这两天简单整理了一下MyBatis
相关api和jar包这里提供一个下载地址,免得找了
链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1jIl1KaE 密码:d2yl
A.简单搭建跑项目

2.进行相关xml配置
放在根目录下

3.配置数据库映射文件
这里给个例子文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.jhdx.mapper.T_CustomerMapper">
<!-- 通过编号查询用户 -->
<select id="getAllCustomer" resultType="Customer">
select * from t_customer
</select>
<select id="getCustomerById" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultType="Customer">
select * from t_customer where id=#{id}
</select>
<select id="getCustomerByName" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="Customer">
select * from t_customer where name like "%"#{name}"%"
</select>
<insert id="insertCustomer" parameterType="Customer">
insert into t_customer(name,age,tel) values(#{name},#{age},#{tel})
</insert>
</mapper>
4.测试,读取配置文件

String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream=null;
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//创建session工厂
SqlSession session=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//调用接口方法
T_CustomerMapper t_CustomerMapper=session.getMapper(T_CustomerMapper.class);
T_Customer t_Customer = new T_Customer();
t_Customer=t_CustomerMapper.getCustomerByName("1");
System.out.println(t_Customer.getName());
这种是通过代理方式
当然也可以直接通过session读取xml写的方法

B.一些技巧
1.直接使用注解进行sql的编写和映射
在dao接口里直接使用注解
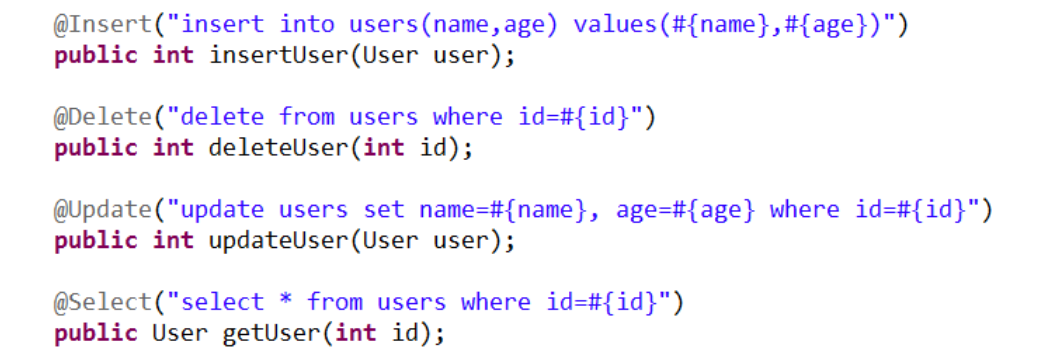
当然,在配置文件还需要配置一下

<mappers>
<!-- 配置映射文件 -->
<mapper resource="com/jhdx/mapper/T_customerMapper.xml" />
<mapper class="com.jhdx.mapper.T_customerMapper" />
</mappers>
如上图,mappers里配置一个class即可
2.关于模糊查询

<select id="getCustomerByName" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="Customer">
select * from t_customer where name like "%"#{name}"%"
</select>
3.关于一对一的关联
a)对结果进行处理,实际只执行一条sql语句,api叫嵌套结果

配置一个resultMap即可
标签分别是数据库的字段与实体类的映射
<association></association>标签里是对对象的映射
注意javaType指的是实体类 column指的是 表连接时使用的字段 例如上图的例子中就是c.teacher_id=t.t_id 使用的是teacher_id
一般配置具体字段的标签使用<id></id>配置主键Id <result></result>配置其他的字段 里面的属性分别是 property对应的是实体类的成员变量 column对应的是数据库的字段
b)对过程进行处理,实际执行多条sql语句,api叫嵌套查询

如图,首先执行的是select * from Class where c_id=#{id}
接着对结果集进行封装 封装到teacher的时候再执行一条查询语句 注意多了一个select的属性 指的就是第二条查询语句
参数通过 teacher_id传递过去 也就是属性里column的值传递过去
4.关于一对多的关联
a)对结果进行处理,实际只执行一条sql语句,api叫嵌套结果

其他和上面的一对一一样
只是配置 一对多 多的集合的时候 使用
<collection></collection>标签 注意属性了不是javaType而是ofType ,当然实体类也要配置相应的集合成员变量
然后column可以不指定 也可以指定 指定的列名是 根据这个列名可以查询到相关集合对象的那个列
里面的标签还是作相应 实体类的成员变量和数据库字段的对应
b)对过程进行处理,实际执行多条sql语句,api叫嵌套查询

和1对1类似 多了一个 collection标签 注意select 选择的第二条查询语句id以及column是用来传值的
如果说实体类的属性没有设置全的话 查询语句要自己设置别名(与实体类一致) 否则会映射失败

<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.jhdx.model.entity.User">
<id column="userId" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="userid" />
<result column="userName" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="username" />
<result column="userPwd" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userpwd" />
<collection property="contents" ofType="Content" column="userId" select="selectAllContents"></collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectAllContents" resultType="Content" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
select * from content where userId=#{userId}
</select>
5.关于sql标签
这个元素可以被用来定义可重用的 SQL 代码段,可以包含在其他语句中。它可以被静态地(在加载参数) 参数化. 不同的属性值通过包含的实例变化. 比如:
<sql id="userColumns"> ${alias}.id,${alias}.username,${alias}.password </sql>
这个 SQL 片段可以被包含在其他语句中,例如:

<select id="selectUsers" resultType="map"> select <include refid="userColumns"><property name="alias" value="t1"/></include>, <include refid="userColumns"><property name="alias" value="t2"/></include> from some_table t1 cross join some_table t2 </select>
属性值可以用于包含的refid属性或者包含的字句里面的属性值,例如:

<sql id="sometable">
${prefix}Table
</sql>
<sql id="someinclude">
from
<include refid="${include_target}"/>
</sql>
<select id="select" resultType="map">
select
field1, field2, field3
<include refid="someinclude">
<property name="prefix" value="Some"/>
<property name="include_target" value="sometable"/>
</include>
</select>
5.关于动态sql
常用的有if,choose(when,otherwise),trim(where,set),foreach,bind
用法类似于jstl标签
详情还是翻看api吧,里面的例子简单明了,这里就不直接列举了
6.关于传入多个参数的问题
常用的有三种方法
1.使用#{0},#{1}....

DAO层的函数方法 Public User selectUser(String name,String area); 对应的Mapper.xml <select id="selectUser" resultMap="BaseResultMap"> select * from user_user_t where user_name = #{0} and user_area=#{1} </select>
2.使用map进行传递(不建议,无法通过接口看到传递的是什么参数)

此方法采用Map传多参数. Dao层的函数方法 Public User selectUser(Map paramMap); 对应的Mapper.xml <select id=" selectUser" resultMap="BaseResultMap"> select * from user_user_t where user_name = #{userName,jdbcType=VARCHAR} and user_area=#{userArea,jdbcType=VARCHAR} </select> Service层调用 Private User xxxSelectUser(){ Map paramMap=new hashMap(); paramMap.put(“userName”,”对应具体的参数值”); paramMap.put(“userArea”,”对应具体的参数值”); User user=xxx. selectUser(paramMap);}
3.使用注解进行传递(建议,简单明了)

Dao层的函数方法 Public User selectUser(@param(“userName”)Stringname,@parm(“userArea”String area); 对应的Mapper.xml <select id=" selectUser" resultMap="BaseResultMap"> select * from user_user_t where user_name = #{userName,jdbcType=VARCHAR} and user_area=#{userArea,jdbcType=VARCHAR} </select>
7.关于注解与缓存
常用注解这里一般是@select,@insert,@delete,@update,@param,@result,@resultMap
这里贴个地址吧,讲的比较详细也比较好
缓存详情还是要翻api
可以简单地配置
<cache/>
这个简单语句的效果如下:
-
• 映射语句文件中的所有select 语句将会被缓存。
-
• 映射语句文件中的所有insert,update 和delete 语句会刷新缓存。
-
• 缓存会使用Least Recently Used(LRU,最近最少使用的)算法来收回。
- • 根据时间表(比如no Flush Interval,没有刷新间隔), 缓存不会以任何时间顺序来刷新。
- • 缓存会存储列表集合或对象(无论查询方法返回什么)的1024 个引用。
- 缓存会被视为是read/write(可读 /可写 )的缓存,意味着对象检索不是共享的 ,而 且可以 安全地被调用者修改 ,而不干扰其他调用者或线程所做的潜在修改。
这是默认的缓存配置规则
<cache
eviction="FIFO"
flushInterval="60000"
size="512"
readOnly="true"/>
这个更高级的配置创建了一个 FIFO 缓存,并每隔 60 秒刷新,存数结果对象或列表的 512 个引用,而且返回的对象被认为是只读的,因此在不同线程中的调用者之间修改它们会 导致冲突。 可用的收回策略有:
-
• LRU– 最近最少使用的:移除最长时间不被使用的对象。
-
• FIFO– 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。
-
• SOFT– 软引用:移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象。
- • WEAK– 弱引用:更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象。
当然可以设置自己的缓存以及导入第三方缓存框架
8.关于插件
之前使用过一个国内大牛的myBatis插件
叫做myBatis-plus 感觉非常好用,这里贴个地址,有兴趣的可以看一下
Q&A
1.关于JdbcType是否有必要
1. mybatis中 jdbcType 时间类型
当jdbcType = DATE 时, 只传入了 年月日
jdbcType = TIMESTAMP , 年月日+ 时分秒
使用时, 没有加jdbcType 正常,
加上jdbcType原因(网络): 当传入字段值为null,时,需要加入. 否则报错.
涉及到数据类型可能要转换的时候带上会好些,比如你传入的是Strring对象,而数据库是decimal, 这样能转换为正确的类型,防止类型不匹配而使用不了某些索引
下面赋一个javaType与jdbcType的对应关系

2.关于MyBaits中${}与#{}的区别
1. #将传入的数据都当成一个字符串,会对自动传入的数据加一个双引号。如:order by #user_id#,如果传入的值是111,那么解析成sql时的值为order by "111", 如果传入的值是id,则解析成的sql为order by "id".
2. $将传入的数据直接显示生成在sql中。如:order by $user_id$,如果传入的值是111,那么解析成sql时的值为order by user_id, 如果传入的值是id,则解析成的sql为order by id.
3. #方式能够很大程度防止sql注入。
4.$方式无法防止Sql注入。
5.$方式一般用于传入数据库对象,例如传入表名.
6.一般能用#的就别用$.
MyBatis排序时使用order by 动态参数时需要注意,用$而不是#
