1. 初始化 - 高效判断是否第一次初始化
private static AtomicBoolean initialized = new AtomicBoolean(false); if (!initialized.compareAndSet(false, true)) { return; }
2. 动态配置,观察者
public interface SentinelProperty<T> { ..... void addListener(PropertyListener<T> listener); ..... void removeListener(PropertyListener<T> listener); ..... boolean updateValue(T newValue); }
public class DynamicSentinelProperty<T> implements SentinelProperty<T> { protected Set<PropertyListener<T>> listeners = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet<PropertyListener<T>>()); ... @Override public void addListener(PropertyListener<T> listener) { listeners.add(listener); listener.configLoad(value); } @Override public void removeListener(PropertyListener<T> listener) { listeners.remove(listener); } @Override public boolean updateValue(T newValue) { if (isEqual(value, newValue)) { return false; } RecordLog.info("[DynamicSentinelProperty] Config will be updated to: " + newValue); value = newValue; for (PropertyListener<T> listener : listeners) { listener.configUpdate(newValue); } return true; } }
private static final class FlowPropertyListener implements PropertyListener<List<FlowRule>> { @Override public void configUpdate(List<FlowRule> value) { Map<String, List<FlowRule>> rules = FlowRuleUtil.buildFlowRuleMap(value); if (rules != null) { flowRules.clear(); flowRules.putAll(rules); } RecordLog.info("[FlowRuleManager] Flow rules received: " + flowRules); } @Override public void configLoad(List<FlowRule> conf) { Map<String, List<FlowRule>> rules = FlowRuleUtil.buildFlowRuleMap(conf); if (rules != null) { flowRules.clear(); flowRules.putAll(rules); } RecordLog.info("[FlowRuleManager] Flow rules loaded: " + flowRules); } }
监听器的同步方式
public static void register2Property(SentinelProperty<List<FlowRule>> property) { AssertUtil.notNull(property, "property cannot be null"); synchronized (LISTENER) { RecordLog.info("[FlowRuleManager] Registering new property to flow rule manager"); currentProperty.removeListener(LISTENER); property.addListener(LISTENER); currentProperty = property; } }
3. 调用统计方法
public class MetricTimerListener implements Runnable { // 监控数据输出方法,buffer写文件等 private static final MetricWriter metricWriter = new MetricWriter(SentinelConfig.singleMetricFileSize(), SentinelConfig.totalMetricFileCount()); @Override public void run() { Map<Long, List<MetricNode>> maps = new TreeMap<Long, List<MetricNode>>();
// 获取集群节点数据集合 for (Entry<ResourceWrapper, ClusterNode> e : ClusterBuilderSlot.getClusterNodeMap().entrySet()) { String name = e.getKey().getName(); ClusterNode node = e.getValue(); Map<Long, MetricNode> metrics = node.metrics();
// 聚合每个节点的数据 aggregate(maps, metrics, name); } aggregate(maps, Constants.ENTRY_NODE.metrics(), Constants.TOTAL_IN_RESOURCE_NAME); if (!maps.isEmpty()) { for (Entry<Long, List<MetricNode>> entry : maps.entrySet()) { try { metricWriter.write(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } catch (Exception e) { RecordLog.warn("[MetricTimerListener] Write metric error", e); } } } } private void aggregate(Map<Long, List<MetricNode>> maps, Map<Long, MetricNode> metrics, String resourceName) { for (Entry<Long, MetricNode> entry : metrics.entrySet()) { long time = entry.getKey(); MetricNode metricNode = entry.getValue(); metricNode.setResource(resourceName); if (maps.get(time) == null) { maps.put(time, new ArrayList<MetricNode>()); } List<MetricNode> nodes = maps.get(time); nodes.add(entry.getValue()); } } }
规则及监控都是基于滑动窗口的设计
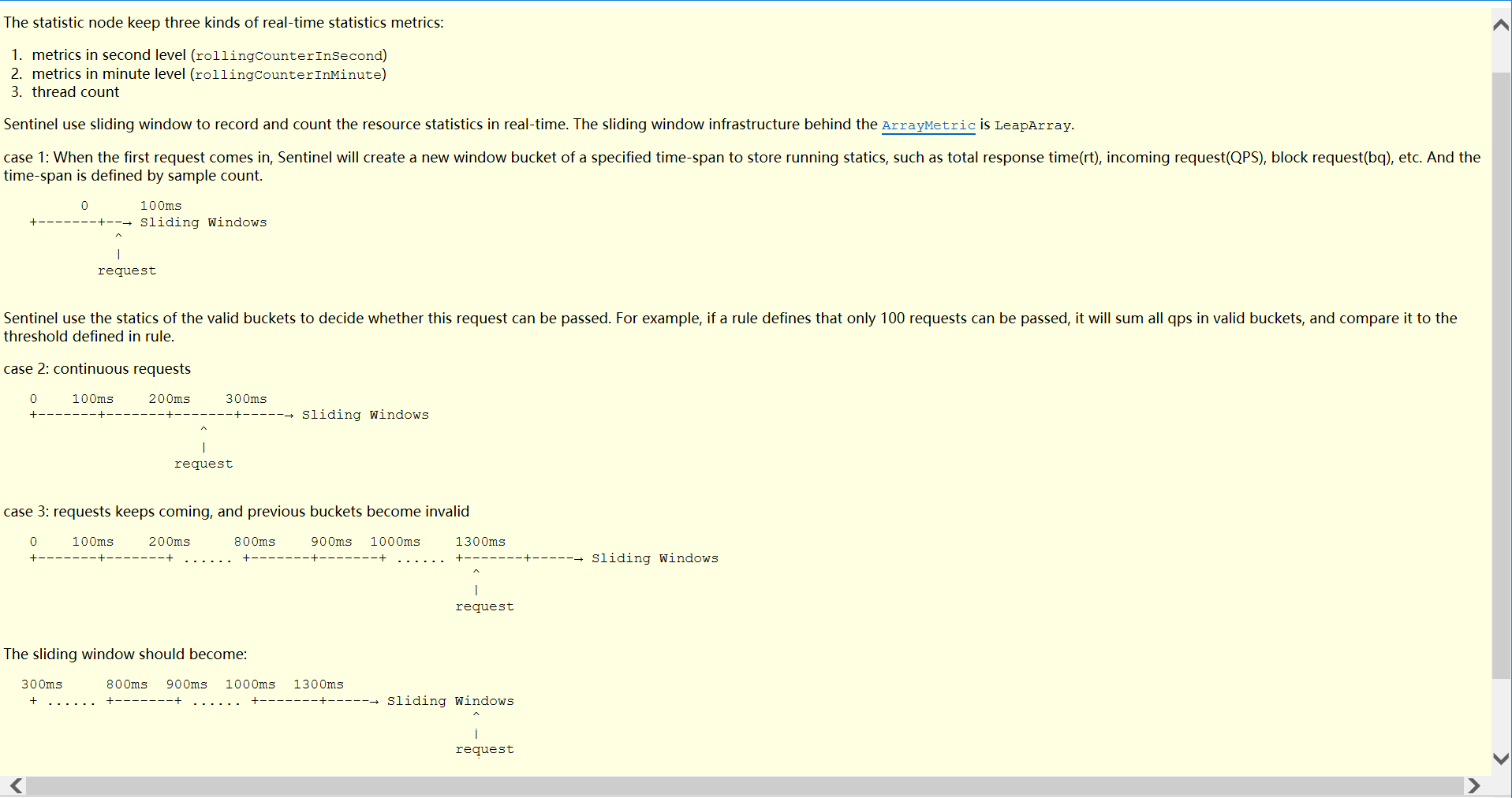
窗口设计
