Time Limit : 2000/1000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 65536/32768K (Java/Other)
Total Submission(s) : 28 Accepted Submission(s) : 18
Font: Times New Roman | Verdana | Georgia
Font Size: ← →
Problem Description
Benny has a spacious farm land to irrigate. The farm land is a rectangle, and is divided into a lot of samll squares. Water pipes are placed in these squares. Different square has a different type of pipe. There are 11 types of pipes, which is marked from A to K, as Figure 1 shows.
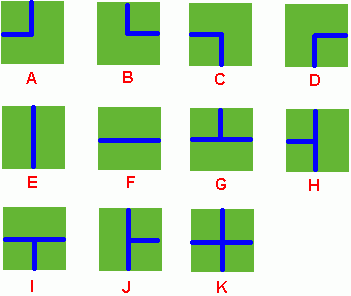
Figure 1
Benny has a map of his farm, which is an array of marks denoting the distribution of water pipes over the whole farm. For example, if he has a map
ADC
FJK
IHE
then the water pipes are distributed like
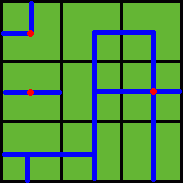
Figure 2
Several wellsprings are found in the center of some squares, so water can flow along the pipes from one square to another. If water flow crosses one square, the whole farm land in this square is irrigated and will have a good harvest in autumn.
Now Benny wants to know at least how many wellsprings should be found to have the whole farm land irrigated. Can you help him?
Note: In the above example, at least 3 wellsprings are needed, as those red points in Figure 2 show.

Benny has a map of his farm, which is an array of marks denoting the distribution of water pipes over the whole farm. For example, if he has a map
ADC
FJK
IHE
then the water pipes are distributed like

Several wellsprings are found in the center of some squares, so water can flow along the pipes from one square to another. If water flow crosses one square, the whole farm land in this square is irrigated and will have a good harvest in autumn.
Now Benny wants to know at least how many wellsprings should be found to have the whole farm land irrigated. Can you help him?
Note: In the above example, at least 3 wellsprings are needed, as those red points in Figure 2 show.
Input
There are several test cases! In each test case, the first line contains 2 integers M and N, then M lines follow. In each of these lines, there are N characters, in the range of 'A' to 'K', denoting the type of water pipe over the corresponding square. A negative M or N denotes the end of input, else you can assume 1 <= M, N <= 50.
Output
For each test case, output in one line the least number of wellsprings needed.
Sample Input
2 2 DK HF 3 3 ADC FJK IHE -1 -1
Sample Output
2 3
从(1,1)开始,向右,向下搜索,如果相同则合并
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
int mp[600][600];
int r[400000],cnt,m,n;
int pp[11][4]= {{1,0,0,1},{1,1,0,0},{0,0,1,1},{0,1,1,0},
{1,0,1,0},{0,1,0,1},{1,1,0,1},{1,0,1,1},{0,1,1,1},{1,1,1,0},{1,1,1,1}
};
void init(int n)
{
int i;
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
r[i]=i;
cnt=n;
}
int findx(int x)
{
int h=x;
while(r[x]!=x)
{
x=r[x];
}
while(h!=x)
{
int tmp=r[h];
r[h]=x;
h=r[h];
}
return x;
}
void merge(int ax,int ay,int bx,int by,int dir)
{
if(bx>n||by>m) return;
int f,w;
bool flag=false;
f=mp[ax][ay];
w=mp[bx][by];
if(dir==1)//向下
{
if(pp[f][2]==1&&pp[w][0]==1) flag=true;
}
else if(dir==2)//向右
{
if(pp[f][1]==1&&pp[w][3]==1) flag=true;
}
if(flag)
{
int fx = findx((ax-1)*m+ay);
int fy = findx((bx-1)*m+by);
if(fx!=fy)
{
r[fy] = fx;
--cnt;
}
}
}
int main()
{
while(cin>>n>>m)
{
if(n==-1&&m==-1) break;
init(n*m);
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
for(int j=1; j<=m; j++)
{
char ch;
cin>>ch;
mp[i][j]=ch-'A';
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
for(int j=1; j<=m; j++)
{
merge(i,j,i+1,j,1);
merge(i,j,i,j+1,2);
}
cout<<cnt<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
#include<iostream> #include<string.h> using namespace std; int n,m; int mp[55][55],vis[55][55]; int di[][2]= { {-1,0},{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1} }; bool pp[][4]= //分别对应 保留图、A、B、C、D…… { {0,0,0,0}, {1,0,0,1},{1,1,0,0},{0,0,1,1},{0,1,1,0}, {1,0,1,0},{0,1,0,1},{1,1,0,1},{1,0,1,1}, {0,1,1,1},{1,1,1,0},{1,1,1,1} }; void dfs(int x,int y) { for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { int xx=x+di[i][0]; int yy=y+di[i][1]; if(!vis[xx][yy]&&pp[mp[x][y]][i]&&pp[mp[xx][yy]][(i+2)%4]) { vis[xx][yy]=true; dfs(xx,yy); } } } int main() { while(cin>>n>>m) { if(n==-1&&m==-1) break; char ch; memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); memset(mp,0,sizeof(mp)); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) { cin>>ch; mp[i][j]=ch-'A'+1; } } int cnt=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) { if(!vis[i][j]) { vis[i][j]=true; cnt++; dfs(i,j); } } } cout<<cnt<<endl; } return 0; }