7. Mybatis高级查询
1. 高级结果映射
1. 一对一
假设在RBAC权限系统中,一个用户只能拥有一个角色,实现在查询用户信息的同时获取用户拥有的角色
现在SysUser对象中引用SysRole
//实现在查询用户信息的同时获取用户拥有的角色
SysUser selectUserAndRoleById(Long id);
<select id="selectUserAndRoleById" resultType="SysUser">
select su.id, user_name, user_password, user_email, su.create_time, user_info, head_img,
sr.id as "sysRole.id",
sr.role_name as "sysRole.roleName",
sr.create_by as "sysRole.createBy",
sr.create_time as "sysRole.createTime"
from sys_user su
inner join sys_user_role sur on su.id = sur.user_id
inner join sys_role sr on sur.role_id = sr.id
where su.id = #{id,jdbcType=BIGINT}
</select>
使用自动映射就是通过别名(可以使用 as 也可以使用 resultMap)让 Mybatis自动将值匹配到对应的字段上,简单的别名映射如user_name对应 userName。除此之外 MyBatis还支持复杂的属性映射,可以多层嵌套,例如将role.role_name映射到role.roleName上。 MyBatis会先查找role属性,如果存在role属性就创建role对象,然后在role对象中继续查找 roleName,将 role_name的值绑定到role对象的roleName属性上。
通过一条查询语句将结果映射到不同对象的方式成为关联的嵌套结果映射
关联的嵌套结果映射:
好处: 关联的嵌套结果映射需要关联多个表将所有需要的值一次性查询出来。这种方式的好处是减少数据库查询次数,减轻数据库的压力
缺点:要写很复杂的SQL,并且当嵌套结果更复杂时,不容易一次写正确,由于要在应用服务器上将结果映射到不同的类上,因此也会增加应用服务器的压力。当一定会使用到嵌套结果,并且整个复杂的SQL执行速度很快时,建议使用关联的嵌套结果映射。要么分多次查询,将多次查询的结果组合在一起
使用resultMap实现上述需求
//实现在查询用户信息的同时获取用户拥有的角色,使用resultMap实现
SysUser selectUserAndRoleById2(Long id);
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.yogurt.model.SysUser" >
<!--
WARNING - @mbggenerated
This element is automatically generated by MyBatis Generator, do not modify.
-->
<id column="id" property="id" jdbcType="BIGINT" />
<result column="user_name" property="userName" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="user_password" property="userPassword" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="user_email" property="userEmail" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="create_time" property="createTime" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP" />
<result column="user_info" property="userInfo" jdbcType="LONGVARCHAR" />
<result column="head_img" property="headImg" jdbcType="LONGVARBINARY" />
</resultMap>
<!--注意这边要让 sr.id sr.create_time 起别名并和column对应,不然会有重复列-->
<resultMap id="UserRoleMap" type="SysUser" extends="BaseResultMap">
<result property="sysRole.id" column="role_id"/>
<result property="sysRole.createTime" column="role_createTime"/>
<result property="sysRole.roleName" column="role_name"/>
<result property="sysRole.createBy" column="create_by"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectUserAndRoleById2" resultMap="UserRoleMap">
select su.id, user_name, user_password, user_email, su.create_time, user_info, head_img,
sr.id as "role_id",