public abstract class LeapArray<T> { protected int windowLengthInMs; protected int sampleCount; protected int intervalInMs; protected final AtomicReferenceArray<WindowWrap<T>> array; /** * The conditional (predicate) update lock is used only when current bucket is deprecated. */ private final ReentrantLock updateLock = new ReentrantLock(); /** * The total bucket count is: {@code sampleCount = intervalInMs / windowLengthInMs}. * * @param sampleCount bucket count of the sliding window * @param intervalInMs the total time interval of this {@link LeapArray} in milliseconds */ public LeapArray(int sampleCount, int intervalInMs) { AssertUtil.isTrue(sampleCount > 0, "bucket count is invalid: " + sampleCount); AssertUtil.isTrue(intervalInMs > 0, "total time interval of the sliding window should be positive"); AssertUtil.isTrue(intervalInMs % sampleCount == 0, "time span needs to be evenly divided"); this.windowLengthInMs = intervalInMs / sampleCount; this.intervalInMs = intervalInMs; this.sampleCount = sampleCount; this.array = new AtomicReferenceArray<>(sampleCount); } /** * Get the bucket at current timestamp. * * @return the bucket at current timestamp */ public WindowWrap<T> currentWindow() { return currentWindow(TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis()); } /** * Create a new statistic value for bucket. * * @param timeMillis current time in milliseconds * @return the new empty bucket */ public abstract T newEmptyBucket(long timeMillis); /** * Reset given bucket to provided start time and reset the value. * * @param startTime the start time of the bucket in milliseconds * @param windowWrap current bucket * @return new clean bucket at given start time */ protected abstract WindowWrap<T> resetWindowTo(WindowWrap<T> windowWrap, long startTime); private int calculateTimeIdx(/*@Valid*/ long timeMillis) { long timeId = timeMillis / windowLengthInMs; // Calculate current index so we can map the timestamp to the leap array. return (int)(timeId % array.length()); } protected long calculateWindowStart(/*@Valid*/ long timeMillis) { return timeMillis - timeMillis % windowLengthInMs; } /** * Get bucket item at provided timestamp. * * @param timeMillis a valid timestamp in milliseconds * @return current bucket item at provided timestamp if the time is valid; null if time is invalid */ public WindowWrap<T> currentWindow(long timeMillis) { if (timeMillis < 0) { return null; } int idx = calculateTimeIdx(timeMillis); // Calculate current bucket start time. long windowStart = calculateWindowStart(timeMillis); /* * Get bucket item at given time from the array. * * (1) Bucket is absent, then just create a new bucket and CAS update to circular array. * (2) Bucket is up-to-date, then just return the bucket. * (3) Bucket is deprecated, then reset current bucket and clean all deprecated buckets. */ while (true) { WindowWrap<T> old = array.get(idx); if (old == null) { /* * B0 B1 B2 NULL B4 * ||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___ * 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 timestamp * ^ * time=888 * bucket is empty, so create new and update * * If the old bucket is absent, then we create a new bucket at {@code windowStart}, * then try to update circular array via a CAS operation. Only one thread can * succeed to update, while other threads yield its time slice. */ WindowWrap<T> window = new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis)); if (array.compareAndSet(idx, null, window)) { // Successfully updated, return the created bucket. return window; } else { // Contention failed, the thread will yield its time slice to wait for bucket available. Thread.yield(); } } else if (windowStart == old.windowStart()) { /* * B0 B1 B2 B3 B4 * ||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___ * 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 timestamp * ^ * time=888 * startTime of Bucket 3: 800, so it's up-to-date * * If current {@code windowStart} is equal to the start timestamp of old bucket, * that means the time is within the bucket, so directly return the bucket. */ return old; } else if (windowStart > old.windowStart()) { /* * (old) * B0 B1 B2 NULL B4 * |_______||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___ * ... 