__' of 'int' objects>, '__rmul__': <slot wrapper '__rmul__' of 'int' objects>, '__repr__': <slot wrapper '__repr__' of 'int' objects>, '__hash__': <slot wrapper '__hash__' of 'int' objects>, 'to_bytes': <method 'to_bytes' of 'int' objects>, 'from_bytes': <method 'from_bytes' of 'int' objects>, 'real': <attribute 'real' of 'int' objects>, '__lt__': <slot wrapper '__lt__' of 'int' objects>, '__invert__': <slot wrapper '__invert__' of 'int' objects>, '__eq__': <slot wrapper '__eq__' of 'int' objects>, '__float__': <slot wrapper '__float__' of 'int' objects>, '__round__': <method '__round__' of 'int' objects>, '__ror__': <slot wrapper '__ror__' of 'int' objects>, '__le__': <slot wrapper '__le__' of 'int' objects>, '__rlshift__': <slot wrapper '__rlshift__' of 'int' objects>, 'bit_length': <method 'bit_length' of 'int' objects>, '__getnewargs__': <method '__getnewargs__' of 'int' objects>, '__index__': <slot wrapper '__index__' of 'int' objects>, '__rsub__': <slot wrapper '__rsub__' of 'int' objects>, '__format__': <method '__format__' of 'int' objects>, '__bool__': <slot wrapper '__bool__' of 'int' objects>, '__or__': <slot wrapper '__or__' of 'int' objects>, '__int__': <slot wrapper '__int__' of 'int' objects>, 'imag': <attribute 'imag' of 'int' objects>, 'conjugate': <method 'conjugate' of 'int' objects>, '__ge__': <slot wrapper '__ge__' of 'int' objects>, '__and__': <slot wrapper '__and__' of 'int' objects>, '__abs__': <slot wrapper '__abs__' of 'int' objects>, '__floor__': <method '__floor__' of 'int' objects>, '__divmod__': <slot wrapper '__divmod__' of 'int' objects>, '__trunc__': <method '__trunc__' of 'int' objects>, '__rrshift__': <slot wrapper '__rrshift__' of 'int' objects>, '__mul__': <slot wrapper '__mul__' of 'int' objects>, '__pow__': <slot wrapper '__pow__' of 'int' objects>, '__str__': <slot wrapper '__str__' of 'int' objects>, '__ne__': <slot wrapper '__ne__' of 'int' objects>, '__getattribute__': <slot wrapper '__getattribute__' of 'int' objects>, '__truediv__': <slot wrapper '__truediv__' of 'int' objects>, '__add__': <slot wrapper '__add__' of 'int' objects>, '__rand__': <slot wrapper '__rand__' of 'int' objects>, '__rfloordiv__': <slot wrapper '__rfloordiv__' of 'int' objects>, '__lshift__': <slot wrapper '__lshift__' of 'int' objects>, '__rxor__': <slot wrapper '__rxor__' of 'int' objects>, 'numerator': <attribute 'numerator' of 'int' objects>, '__rpow__': <slot wrapper '__rpow__' of 'int' objects>}
25、import 模块
1、先创建一个test.py文件
写入内容如下:
1 def say_hi():
2 print('你好啊林师傅')
2、再调用这个模块
1 import test #导入一个模块,模块就是一个py文件 2 test.say_hi()
执行结果:
1 你好啊林师傅
26、__import__ :导入一个字符串类型模块,就要用__import__
1、先创建一个test.py文件
写入内容如下:
1 def say_hi():
2 print('你好啊林师傅')
2、再调用这个模块
1 module_name='test' 2 m=__import__(module_name) #有字符串的模块 3 m.say_hi()
执行结果:
1 你好啊林师傅
map()和filter
map():遍历序列,对序列中的每个元素进行操作,最终获取新的序列
>>> l = [1,21,3] >>> l2 = map(lambda x:x+100,l)#返回的是一个map类型对象 >>> list(l2) [101, 121, 103]
filter:
对于序列中的元素进行筛选,最终获取符合条件序列