sr.role_name,
sr.create_by,
sr.create_time as "role_createTime"
from sys_user su
inner join sys_user_role sur on su.id = sur.user_id
inner join sys_role sr on sur.role_id = sr.id
where su.id = #{id,jdbcType=BIGINT}
</select>
自定义的resultMap使用extends属性继承了MBG自动生成的BaseResultMap然后需要注意的是:让 sr.id、sr.create_time 起别名并和column对应,不然会有重复列
2.association标签
2.1 association一对一配置关联(java类或者resultMap)
这里在UserRoleMap配置的是SysRole的映射,我们在MBG生成Mapper文件时生成了一个BaseResultMap所以我们可以使用association把两部分关联起来
在 resultmap中, association标签用于和一个复杂的类型进行关联,即用于一对的关联配置。可以关联java类(Javatype)也可以直接关联resultMap(resultMap)
association标签包含以下属性:
property:对应实体类中的属性名,必填项。
Javatype:属性对应的Java类型
resultMap:可以直接使用现有的 resultmap,而不需要在这里配置。
columnPrefix:查询列的前缀,配置前缀后,在子标签配置 result的column时可以省略前缀。
涉及到跨文件共享resultMap :
association中的resultMap必须加上你想要引用的resultMap所在文件的namespace
<!--注意这边要让 sr.id sr.create_time 起别名并和column对应,不然会有重复列-->
<resultMap id="UserRoleMap" type="SysUser" extends="userMap">
<!--
property 对应实体类中的属性名
columnPrefix="role_" 配置以后在子result标签中的column自动添加前缀role_
-->
<association property="sysRole" columnPrefix="role_" resultMap="com.yogurt.dao.SysRoleMapper.roleMap"/>
</resultMap>
这样做之后原来的sql从表中的属性就必须加上role_前缀,包括role_name改成role_role_name
sr.id as "role_id",
sr.role_name "role_role_name",
sr.create_by "role_create_by",
sr.create_time as "role_createTime"
2.2 association标签的嵌套查询
前面是通过复杂Sql查询一次得出结果,还可以使用多次简单Sql查询得到结果,这种和业务逻辑手动执行多次简单查询得到结果组合成一个对象一样
association标签的嵌套查询常用的属性如下
- select:另一个映射查询的id, Mybatis会额外执行这个查询获取嵌套对象的结果
- column:列名(或别名),将主查询中列的结果作为嵌套查询的参数,配置方式如column={ prop1=col1,prop2=co12},prop1和prop2将作为嵌套查询的参数。这边的prop1要和接下来执行的sql参数名一致,col1要和查询出来的列名一致
- fetchtype:数据加载方式,可选值为1azy和 eager,分别为延退加载和积极加载,这个配置会覆盖全局的lazyloadingenabled配置。
修改上面需求的实现方式
//实现在查询用户信息的同时获取用户拥有的角色,使用association标签的嵌套查询
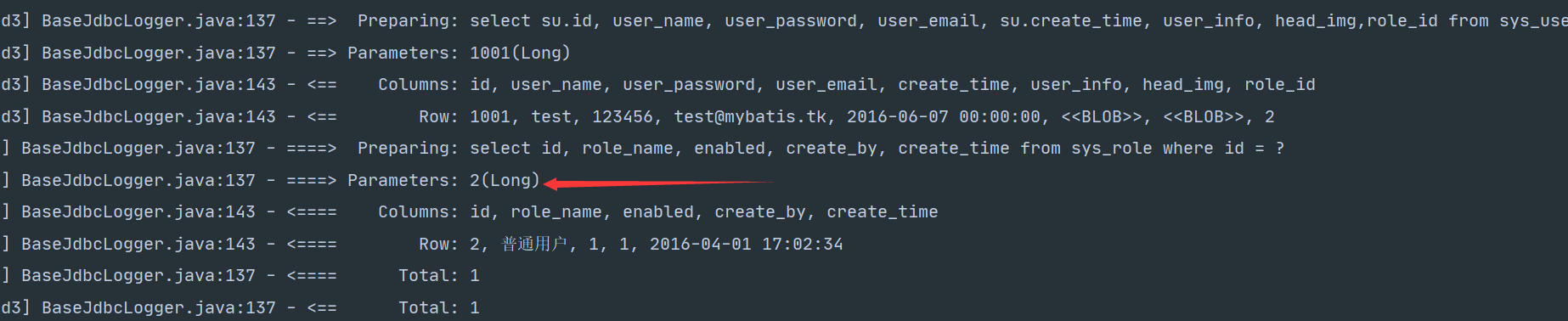
SysUser selectUserAndRoleById3(Long id);
<resultMap id="UserRoleMap2" type="SysUser">
<association property="sysRole" column="{id=role_id}" select="com.yogurt.dao.SysRoleMapper.selectByPrimaryKey"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectUserAndRoleById3" resultMap="UserRoleMap2">
select su.id, user_name, user_password, user_email, su.create_time, user_info, head_img,role_id
from sys_user su
inner join sys_user_role sur on su.id = sur.user_id
where su.id = #{id,jdbcType=BIGINT}
</select>
selectByPrimaryKey是MGB自动生成的,但是生成的时候有一个paramType属性要去掉才不会出错???但根据打印的sql语句传进去的参数确实是Long....不懂
2.3 延迟加载
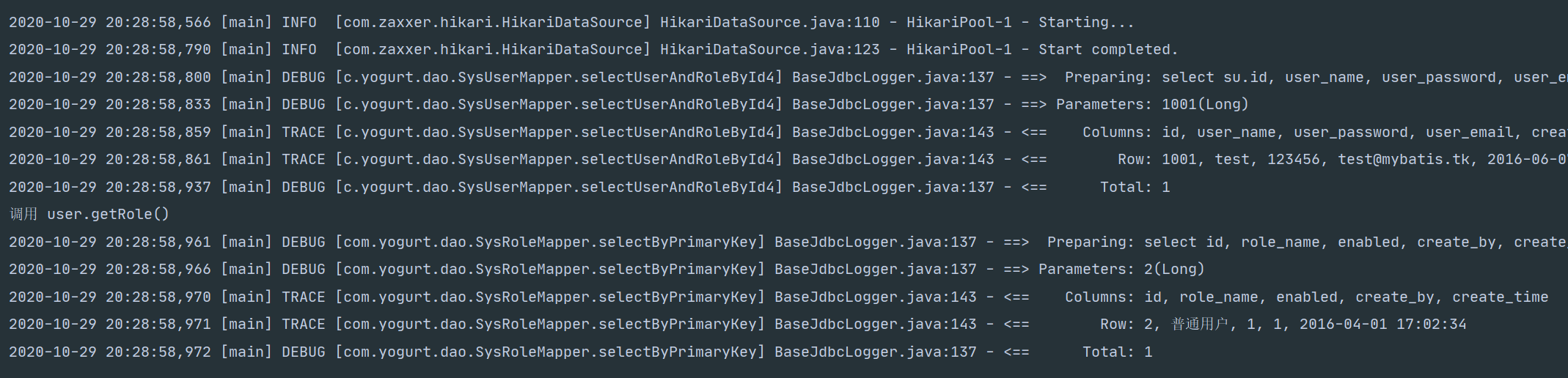
那么执行多条sql语句就有了更多的问题,我们要不要时时刻刻执行第二条sql语句呢(也就是说我们需不需要sysRole对象呢),如果返回的是N条数据(selectAll)那么就会执行N次selectByPrimaryKey,这样是很不值的。这也叫做 N+1 问题