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200 timestamp * ^ * time=1676 * startTime of Bucket 2: 400, deprecated, should be reset * * If the start timestamp of old bucket is behind provided time, that means * the bucket is deprecated. We have to reset the bucket to current {@code windowStart}. * Note that the reset and clean-up operations are hard to be atomic, * so we need a update lock to guarantee the correctness of bucket update. * * The update lock is conditional (tiny scope) and will take effect only when * bucket is deprecated, so in most cases it won't lead to performance loss. */ if (updateLock.tryLock()) { try { // Successfully get the update lock, now we reset the bucket. return resetWindowTo(old, windowStart); } finally { updateLock.unlock(); } } else { // Contention failed, the thread will yield its time slice to wait for bucket available. Thread.yield(); } } else if (windowStart < old.windowStart()) { // Should not go through here, as the provided time is already behind. return new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis)); } } } /** * Get the previous bucket item before provided timestamp. * * @param timeMillis a valid timestamp in milliseconds * @return the previous bucket item before provided timestamp */ public WindowWrap<T> getPreviousWindow(long timeMillis) { if (timeMillis < 0) { return null; } long timeId = (timeMillis - windowLengthInMs) / windowLengthInMs; int idx = (int)(timeId % array.length()); timeMillis = timeMillis - windowLengthInMs; WindowWrap<T> wrap = array.get(idx); if (wrap == null || isWindowDeprecated(wrap)) { return null; } if (wrap.windowStart() + windowLengthInMs < (timeMillis)) { return null; } return wrap; } /** * Get the previous bucket item for current timestamp. * * @return the previous bucket item for current timestamp */ public WindowWrap<T> getPreviousWindow() { return getPreviousWindow(TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis()); } /** * Get statistic value from bucket for provided timestamp. * * @param timeMillis a valid timestamp in milliseconds * @return the statistic value if bucket for provided timestamp is up-to-date; otherwise null */ public T getWindowValue(long timeMillis) { if (timeMillis < 0) { return null; } int idx = calculateTimeIdx(timeMillis); WindowWrap<T> bucket = array.get(idx); if (bucket == null || !bucket.isTimeInWindow(timeMillis)) { return null; } return bucket.value(); } /** * Check if a bucket is deprecated, which means that the bucket * has been behind for at least an entire window time span. * * @param windowWrap a non-null bucket * @return true if the bucket is deprecated; otherwise false */ public boolean isWindowDeprecated(/*@NonNull*/ WindowWrap<T> windowWrap) { return isWindowDeprecated(TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis(), windowWrap); } public boolean isWindowDeprecated(long time, WindowWrap<T> windowWrap) { return time - windowWrap.windowStart() > intervalInMs; } /** * Get valid bucket list for entire sliding window. * The list will only contain "valid" buckets. * * @return valid bucket list for entire sliding window. */ public List<WindowWrap<T>> list() { return list(TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis()); } public List<WindowWrap<T>> list(long validTime) { int size = array.length(); List<WindowWrap<T>> result = new