Spring Ioc容器初始化Bean的过程,Spring Ioc容器的本质目的就是为了管理Bean,对于Bean而言,在容器存在其生命周期,他的初始化和销毁也需要一个过程,在一些需要自定义的过程中,我们可以插入代码去改变他们的一些行为,以满足特定的需求,这就需要使用Spring Bean生命周期的知识了。
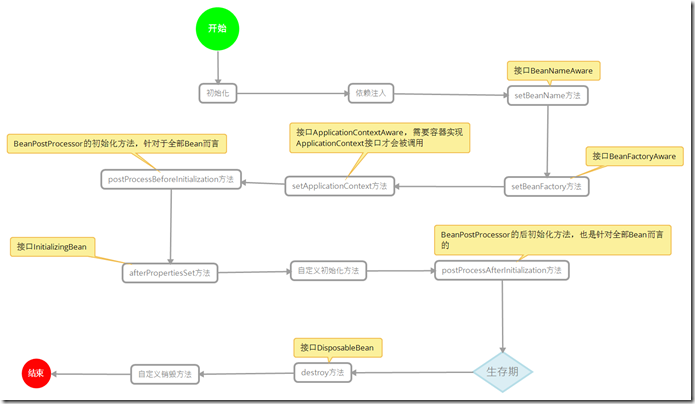
生命周期主要为了了解Spring Ioc容器初始化和销毁Bean的过程。下图展示了Spring Ioc容器初始化和销毁Bean的过程
介绍一下步骤:
1.如果Bean 实现了接口BeanNameAware的setBeanName方法,那么被Spring Ioc容器管理的Bean就会调用这个方法。
2.如果Bean实现了接口BeanFactoryBean的setBeanFactory方法,那么它就会调用这个方法。
3.如果Bean实现了接口ApplicationContextAware的setApplicationContext方法,且Spring Ioc容器也必须是一个ApplicationContext接口的实现类,那么就会调用这个方法,否则不会调用。
4.如果Bean实现了接口BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,那么它就会调用这个方法。
5.如果Bean实现了接口BeanFactoryPostProcessor的afterPropertiesSet方法,那么他就会调用这个方法。
6.如果Bean自定义了初始化的方法,那么它就会调用自定义的初始化方法。
7.如果Bean实现了接口BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialzation方法,完成这些调用,这个时候Bean就完成了初始化,也存在了Spring Ioc容器当中,使用者可以从中获取Bean的服务。
当服务器关闭时或Spring ioc遇到情况关闭时,他就会对被调用的Bean进行销毁,步骤如下
8.如果Bean实现了接口DisposableBean的destroy方法,那么就会调用它。
9.如果自己定义了销毁方法,那么就会执行自定义的方法。
说了很多理论,那么我们就下面就实际操作证明一下吧
1,首先定义一个BeanPostProcessImpl 类,让Spring Ioc容器对其进行管理,这个时候我们需要实现BeanPostProcessor接口,证明4和7条。
package pro.jamal.blog.domain; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; /** * @author: lyj * @Date: 2019/6/2 */ public class BeanPostProcessImpl implements BeanPostProcessor { /** * 在初始化之前的方法 */ @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String s) throws BeansException { System.out.println("["+bean.getClass().getSimpleName()+"]: 初始化开始..."); return bean; } /** * 初始化后的处理方法 */ @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String s) throws BeansException { System.out.println("["+bean.getClass().getSimpleName()+"]: 实例化结束... bye"); return bean; } }
2,在定义一个类,实现1,2,3,5接口,再自定义一个初始化方法,证明第6条理论,简单的打印
package pro.jamal.blog.domain; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.*; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; /** * @author: lyj * @Date: 2019/6/2 */ public class Person implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean { private String name; private Integer age; @Override public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { System.out.println("["+this.getClass().getSimpleName()+"]"+ "调用了BeanFactoryAware接口的setBeanFactory方法"); } @Override public void setBeanName(String s) { System.out.println("["+this.getClass().getSimpleName()+"]"+ "调用了BeanNameAware接口的setBeanName方法"); } @Override public void destroy() throws Exception { System.out.println("["+this.getClass().getSimpleName()+"]"+ "调用了DisposableBean接口的destroy方法"); } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out.println("["+this.getClass().getSimpleName()+"]"+ "调用了InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet方法"); } @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { System.out.println("["+this.getClass().getSimpleName()+"]"+ "调用了ApplicationContextAware接口的setApplicationContext方法"); } public void diyInit(){ System.out.println("["+this.getClass().getSimpleName()+"]:"+"自定义初始化开始"); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } }
3、xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean class="pro.jamal.blog.domain.BeanPostProcessImpl"/> <bean class="pro.jamal.blog.domain.Person" init-method="diyInit"> <property name="name" value="yongjar"/> <property name="age" value="14"/> </bean> </beans>
4.测试
public class BeanCycleTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); Person bean = context.getBean(Person.class); System.out.println(bean.getName() +"," + bean.getAge()); context.close(); } }
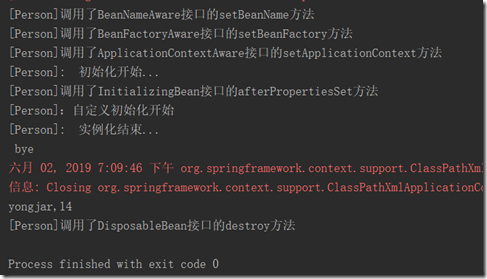
打印结果