那么就有了延迟加载,只有当调用getRole()的时候Mybatis才回去执行嵌套的sql语句,修改代码如下
-
开启全局配置 aggressive 侵略性的
<!--默认值为true 开启时,任一方法的调用都会加载该对象的所有延迟加载属性。 否则,每个延迟加载属性会按需加载--> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/> <!--延迟加载的全局开关。当开启时,所有关联对象都会延迟加载。 特定关联关系中可通过设置 fetchType 属性来覆盖该项的开关状态。 默认为false--> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> -
修改resultMap
<resultMap id="UserRoleMap3" type="SysUser"> <association property="sysRole" fetchType="lazy" column="{id=role_id}" select="com.yogurt.dao.SysRoleMapper.selectByPrimaryKey" /> </resultMap> -
测试 千万不要在调用getRole()打印对象,这会触发一次延迟加载
@Test void selectUserAndRoleById4() { SysUser sysUser = userMapper.selectUserAndRoleById4(1001L); //log.info(sysUser.toString());不要使用打印语句这会调用getRole()方法执行一次延迟加载 System.out.println("调用 user.getRole() "); Assert.assertNotNull(sysUser.getSysRole()); } -
结果
NOTE:
有时候调用延迟加载会报错,这与sqlSession的生命周期有关,而SqlSession生命周期与某些框架有关(boot)在和 Spring集成时,要确保只能在 Service层调用延迟加载的属性。当结果从 Service层返回至 Controller层时,如果获取延迟加载的属性值,会因为SqlSession已经关闭而抛出异常.
解决办法 :
使用setting lazyLoadTriggerMethods(指定对象的哪些方法触发一次延迟加载 默认值:equals,clone,hashCode,toString)
所以之前我一直没有在日志中看出延迟加载就是因为这个属性...
**总结 : **
实现一对一映射有四种方式:
- 直接在sql语句中起别名
- 使用association关联对象~SysRole
- 使用association关联resluMap~SysRoleMap
- 使用association嵌套查询
3. 一对多
一对多映射只有两种配置方式,都是使用collection标签进行的。
1. collection的嵌套结果映射
和 association类似,集合的嵌套结果映射就是指通过一次SQL查询将所有的结果查询出来,然后通过配置的结果映射,将数据映射到不同的对象中去。在一对多的关系中,主表的一条数据会对应关联表中的多条数据。
一个用户有多个角色,查询出所有用户以及用户所拥有的角色
//一个用户有多个角色,查询出所有用户以及用户所拥有的角色
List<SysUser> selectAllUserAndRoles();
<resultMap id="UserRoleListMap" type="SysUser" extends="userMap">
<collection property="roleList" resultMap="com.yogurt.dao.SysRoleMapper.roleMap" columnPrefix="role_"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectAllUserAndRoles" resultMap="UserRoleListMap">
select su.id, user_name, user_password, user_email, su.create_time, user_info, head_img,
sr.id as "role_id",
sr.role_name "role_role_name",
sr.create_by "role_create_by",
sr.enabled "role_enabled",
sr.create_time as "role_createTime"
from sys_user su
inner join sys_user_role sur on su.id = sur.user_id
inner join sys_role sr on sur.role_id = sr.id
</select>
测试与测试结果
@Test
void selectAllUserAndRoles() {
List<SysUser> users = userMapper.selectAllUserAndRoles();
for (SysUser user : users) {
log.info(user.toString());
List<SysRole> roleList = user.getRoleList();
for (SysRole role : roleList) {
log.info(role.toString());
}
}
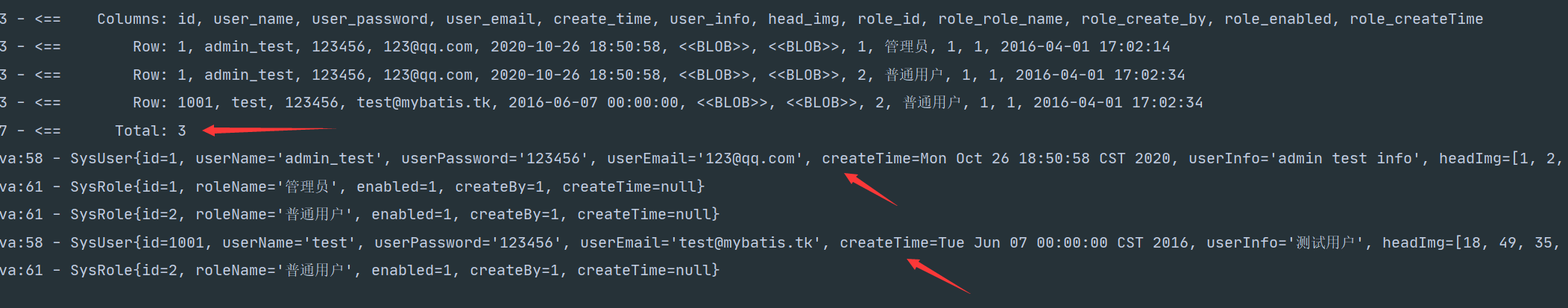
问题 :为什么mybatis会知道哪个用户拥有哪个角色呢?
