总结
- iO流用来处理设备之间的数据传输。
- Java程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以”流(stream)” 的方式进行
- 输入input:读取外部数据(磁盘、光盘等存储设备的数据)到程序(内存)中。
- 输出output:将程序(内存)数据输出到磁盘、光盘等存储设备中
IO流体系
- 按操作数据单位不同分为:字节流(8 bit),字符流(16 bit)
- 按数据流的流向不同分为:输入流,输出流
- 按流的角色的不同分为:节点流,处理流
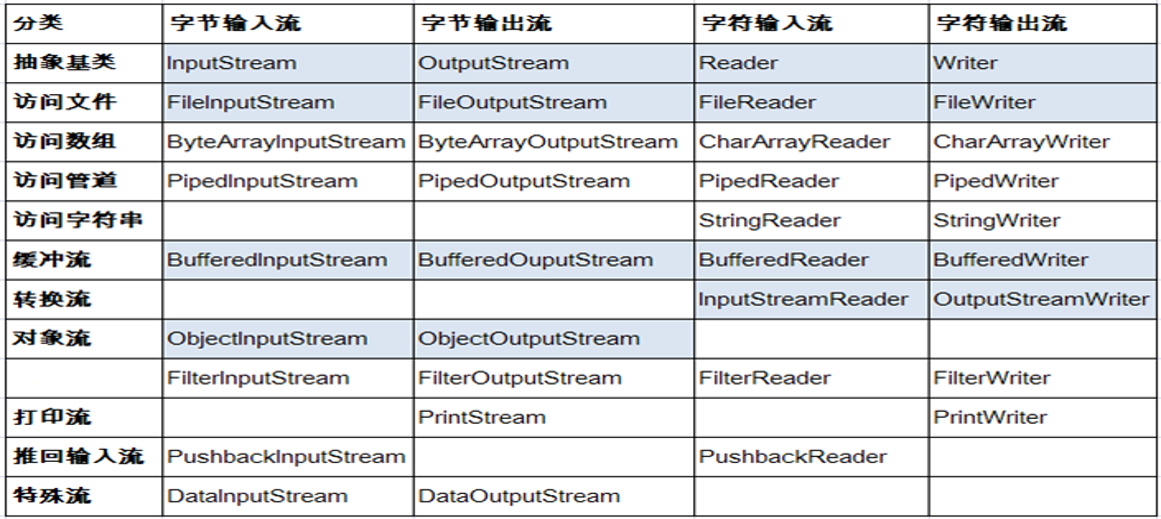
- Java的IO流共涉及40多个类,实际上非常规则,都是从如下4个抽象基类派生的。
由这四个类派生出来的子类名称都是以其父类名作为子类名后缀。
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//文件字节输入流
Test3.testFileInputStream();
//文件字节输出流
Test3.testOutputStream();
}
//文件字节输入流
public static void testFileInputStream() {
try {
//创建FileInputStream对象
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("D:\test\tt.txt");
//定义byte类型的数组,设置一个读取数据的长度
byte[] b = new byte[10];
//in.read(b)方法有一个返回值,返回值是读取的数据的长度,如果读取到最后一个数据,还会向后读一个
//也就意味着当in.read(b)的返回值是-1时,整个文件读取完毕了
// in.read(b);
// System.out.println(new String(b));//打印要转string字符
// System.out.println(b);//[B@123772c4
// in.close();
int len = 0;
while((len=in.read(b)) != -1) {
//参数1是缓冲数据的数组,参数2是数组的哪个位置开始转化字符串,参数总共转化几个字符
System.out.println(new String(b,0,len));
}
in.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//文件字节输出流
public static void testOutputStream() {
try {
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("D:\test\tt1.txt");
String str = "abdadf11232";
out.write(str.getBytes());//将数据写到内存
out.flush();//将内存中的数据刷写到硬盘
out.close();//关闭流
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
文件字节流拷贝文件
/**
* 文件字节流非常通用,可以用来操作字符的文档,还可以操作任何的其他类型文件(图片,压缩包等等),引用字节流直接使用二进制
* @author Zw
*
*/
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test4.copyFile("D:/test/tt.txt", "D:/test/aa/tt3.txt");
}
public static void copyFile(String inPath,String outPath) {
try {
//创建输入流对象,原文件
//在读取文件时,必须保证该文件已存在,否则出异常
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(inPath);
//输出流,复制到哪
//在写入一个文件时,如果目录下有同名文件将被覆盖
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(outPath);
//定义byte数组
byte[] b = new byte[100];
//定义缓冲长度
int len = 0;
//边读边写
while((len = in.read(b)) !=-1) {//读取文件
out.write(b, 0, len);//写入指定位置
}
out.flush();//从内存刷入硬盘
out.close();//先关闭输出流
in.close();//后关闭输入流
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO 自动生成的 catch 块
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
文件字符流拷贝文件
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test5.copyFile("D:/test/aa/tt.txt", "D:/test/bb/tt.txt");
}
public static void copyFile(String inPath,String outPath) {
try {
//创建流对象,建立数据存放文件
FileReader fr = new FileReader(inPath);//创建文件字节输入流对象
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(outPath);//目标路径
char[] ch = new char[1024];//创建一个临时存储数据的字符数组
//缓冲长度
int len = 0;//定义一个输入流的读取长度
while((len=fr.read())!=-1) {//读取字符流
//调用流对象的写入方法,将数据写入流
fw.write(ch, 0, len);
}
//输出流关闭之前需要清空缓存
fw.flush();
//关闭流资源
fw.close();
fr.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
缓冲字节流
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// Test.testBufferedInputStream();
// Test.testBufferedOutputStream();
Test.copyFile();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 缓冲字节输入流
* BufferedInputStream
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void testBufferedInputStream() throws Exception{
//文件字节输入流对象
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("E:\eclipse-workspace\javademo\src\com\day09\tt.txt");
//把文件字节输入流放到缓冲字节输入流对象
BufferedInputStream br = new BufferedInputStream(in);
byte[] b = new byte[10];
int len = 0;
while((len = br.read(b)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(b,0,len));
}
//关闭流的时候,本着一个最晚开的最早关,依次关
br.close();
in.close();
}
/**
* 缓冲字节输出流
* BufferedOutputStream
*/
public static void testBufferedOutputStream() throws Exception{