ArrayList<WindowWrap<T>>(size); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { WindowWrap<T> windowWrap = array.get(i); if (windowWrap == null || isWindowDeprecated(validTime, windowWrap)) { continue; } result.add(windowWrap); } return result; } /** * Get all buckets for entire sliding window including deprecated buckets. * * @return all buckets for entire sliding window */ public List<WindowWrap<T>> listAll() { int size = array.length(); List<WindowWrap<T>> result = new ArrayList<WindowWrap<T>>(size); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { WindowWrap<T> windowWrap = array.get(i); if (windowWrap == null) { continue; } result.add(windowWrap); } return result; } /** * Get aggregated value list for entire sliding window. * The list will only contain value from "valid" buckets. * * @return aggregated value list for entire sliding window */ public List<T> values() { return values(TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis()); } public List<T> values(long timeMillis) { if (timeMillis < 0) { return new ArrayList<T>(); } int size = array.length(); List<T> result = new ArrayList<T>(size); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { WindowWrap<T> windowWrap = array.get(i); if (windowWrap == null || isWindowDeprecated(timeMillis, windowWrap)) { continue; } result.add(windowWrap.value()); } return result; } /** * Get the valid "head" bucket of the sliding window for provided timestamp. * Package-private for test. * * @param timeMillis a valid timestamp in milliseconds * @return the "head" bucket if it exists and is valid; otherwise null */ WindowWrap<T> getValidHead(long timeMillis) { // Calculate index for expected head time. int idx = calculateTimeIdx(timeMillis + windowLengthInMs); WindowWrap<T> wrap = array.get(idx); if (wrap == null || isWindowDeprecated(wrap)) { return null; } return wrap; } /** * Get the valid "head" bucket of the sliding window at current timestamp. * * @return the "head" bucket if it exists and is valid; otherwise null */ public WindowWrap<T> getValidHead() { return getValidHead(TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis()); } /** * Get sample count (total amount of buckets). * * @return sample count */ public int getSampleCount() { return sampleCount; } /** * Get total interval length of the sliding window in milliseconds. * * @return interval in second */ public int getIntervalInMs() { return intervalInMs; } /** * Get total interval length of the sliding window. * * @return interval in second */ public double getIntervalInSecond() { return intervalInMs / 1000.0; } public void debug(long time) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); List<WindowWrap<T>> lists = list(time); sb.append("Thread_").append(Thread.currentThread().getId()).append("_"); for (WindowWrap<T> window : lists) { sb.append(window.windowStart()).append(":").append(window.value().toString()); } System.out.println(sb.toString()); } public long currentWaiting() { // TODO: default method. Should remove this later. return 0; } public void addWaiting(long time, int acquireCount) { // Do nothing by default. throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } }
4. 配置类参考 - 用的时候直接SentinelConfig.charset()