是因为mybatis在处理结果时会根据判断结果是否相同,如果结果相同则只会保留第一个结果,mybatis判断结果是否相同最简单也是效率最高的就是在UserMap中配置id标签
<id column="id" property="id" jdbcType="BIGINT" />
mybatisResult只用于结果如何映射,并不知道表的结构。所以id标签的唯一作用是在嵌套的映射配置中判断数据是否相同。这样一来就不能那理解虽然返回的是三条数据但是前两条的Id相同,所以前两条数据会合并到一个用户中。
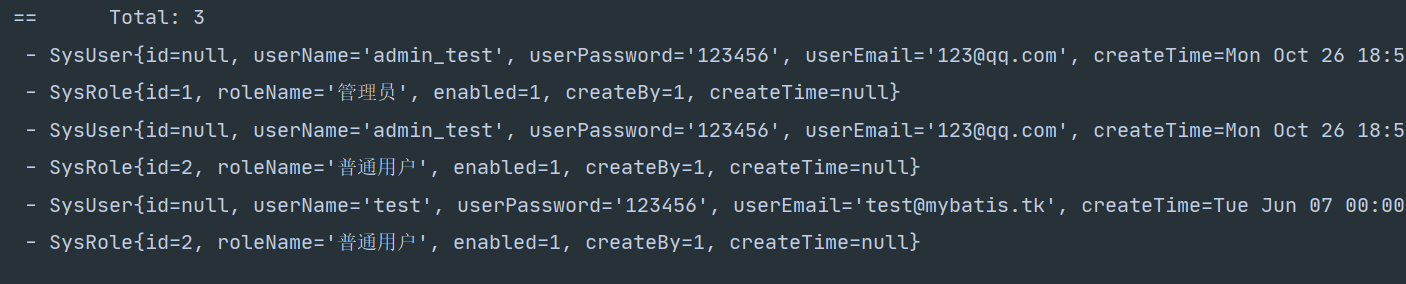
当你把id属性修改成password时会得到如下结果
<id column="user_password" property="userPassword"/>
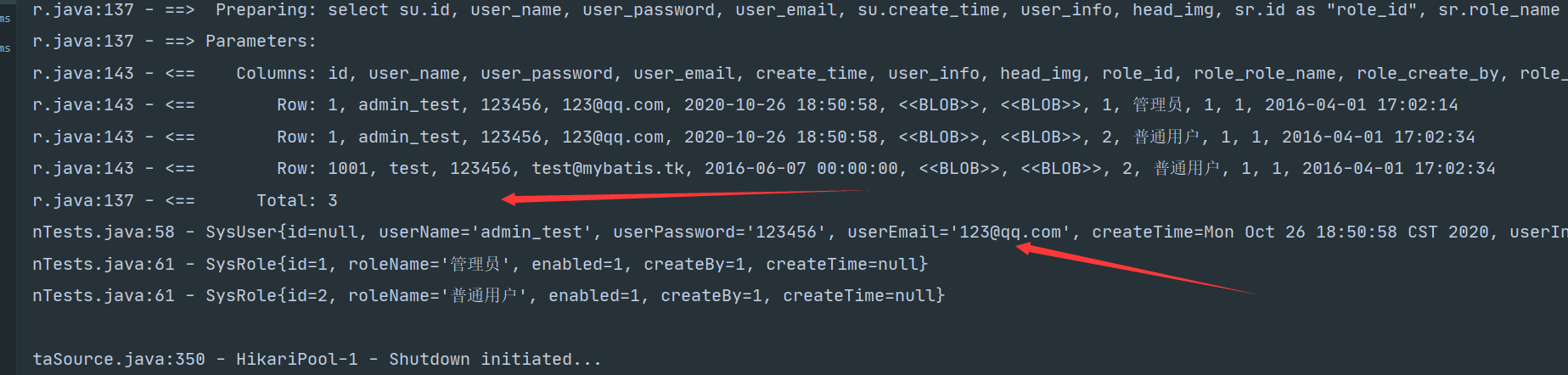
这里的SysRole只有两条是因为 “普通用户” 角色重复只保留第一条
NOTE :
在UserMap里面配置id属性且查询语句中没有id属性,那么id属性会为Null,这会使得嵌套集合中只有一条数据
如果把UserMap的id标签改成result标签结果是正确的,但是Mybatis会比较所有的result标签所对应的字段,使得效率大大降低,
比如返查询的结果是N条,字段是M个,那么mybatis会进行M*N次比对,而配置了Id标签只会比N次,所以必须加id标签
**比较规则 : **
Mybatis会对没一层级的对象进行比较,Mybatis会对顶级对象进行比较,如果SysRole相同那么就比较SysRole对象,如果SysRole不同,就会添加一个SysRole,如果相同就会保留前一个SysRole。如果SysRole还有下一级就以此类推。
需求:,除了一个用户对应多个角色外,每一个角色还会对应多个权限。所以在现有例子的基础上可以再增加一级,获取角色对应的所有权限。
思路:
- 有了一层嵌套以后,第二层嵌套应该在roleMap里面添加,在sql语句中联privilege表,并返回相关字段,来让Mybatis进行映射
实现
-
在SysRole里面添加映射,用于保存角色权限
//该角色拥有的权限 private List<SysPrivilege> privilegeList; -
在SysRoleMapper.xml文件中添加rolePrivilegeListMap
<resultMap id="rolePrivilegeListMap" type="com.yogurt.model.SysRole" extends="roleMap"> <collection property="privilegeList" columnPrefix="privilege_" resultMap="com.yogurt.dao.SysPrivilegeMapper.privilegeMap"/> </resultMap> -
在SysUserMapper.xml中修改userRoleListMap,修改sql语句
<resultMap id="UserRoleListMap2" type="SysUser" extends="userMap"> <collection property="roleList" resultMap="com.yogurt.dao.SysRoleMapper.rolePrivilegeListMap" columnPrefix="role_"/> </resultMap> <select id="selectAllUserAndRolesAndPrivileges" resultMap="UserRoleListMap2"> select