//创建字节输出流对象
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("E:\eclipse-workspace\javademo\src\com\day09\tt2.txt");
//把字节输出流对象放到缓冲字节输出流中
BufferedOutputStream bo = new BufferedOutputStream(out);
String s = "hello world";
bo.write(s.getBytes());//写到内存中
bo.flush();//刷到硬盘上
//关闭流的时候,本着一个最晚开的最早关,依次关
bo.close();
out.close();
}
/**
* 缓冲流实现文件的复制
*/
public static void copyFile() throws Exception{
//缓冲输入流
BufferedInputStream br = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:\eclipse-workspace\javademo\src\com\day09\tt.txt"));
//缓冲输出流
BufferedOutputStream bo = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:\eclipse-workspace\javademo\src\com\day09\tt2.txt"));
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;//设置一个没出读取到的数据的长度,直到br.read方法执行到最后(比如说文件中只有hello world,执行到最后一个就读取d的后面,这个时候返回值就是-1)
while((len = br.read(b)) != -1){
bo.write(b, 0, len);//写到内存
}
bo.flush();//刷到硬盘
bo.close();
br.close();
}
}
输入转换流
-
转换流提供了在字节流和字符流之间的转换
-
Java API提供了两个转换流:
InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter
-
字节流中的数据都是字符时,转成字符流操作更高效。
-
用于将字节流中读取到的字节按指定字符集解码成字符。需要和InputStream“套接”。
-
构造方法
InputStreamReader(InputStream in) public InputSreamReader(InputStream in,String charsetName) Reader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in,”ISO5334_1”);
输出转化流
- OutputStreamWriter用于将要写入到字节流中的字符按指定字符集编码成字节。需要和OutputStream“套接”。
- 构造方法
public OutputSreamWriter(OutputStream out,String charsetName)
转化流代码
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// Test2.testInputStreamReader();
Test2.testOutputStreamWriter();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/*
* 输入流转化
* InputStreamReader
*/
public static void testInputStreamReader() throws Exception {
//字节输入流
FileInputStream fs = new FileInputStream("E:\eclipse-workspace\javademo\src\com\day09\tt3.txt");
//创建字符输入流对象
InputStreamReader sr = new InputStreamReader(fs,"GBK");//第一个参数:字节输入流对象,第二个参数:编码格式,编码格式要与输入的文件一致,否则会出现乱码
//临时数组
char [] c = new char[1024];
int len = 0;
//读取输入流
while((len=sr.read(c))!=-1) {
System.out.println(new String(c,0,len));
}
sr.close();
fs.close();
}
/*
* OutputStreamWriter
* 输出流转化
*/
public static void testOutputStreamWriter() throws Exception{
FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream("E:\eclipse-workspace\javademo\src\com\day09\tt4.txt");
OutputStreamWriter os = new OutputStreamWriter(fo,"GBK");
os.write("哈哈哈");
os.flush();
os.close();
fo.close();
}
}
标准输入
-
System.in和System.out分别代表了系统标准的输入和输出设备,默认输入设备是键盘,输出设备是显示器
-
System.in的类型是InputStream
-
System.out的类型是PrintStream,其是OutputStream的子类FilterOutputStream 的子类
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// Test3.testSystemIn();
Test3.testTXT();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/*
* 标准输入流
* testSystemIn
*/
public static void testSystemIn()throws Exception {
//创建用户字符输入流
InputStreamReader sr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
//写入到缓冲中
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(sr);
//定义一个临时字符串
String str = "";
while((str=br.readLine())!=null) {
System.out.println(str);
}
br.close();
sr.close();
}
/*
* 把控制台输入的内容写到指定的TXT文件中,当接收到字符串over,就结束程序的运行
*/
public static void testTXT()throws Exception {
//创建用户字符输入流
InputStreamReader sr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
//写入到缓冲中
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(sr);
//缓冲输出流,用来写入到文件
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("E:\eclipse-workspace\javademo\src\com\day09\tt5.txt"));
//定义一个临时字符串
String str = "";
while((str=br.readLine())!=null) {
if(str.equals("over")) {
break;
}
bw.write(str+"
");
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
sr.close();
}
}