package com.qxwz.sentinel.config; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArraySet; import com.qxwz.sentinel.log.LogBase; import com.qxwz.sentinel.log.RecordLog; import com.qxwz.sentinel.util.AppNameUtil; import com.qxwz.sentinel.util.AssertUtil; /** * The universal local config center of Sentinel. The config is retrieved from command line arguments * and {@code ${user.home}/logs/csp/${appName}.properties} file by default. * * @author leyou * @author Eric Zhao */ public class SentinelConfig { /** * The default application type. * * @since 1.6.0 */ public static final int APP_TYPE_COMMON = 0; private static final Map<String, String> props = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); private static int appType = APP_TYPE_COMMON; public static final String APP_TYPE = "csp.sentinel.app.type"; public static final String CHARSET = "csp.sentinel.charset"; public static final String SINGLE_METRIC_FILE_SIZE = "csp.sentinel.metric.file.single.size"; public static final String TOTAL_METRIC_FILE_COUNT = "csp.sentinel.metric.file.total.count"; public static final String COLD_FACTOR = "csp.sentinel.flow.cold.factor"; public static final String STATISTIC_MAX_RT = "csp.sentinel.statistic.max.rt"; static final String DEFAULT_CHARSET = "UTF-8"; static final long DEFAULT_SINGLE_METRIC_FILE_SIZE = 1024 * 1024 * 50; static final int DEFAULT_TOTAL_METRIC_FILE_COUNT = 6; static final int DEFAULT_COLD_FACTOR = 3; static final int DEFAULT_STATISTIC_MAX_RT = 4900; static { try { initialize(); loadProps(); resolveAppType(); RecordLog.info("[SentinelConfig] Application type resolved: " + appType); } catch (Throwable ex) { RecordLog.warn("[SentinelConfig] Failed to initialize", ex); ex.printStackTrace(); } } private static void resolveAppType() { try { String type = getConfig(APP_TYPE); if (type == null) { appType = APP_TYPE_COMMON; return; } appType = Integer.parseInt(type); if (appType < 0) { appType = APP_TYPE_COMMON; } } catch (Exception ex) { appType = APP_TYPE_COMMON; } } private static void initialize() { // Init default properties. SentinelConfig.setConfig(CHARSET, DEFAULT_CHARSET); SentinelConfig.setConfig(SINGLE_METRIC_FILE_SIZE, String.valueOf(DEFAULT_SINGLE_METRIC_FILE_SIZE)); SentinelConfig.setConfig(TOTAL_METRIC_FILE_COUNT, String.valueOf(DEFAULT_TOTAL_METRIC_FILE_COUNT)); SentinelConfig.setConfig(COLD_FACTOR, String.valueOf(DEFAULT_COLD_FACTOR)); SentinelConfig.setConfig(STATISTIC_MAX_RT, String.valueOf(DEFAULT_STATISTIC_MAX_RT)); } private static void loadProps() { // Resolve app name. AppNameUtil.resolveAppName(); try { String appName = AppNameUtil.getAppName(); if (appName == null) { appName = ""; } // We first retrieve the properties from the property file. String fileName = LogBase.getLogBaseDir() + appName + ".properties"; File file = new File(fileName); if (file.exists()) { RecordLog.info("[SentinelConfig] Reading config from " + fileName); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName); Properties fileProps = new Properties(); fileProps.load(fis); fis.close(); for (Object key : fileProps.keySet()) { SentinelConfig.setConfig((String)key, (String)fileProps.get(key)); } } } catch (Throwable ioe) { RecordLog.info(ioe.getMessage(), ioe); } // JVM parameter override file config. for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>(System.getProperties().entrySet())) { String configKey = entry.getKey().toString(); String configValue = entry.getValue().toString(); String configValueOld = getConfig(configKey); SentinelConfig.setConfig(configKey, configValue); if (configValueOld != null) { RecordLog.info("[SentinelConfig] JVM parameter overrides {0}: {1} -> {2}", configKey, configValueOld, configValue); } } } /** * Get config value of the specific key. * * @param key config key * @return the config value. */ public static String getConfig(String key) { AssertUtil.notNull(key, "key cannot be null"); return props.get(key); } public static void setConfig(String key, String value) { AssertUtil.notNull(key, "key cannot be null"); AssertUtil.notNull(value, "value cannot be null"); props.put(key, value); } public static String removeConfig(String key) { AssertUtil.notNull(key, "key cannot be null"); return