su.id, user_name, user_password, user_email, su.create_time, user_info, head_img, sr.id "role_id", sr.role_name "role_role_name", sr.create_by "role_create_by", sr.enabled "role_enabled", sr.create_time "role_createTime", sp.id "role_privilege_id", sp.privilege_name "role_privilege_privilege_name", sp.privilege_url "role_privilege_privilege_url" from sys_user su inner join sys_user_role sur on su.id = sur.user_id inner join sys_role sr on sur.role_id = sr.id inner join sys_role_privilege srp on sr.id = srp.role_id inner join sys_privilege sp on srp.privilege_id = sp.id </select>**NOTE **collection标签中的column字段是叠加的,因为rolePrivilegeListMap也有collection标签且继承了roleMap那么要是的Mybatis正确的映射到SysRole类中的privilegeList属性,那么对应的列名加前缀
role_privilege_例如sp.privilege_name "role_privilege_privilege_name" -
测试
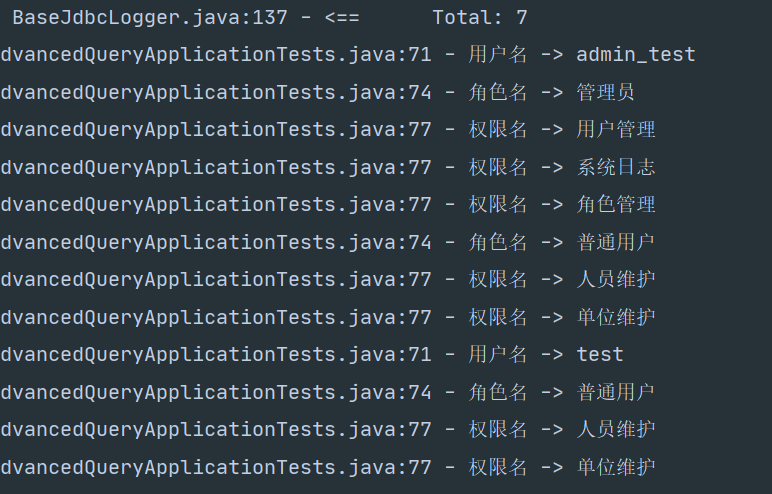
@Test void selectAllUserAndRolesAndPrivileges() { List<SysUser> users = userMapper.selectAllUserAndRolesAndPrivileges(); for (SysUser user : users) { log.info("用户名 -> "+user.getUserName()); List<SysRole> roleList = user.getRoleList(); for (SysRole role : roleList) { log.info("角色名 -> "+role.getRoleName()); List<SysPrivilege> privilegeList = role.getPrivilegeList(); for (SysPrivilege sysPrivilege : privilegeList) { log.info("权限名 -> "+sysPrivilege.getPrivilegeName()); } } } } -
测试结果
一个复杂的嵌套查询,因该从基础映射一步步开始配置,添加一层就检测一层
2.collection集合的嵌套查询
association关联的嵌套查询会使得映射配置简单很多,collection也一样
需求:通过用户Id获取用户,以及用户的所有角色,以及角色所有的权限
//一个用户有多个角色,查询出所有用户以及用户所拥有的角色以及角色拥有的权限
//基于collection的集合嵌套查询
SysUser selectUserAllRolesAndPrivilegesById(Long id);
xml实现
