一.什么是面向切面编程
- AOP简介
AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意为:面向对象编程,通过预编译方式和运行期间动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。
- 为什么使用AOP编程范式?
分离功能性需求和非功能性需求
集中处理某一关注点
侵入性少,增强代码可读性及可维护性
- AOP应用场景
权限控制、缓存控制、事务控制、分布式追踪、异常处理等
- 举个例子
如果你要在Service层的某些特定方法需加上权限验证,使用OOP思想的话只能在方法内部添加验证身份的代码,例如
public void insert() { checkUserAdmin.check(); //加入权限验证方法 repository.insert(); //调用dao层插入数据库一条记录 }
这样看起来功能是实现了,但如果service层有很多insert和delete方法呢?这样插入代码的方式不易于我们去统一管理,且修改了原代码,具有侵入性。
那么使用了AOP之后呢?你可以建一个切面类,对要进行权限验证的方法进行切入。
即在程序运行时,动态地将代码切入到类的指定方法或位置上的思想,就是面向切面编程。
二.AOP常用术语
- 要想使用面向对象编程的思想,首先要了解几个专有名词
• Target:目标类,即需要被代理的类。例如:UserService
• Joinpoint(连接点):所谓连接点是指那些可能被拦截到的方法。例如:所有的方法
• PointCut 切入点:已经被增强的连接点。例如:addUser()
• Advice 通知/增强,增强代码。例如:after、before
• Weaving(织入):是指把增强advice应用到目标对象target来创建新的代理对象proxy的过程.
• Proxy 代理类
• Aspect(切面): 是切入点pointcut和通知advice的结合
三.Advice-五种增强方式
- 例如在执行某个特定方法的时候,我们可以选择不同的增强方式(如前置通知/增强,在方法运行前执行),达到我们织入后的不同效果。
前置通知:在我们执行目标方法之前运行(@Before)
@Pointcut("within(com.example.demo.Service.*)")
public void matchType(){}
@Before("matchType()") //可在此加入JoinPoint打印切点信息
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("------【前置通知】------" + joinPoint);
}
后置通知:在我们目标方法运行结束之后 ,不管有没有异常(@After)
@After(value="execution(* com.example.aspectJ.demo1.ProductDao.findAll(..))") public void after() { System.out.println("最终通知=================="); }
返回通知:在我们的目标方法正常返回值后运行(@AfterReturning)
@AfterReturning(value="execution(* com.example.aspectJ.demo1.ProductDao.update(..))" ,returning = "result") public void afterReturning(Object result){ //通过returning属性,定义方法返回值作为参数 System.out.println("后置通知========="+result); }
异常通知:在我们的目标方法出现异常后运行(@AfterThrowing)
//通过设置throwing属性,可以设置发生异常对象参数 @AfterThrowing(value = "execution(* com.example.aspectJ.demo1.ProductDao.findOne(..))",throwing = "e") public void afterThrowing(Throwable e){ System.out.println("抛出异常通知"+e.getMessage()); }
环绕通知:动态代理, 需要手动执行joinPoint.procced()(其实就是执行我们的目标方法执行之前相当于前置通知, 执行之后就相当于我们后置通知(@Around)