props.remove(key); } public static void setConfigIfAbsent(String key, String value) { AssertUtil.notNull(key, "key cannot be null"); AssertUtil.notNull(value, "value cannot be null"); String v = props.get(key); if (v == null) { props.put(key, value); } } public static String getAppName() { return AppNameUtil.getAppName(); } /** * Get application type. * * @return application type, common (0) by default * @since 1.6.0 */ public static int getAppType() { return appType; } public static String charset() { return props.get(CHARSET); } public static long singleMetricFileSize() { try { return Long.parseLong(props.get(SINGLE_METRIC_FILE_SIZE)); } catch (Throwable throwable) { RecordLog.warn("[SentinelConfig] Parse singleMetricFileSize fail, use default value: " + DEFAULT_SINGLE_METRIC_FILE_SIZE, throwable); return DEFAULT_SINGLE_METRIC_FILE_SIZE; } } public static int totalMetricFileCount() { try { return Integer.parseInt(props.get(TOTAL_METRIC_FILE_COUNT)); } catch (Throwable throwable) { RecordLog.warn("[SentinelConfig] Parse totalMetricFileCount fail, use default value: " + DEFAULT_TOTAL_METRIC_FILE_COUNT, throwable); return DEFAULT_TOTAL_METRIC_FILE_COUNT; } } public static int coldFactor() { try { int coldFactor = Integer.parseInt(props.get(COLD_FACTOR)); // check the cold factor larger than 1 if (coldFactor <= 1) { coldFactor = DEFAULT_COLD_FACTOR; RecordLog.warn("cold factor=" + coldFactor + ", should be larger than 1, use default value: " + DEFAULT_COLD_FACTOR); } return coldFactor; } catch (Throwable throwable) { RecordLog.warn("[SentinelConfig] Parse coldFactor fail, use default value: " + DEFAULT_COLD_FACTOR, throwable); return DEFAULT_COLD_FACTOR; } } public static int statisticMaxRt() { try { return Integer.parseInt(props.get(STATISTIC_MAX_RT)); } catch (Throwable throwable) { RecordLog.warn("[SentinelConfig] Parse statisticMaxRt fail, use default value: " + DEFAULT_STATISTIC_MAX_RT, throwable); return DEFAULT_STATISTIC_MAX_RT; } } }
5. 处理单元组织

SlotChainBuilder
public class DefaultSlotChainBuilder implements SlotChainBuilder { @Override public ProcessorSlotChain build() { ProcessorSlotChain chain = new DefaultProcessorSlotChain(); chain.addLast(new NodeSelectorSlot()); chain.addLast(new ClusterBuilderSlot()); chain.addLast(new LogSlot()); chain.addLast(new StatisticSlot()); chain.addLast(new SystemSlot()); chain.addLast(new AuthoritySlot()); chain.addLast(new FlowSlot()); chain.addLast(new DegradeSlot()); return chain; } }
具体的一个slot:
public class FlowSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<DefaultNode> { private final FlowRuleChecker checker; public FlowSlot() { this(new FlowRuleChecker()); } /** * Package-private for test. * * @param checker flow rule checker * @since 1.6.1 */ FlowSlot(FlowRuleChecker checker) { AssertUtil.notNull(checker, "flow checker should not be null"); this.checker = checker; } @Override public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable { checkFlow(resourceWrapper, context, node, count, prioritized); fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args); } void checkFlow(ResourceWrapper resource, Context context, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized) throws BlockException { checker.checkFlow(ruleProvider, resource, context, node, count, prioritized); } @Override public void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) { fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args); } private final Function<String, Collection<FlowRule>> ruleProvider = new Function<String, Collection<FlowRule>>() { @Override public Collection<FlowRule> apply(String resource) { // Flow rule map should not be null. Map<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRules = FlowRuleManager.getFlowRuleMap(); return flowRules.get(resource); } }; }