<resultMap id="UserRoleListMap3" type="SysUser" extends="userMap">
<collection property="roleList" column="{user_id = id}" select="com.yogurt.dao.SysRoleMapper.selectRoleByUserId"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectUserAllRolesAndPrivilegesById" resultMap="UserRoleListMap3">
select id,
user_name,
user_password,
user_email,
su.create_time,
user_info,
head_img
from sys_user su
where id = #{id}
</select>
<resultMap id="rolePrivilegeListMap2" type="com.yogurt.model.SysRole" extends="roleMap">
<collection property="privilegeList" column="{role_id = id}" select="com.yogurt.dao.SysPrivilegeMapper.selectPrivilegeByRoleId"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectRoleByUserId" resultMap="rolePrivilegeListMap2">
select id, role_name, enabled, create_by, create_time
from sys_role
inner join sys_user_role sur on sys_role.id = sur.role_id
where user_id = #{user_id}
</select>
<select id="selectPrivilegeByRoleId" resultMap="privilegeMap">
select id, privilege_name, privilege_url
from sys_privilege
right join sys_role_privilege srp on sys_privilege.id = srp.privilege_id
where role_id = #{role_id}
</select>
测试
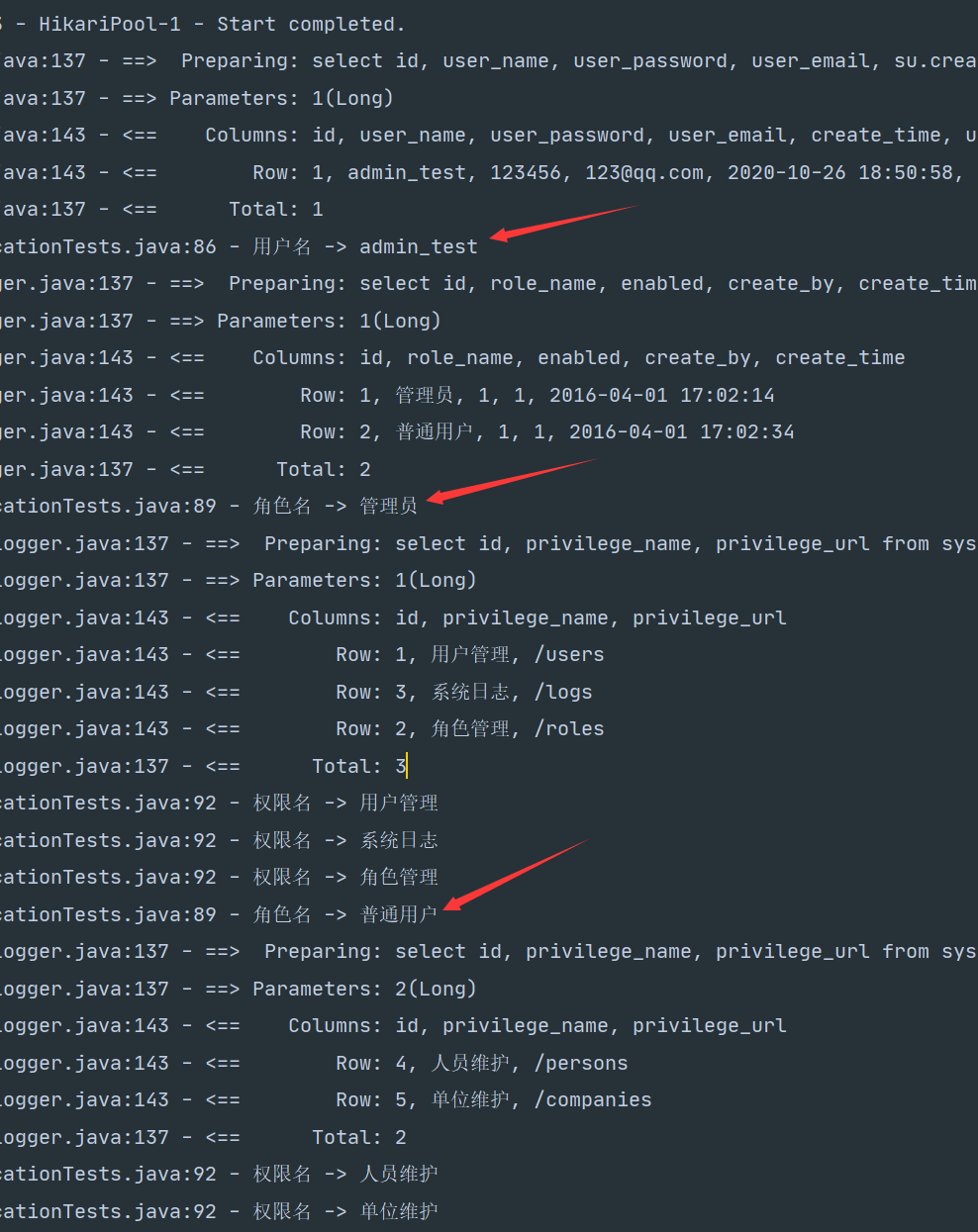
@Test
void selectUserAllRolesAndPrivilegesById() {
SysUser user = userMapper.selectUserAllRolesAndPrivilegesById(1L);
log.info("用户名 -> "+user.getUserName());
List<SysRole> roleList = user.getRoleList();
for (SysRole role : roleList) {
log.info("角色名 -> "+role.getRoleName());
List<SysPrivilege> privilegeList = role.getPrivilegeList();
for (SysPrivilege sysPrivilege : privilegeList) {
log.info("权限名 -> "+sysPrivilege.getPrivilegeName());
}