@Around(value = "execution(* com.example.aspectJ.demo1.ProductDao.delete(..))") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { System.out.println("环绕前通知"); Object obj = joinPoint.proceed(); //执行目标方法 System.out.println("环绕后通知"); return obj; }
四.SpringAOP使用详解
切面表达式
- 下面是一张思维导图总结
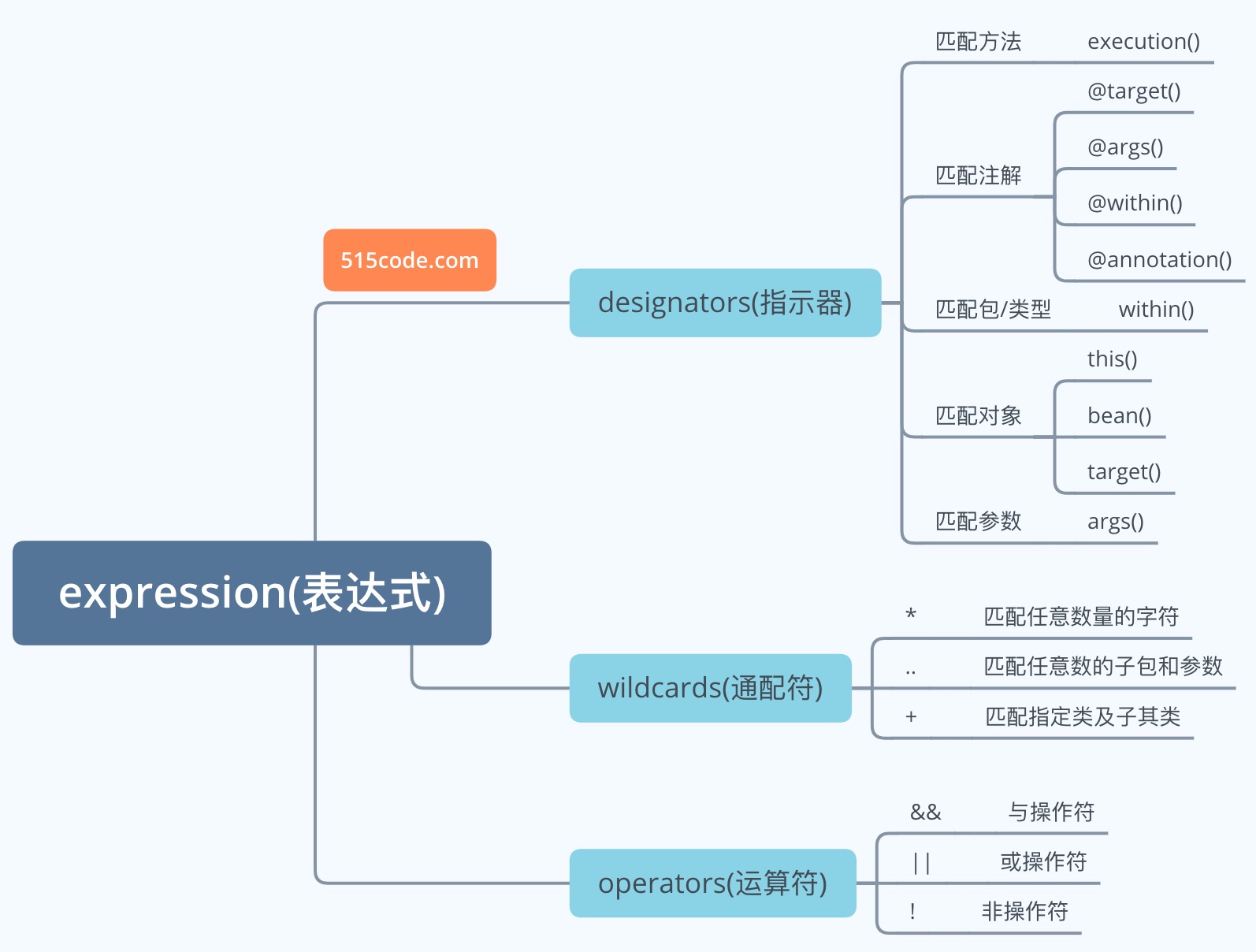
excution表达式
-
execution(
- 修饰符pattern
- 返回值pattern
- 描述包名
- 方法名(参数)
- 方法抛出异常pattern
)
-
代码示例
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.example.controller.*Controller.*(..))") public void match(){} @Before("match()") public void before(){ //前置通知... }
within表达式
-
代码示例
//匹配StudentService类里所有方法 @Pointcut("within(com.example.service.StudentService)") public void matchType(){} //匹配com.example包及子包下所有类方法 @Pointcut("within(com.example..*)") public void matchPackage(){}
对象匹配
-
代码示例
/*public class serviceImpl implements service*/ //匹配AOP对象的目标对象为指定类型方法,即serviceImpl的aop代理对象方法 @Pointcut("this(com.example.serviceImpl)") public void thisDemo(){} //匹配实现service接口的目标对象(非aop代理后的对象)方法,这里指的就是serviceImpl的方法 @Pointcut("target(com.example.service)") public void targetDemo(){} //匹配所有以Service结尾的bean中方法 @Pointcut("bean(*Service)") public void beanDemo(){}
参数匹配
-
代码示例
//匹配任何以find开头且只有一个Long参数的方法 @Pointcut("execution(* *..find*(Long))") public void argsDemo1(){} //匹配任何只有一个Long参数的方法 @Pointcut("args(Long)") public void argsDemo2(){} //匹配任何以find开头且第一个参数为Long的方法 @Pointcut("execution(* *..find*(Long,..))") public void argsDemo3(){} //匹配第一个参数为Long的方法 @Pointcut("args(Long,..)") public void argsDemo4(){}
注解匹配
-
代码示例
//匹配方法注解有@AdminOnly的方法 @Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.security.AdminOnly)") public void annoDemo(){} //匹配注解有@Test1的类下所有方法,要求注解的RetentionPolicy级别为CLASS @Pointcut("@within(com.example.annotation.Test1)") public void annoWithinDemo(){} //匹配注解有@Test2类下所有方法,要求注解的RetentionPolicy级别为RUNTIME @Pointcut("@target(com.example.repository.Test2)") public void annoTargetDemo(){} //匹配传入参数类具有@Test3的注解的方法(例如student实体类有注解@Test3,只要方法传入student类就会被拦截) @Pointcut("@args(org.example.repository.Test3)") public void annoArgsDemo(){}
至于AOP的实现原理,这里暂时不讲,有兴趣的可以去了解下jdk的动态代理,AOP就是基于此实现的。
原文链接 https://developer.aliyun.com/article/759614?spm=a2c6h.14164896.0.0.58341be1BjQF3Z