6. 调用关系
SentinelResourceAspect.invokeResourceWithSentinel -> SphU.entry -> CtSph...lookProcessChain -> FlowSlot(checkFlow/fireEntry) -> DefaultController(canpass)
7. 上下文工具
public class ContextUtil { /** * Store the context in ThreadLocal for easy access. */ private static ThreadLocal<Context> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>(); /** * Holds all {@link EntranceNode}. Each {@link EntranceNode} is associated with a distinct context name. */ private static volatile Map<String, DefaultNode> contextNameNodeMap = new HashMap<>(); private static final ReentrantLock LOCK = new ReentrantLock(); private static final Context NULL_CONTEXT = new NullContext(); static { // Cache the entrance node for default context. initDefaultContext(); } private static void initDefaultContext() { String defaultContextName = Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME; EntranceNode node = new EntranceNode(new StringResourceWrapper(defaultContextName, EntryType.IN), null); Constants.ROOT.addChild(node); contextNameNodeMap.put(defaultContextName, node); } /** * Not thread-safe, only for test. */ static void resetContextMap() { if (contextNameNodeMap != null) { RecordLog.warn("Context map cleared and reset to initial state"); contextNameNodeMap.clear(); initDefaultContext(); } } /** * <p> * Enter the invocation context, which marks as the entrance of an invocation chain. * The context is wrapped with {@code ThreadLocal}, meaning that each thread has it's own {@link Context}. * New context will be created if current thread doesn't have one. * </p> * <p> * A context will be bound with an {@link EntranceNode}, which represents the entrance statistic node * of the invocation chain. New {@link EntranceNode} will be created if * current context does't have one. Note that same context name will share * same {@link EntranceNode} globally. * </p> * <p> * The origin node will be created in {@link com.qxwz.sentinel.slots.clusterbuilder.ClusterBuilderSlot}. * Note that each distinct {@code origin} of different resources will lead to creating different new * {@link Node}, meaning that total amount of created origin statistic nodes will be:<br/> * {@code distinct resource name amount * distinct origin count}.<br/> * So when there are too many origins, memory footprint should be carefully considered. * </p> * <p> * Same resource in different context will count separately, see {@link NodeSelectorSlot}. * </p> * * @param name the context name * @param origin the origin of this invocation, usually the origin could be the Service * Consumer's app name. The origin is useful when we want to control different * invoker/consumer separately. * @return The invocation context of the current thread */ public static Context enter(String name, String origin) { if (Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME.equals(name)) { throw new ContextNameDefineException( "The " + Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME + " can't be permit to defined!"); } return trueEnter(name, origin); } protected static Context trueEnter(String name, String origin) { Context context = contextHolder.get(); if (context == null) { Map<String, DefaultNode> localCacheNameMap = contextNameNodeMap; DefaultNode node = localCacheNameMap.get(name); if (node == null) { if (localCacheNameMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) { setNullContext(); return NULL_CONTEXT; } else { try { LOCK.lock(); node = contextNameNodeMap.get(name); if (node == null) { if (contextNameNodeMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) { setNullContext(); return NULL_CONTEXT; } else { node = new EntranceNode(new StringResourceWrapper(name, EntryType.IN), null); // Add entrance node. Constants.ROOT.addChild(node); Map<String, DefaultNode> newMap = new HashMap<>(contextNameNodeMap.size() + 1); newMap.putAll(contextNameNodeMap); newMap.put(name, node); contextNameNodeMap = newMap; } } } finally { LOCK.unlock(); } } } context = new Context(node, name); context.setOrigin(origin); contextHolder.set(context); } return context; } private static boolean shouldWarn = true; private static void setNullContext() { contextHolder.set(NULL_CONTEXT); // Don't need to be thread-safe. if (shouldWarn) { RecordLog.warn("[SentinelStatusChecker] WARN: Amount of context exceeds the threshold " + Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE + ". Entries in new contexts will NOT take effect!"); shouldWarn = false; } } /** * <p> * Enter the invocation context, which marks as the entrance of an invocation chain. * The context is wrapped with {@code ThreadLocal}, meaning that each thread has it's own {@link Context}. * New context will be created if current thread doesn't have one. * </p> * <p> * A context will be bound with an {@link EntranceNode}, which represents the entrance statistic node * of the invocation chain. New {@link EntranceNode} will be created if * current context does't have one. Note that same context name will share * same {@link EntranceNode} globally. * </p> * <p> * Same resource in different context will count separately, see {@link NodeSelectorSlot}. * </p> * * @param name the context name * @return The invocation context of the current thread */ public static Context enter(String name) { return enter(name, ""); } /** * Exit context of current thread, that is removing {@link Context} in the * ThreadLocal. */ public static void exit() { Context context = contextHolder.get(); if (context != null && context.getCurEntry() == null) { contextHolder.set(null); } } /** * Get current size of context entrance node map. * * @return current size of context entrance node map * @since 0.2.0 */ public static int contextSize() { return contextNameNodeMap.size(); } /** * Check if provided context is a default auto-created context. * * @param context context to check * @return true if it is a default context, otherwise false * @since 0.2.0 */ public static boolean isDefaultContext(Context context) { if (context == null) { return false; } return Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME.equals(context.getName()); } /** * Get {@link Context} of current thread. * * @return context of current thread. Null value will be return if current * thread does't have context. */ public static Context getContext() { return contextHolder.get(); } /** * <p> * Replace current context with the provided context. * This is mainly designed for context switching (e.g. in asynchronous invocation). * </p> * <p> * Note: When switching context manually, remember to restore the original context. * For common scenarios, you can use {@link #runOnContext(Context, Runnable)}. * </p> * * @param newContext new context to set * @return old context * @since 0.2.0 */ static Context replaceContext(Context newContext) { Context backupContext = contextHolder.get(); if (newContext == null) { contextHolder.remove(); } else { contextHolder.set(newContext); } return backupContext; } /** * Execute the code within provided context. * This is mainly designed for context switching (e.g. in asynchronous invocation). * * @param context the context * @param f lambda to run within the context * @since 0.2.0 */ public static void runOnContext(Context context, Runnable f) { Context curContext = replaceContext(context); try { f.run(); } finally { replaceContext(curContext); } } }