}
}
结果:由于之前的全局配置,现在嵌套类型都是延迟加载的
我做多层嵌套查询的时候是自上而下的,一层写完测试一下再写下一层,书中是自下而上的,额,这个以后再说
3.鉴别器映射
有时一个单独的数据库査询会返回很多不同数据类型(希望有些关联)的结果集。discriminator鉴别器标签就是用来处理这种情况的。鉴别器非常容易理解,因为它很像 Java语言中的 switch语句。
discriminator标签常用的两个属性如下:
- column:该属性用于设置要进行鉴别比较值的列。
- Javatype:该属性用于指定列的类型,保证使用相同的Java类型来比较值。
discriminator标签可以有1个或多个case标签,case标签包含以下三个属性:
- value:该值为 discriminator指定 column用来匹配的值
- resultMap:当 column的值和 value的值匹配时,可以配置使用 resultMap指定的映射,resultMap优先级高于 resultType
- resultType:当 column的值和 value的值匹配时,用于配置使用 resultType指定的映射。
case标签下面可以包含的标签和resultMap一样,用法也一样。
需求:通过用户Id获取用户,以及用户的所有角色,以及角色所有的权限,
当SysRole的enable标签为1时表示该角色权限可用查出该用户的权限,反之则不用查询该角色的权限
修改上面的例子,在roleMapper.xml中添加如下代码
<resultMap id="rolePrivilegeListMapChoose" type="SysRole">
<discriminator column="enabled" javaType="Integer">
<case value="0" resultMap="roleMap"/>
<case value="1" resultMap="rolePrivilegeListMap2"/>
</discriminator>
</resultMap>
在数据库中修改普通用户的enable使其等于0,测试结果如下
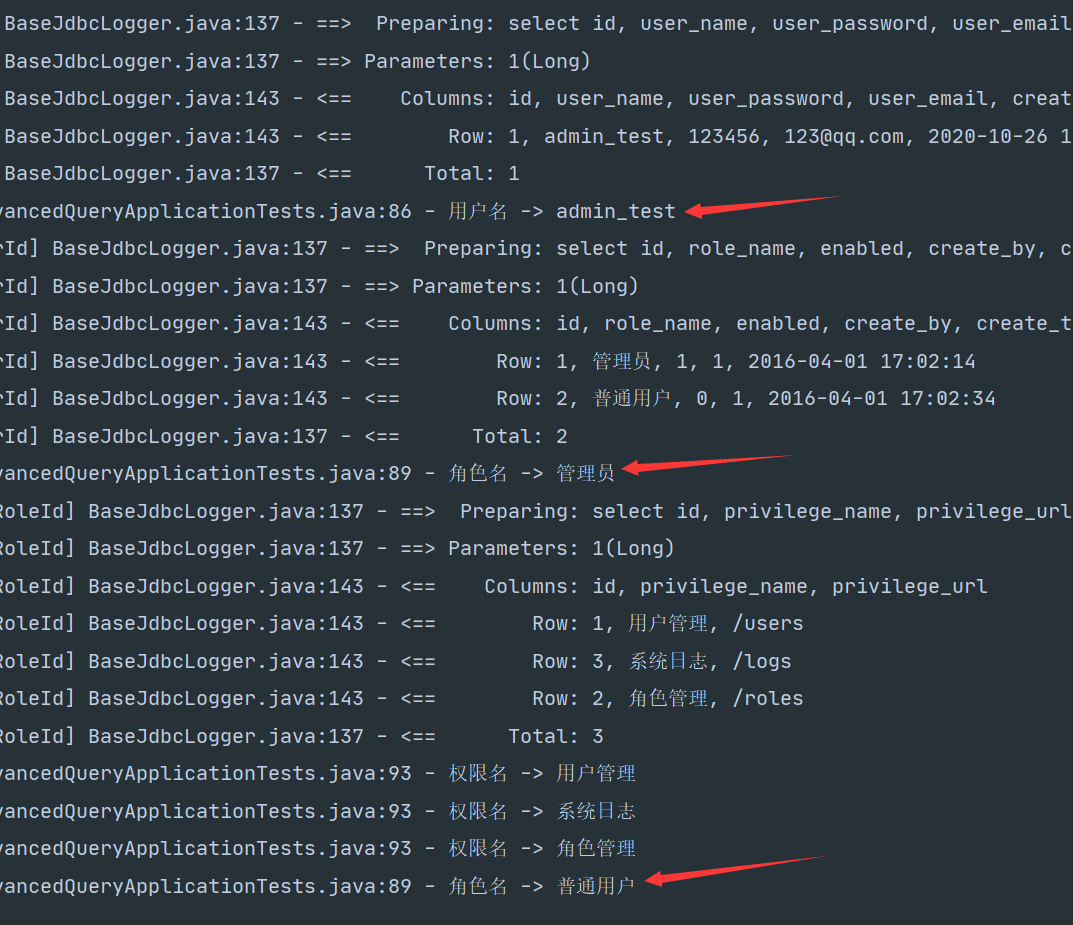
可见当他的enable为0时不会执行嵌套循环。
2.存储过程
存储过程(Stored Procedure)是在大型数据库系统中,一组为了完成特定功能的SQL 语句集,存储在数据库中,经过第一次编译后再次调用不需要再次编译,用户通过指定存储过程的名字并给出参数(如果该存储过程带有参数)来执行它。存储过程是数据库中的一个重要对象。
——百度百科
存储过程使用移步:MySQL数据库存储过程
1.第一个存储过程
在mysql数据库中定义存储过程
#MySQL默认以";"为分隔符,如果没有声明分割符,则编译器会把存储过程当成SQL语句进行处理,因此编译过程会报错,
#所以要事先用“DELIMITER ;;”声明当前段分隔符,让编译器把两个";;"之间的内容当做存储过程的代码,不会执行这些代码;“DELIMITER ;”的意为把分隔符还原。
# 第一个存储过程
# 根据用户 id 查询用户其他信息
# 方法看着很奇葩,但是展示了多个输出参数
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS `select_user_by_id`;
DELIMITER ;;
CREATE PROCEDURE `select_user_by_id`(
IN userId BIGINT,
OUT userName VARCHAR(50),
OUT userPassword VARCHAR(50),
