1. 阻塞队列首先它是一个队列,是队列就会遵循先进先出(FIFO)的原则,又因为它是阻塞的,故与普通的队列有两点区别:
A. 当一个线程向队列里面添加数据时,如果队列是满的,那么将阻塞该线程,暂停添加数据。
B. 当一个线程从队列里面取出数据时,如果队列是空的,那么将阻塞该线程,暂停取出数据。
2. JUC中实现一个阻塞队列一般都会实现BlockingQueue接口,主要方法说明:
| 方法/处理方式 | 抛出异常 | 返回特殊值 | 一直阻塞 | 超时退出 |
| 插入数据方法 | add(e) | offer(e) | put(e) | offer(e, timeout, unit) |
| 移除数据方法 | remove() | poll() | take() | pull(timeout, unit) |
| 检查方法 | element() | peek() | 不可用 | 不可用 |

注:"返回特殊值"的意思是说当向队列插入(offer)数据时,会返回数据是否插入成功,成功返回true。如果是移除方法(poll),则是从队列里面取出一个数据,如果没有就返回null。
3. jdk里提供的阻塞队列
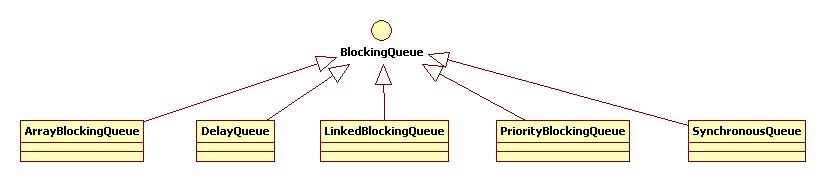
1). ArrayBlockingQueue
基于数组的阻塞队列实现,其内部维护一个定长的数组,用于存储队列元素。线程阻塞的实现是通过ReentrantLock来完成的,数据的插入与取出共用同一个锁,因此ArrayBlockingQueue并不能实现生产、消费同时进行。而且在创建ArrayBlockingQueue时,我们还可以控制对象的内部锁是否采用公平锁,默认采用非公平锁。
2). LinkedBlockingQueue
基于单向链表的阻塞队列实现,在初始化LinkedBlockingQueue的时候可以指定对立的大小,也可以不指定,默认类似一个无限大小的容量(Integer.MAX_VALUE),不指队列容量大小也是会有风险的,一旦数据生产速度大于消费速度,系统内存将有可能被消耗殆尽,因此要谨慎操作。另外LinkedBlockingQueue中用于阻塞生产者、消费者的锁是两个(锁分离),因此生产与消费是可以同时进行的。
3). PriorityBlockingQueue 一个支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列
4). SynchronousBlockingQueue 一个不存储原色的阻塞队列
5). DelayQueue 一个使用优先级队列队列实现的无界阻塞队列
4. 实现一个简单的阻塞队列,基于List实现,生产、消费共用同一个锁,而且是一个有界的队列
1). 实现阻塞队:MyBlockingQueue
1 package com.winter.juc; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; 5 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; 6 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 7 8 public class MyBlockingQueue<E> { 9 10 private int count; 11 private int capacity; 12 private final List<E> containor; 13 14 private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 15 private final Condition notFull = lock.newCondition(); 16 private final Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition(); 17 18 public MyBlockingQueue(int capacity) { 19 containor = new ArrayList<E>(capacity); 20 this.count = 0; 21 this.capacity = capacity; 22 } 23 24 public void put(E data) throws InterruptedException { 25 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 26 try { 27 while (count == capacity) { 28 notFull.await(); 29 } 30 containor.add(data); 31 this.count++; 32 notEmpty.signal(); 33 } finally { 34 lock.unlock(); 35 } 36 } 37 38 public E take() throws InterruptedException { 39 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 40 try { 41 while (count == 0) { 42 notEmpty.await(); 43 } 44 this.count--; 45 notFull.signal(); 46 E node = containor.get(0); 47 containor.remove(0); 48 return node; 49 } finally { 50 lock.unlock(); 51 } 52 } 53 }
2).接下来使用该队列
生产者:
1 package com.winter.juc; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 4 import org.apache.commons.lang3.RandomUtils; 5 6 public class Productor implements Runnable { 7 private MyBlockingQueue<NodeItem> queue; 8 9 public Productor(MyBlockingQueue<NodeItem> queue) { 10 this.queue = queue; 11 } 12 13 public void run() { 14 while (true) { 15 try { 16 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(RandomUtils.nextInt(0, 5)); 17 NodeItem node = new NodeItem(); 18 node.setKey(GlobalKey.get()); 19 System.out.println("produce a node" + node); 20 queue.put(node); 21 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 } 24 } 25 } 26 }
消费者:
1 package com.winter.juc; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 4 import org.apache.commons.lang3.RandomUtils; 5 6 public class Customer implements Runnable { 7 private MyBlockingQueue<NodeItem> queue; 8 public Customer(MyBlockingQueue<NodeItem> queue) { 9 this.queue = queue; 10 } 11 12 public void run() { 13 while (true) { 14 try { 15 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(RandomUtils.nextInt(0, 5)); 16 NodeItem node = queue.take(); 17 System.out.println("consume a node" + node); 18 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 } 22 23 } 24 }
元素实体:
1 package com.winter.juc; 2 public class NodeItem { 3 4 private int key; 5 6 public int getKey() { 7 return key; 8 } 9 10 public void setKey(int key) { 11 this.key = key; 12 } 13 14 @Override 15 public String toString() { 16 return "NodeItem{" + 17 "key=" + key + 18 '}'; 19 } 20 }
全局键值:
1 package com.winter.juc; 2 import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; 3 public class GlobalKey { 4 5 private static AtomicInteger key = new AtomicInteger(1); 6 7 public static int get() { 8 return key.getAndIncrement(); 9 } 10 }
main方法:
1 package com.winter.juc; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 4 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 5 6 public class ProviderService { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 9 final MyBlockingQueue blockingQueue = new MyBlockingQueue(3); 10 11 ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); 12 13 exec.submit(new Productor(blockingQueue)); 14 exec.submit(new Customer(blockingQueue)); 15 } 16 }
执行结果:
product a nodeNodeItem{key=1}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=1}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=2}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=2}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=3}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=3}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=4}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=4}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=5}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=6}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=5}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=7}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=6}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=7}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=8}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=8}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=9}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=9}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=10}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=11}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=12}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=10}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=11}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=13}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=14}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=12}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=15}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=13}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=16}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=17}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=14}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=18}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=15}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=19}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=16}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=17}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=18}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=20}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=19}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=20}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=21}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=21}
product a nodeNodeItem{key=22}
custom a nodeNodeItem{key=22}
可以看到product和custom是对应执行的。
后续会继续实现一个类似LinkedBlockingQueue的阻塞队列,支持锁分离。
注:本人水平有限,如有问题,欢迎交流指出。