OUT userEmail VARCHAR(50),
OUT userInfo TEXT,
OUT headImg BLOB,
OUT createTime DATETIME)
BEGIN
# 根据用户 id 查询其他数据
SELECT user_name,user_password,user_email,user_info,head_img,create_time
INTO userName,userPassword,userEmail,userInfo,headImg,createTime
FROM sys_user
WHERE id = userId;
END
;;
DELIMITER ;
mybatis的调用过程
//调用存储过程select_user_by_id,返回的值会存放在sysUser属性中
void selectUserById(SysUser sysUser);
这边返回值的void,他会把值赋值进sysUser
<select id="selectUserById" statementType="CALLABLE" useCache="false">
{call select_user_by_id(
#{id,mode = IN},
#{userName,mode = OUT,jdbcType = VARCHAR},
#{userPassword,mode = OUT,jdbcType = VARCHAR},
#{userEmail,mode = OUT,jdbcType = VARCHAR},
#{userInfo,mode = OUT,jdbcType = VARCHAR},
#{headImg,mode = OUT,jdbcType = BLOB,javaType = _byte[]},
#{createTime,mode = OUT,jdbcType = TIMESTAMP}
)}
</select>
OUT模式的参数必须指定jdbcType。这是因为在IN模式下, Mybatis提供了默认的 jdbcType,在OUT模式下没有提供。
jdbcType、mode 指定的值所有字母都要大写
headImg 还制定了javaType,这是因为在mybatis中BLOB对应的javaType是Byte
useCache="false" 不支持mybatis二级缓存
select标签中call里面定义的出入参的顺序要和之前sql语句中定义的出入参顺序一样
mybatis为啥不支持使用基本数据类型?
1.基本数据类型都是有默认值的,在动态sql中,比如说int age默认值为0,那么判断的时候 age != null 恒为true
2.不支持null值,数据库查询的时候很多时候返回的都是null值
2.第二个存储过程
# 第二个存储过程
# 简单的根据用户名和分页参数进行查询,返回总数和分页数据
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS `select_user_page`;
DELIMITER ;;
CREATE PROCEDURE `select_user_page`(
IN userName VARCHAR(50),
IN _offset BIGINT,
IN _limit BIGINT,
OUT total BIGINT)
BEGIN
# 查询数据总数
SELECT COUNT(*) INTO total
FROM sys_user
WHERE user_name LIKE CONCAT('%', userName, '%');
# 分页查询数据
SELECT *
FROM sys_user
WHERE user_name LIKE CONCAT('%', userName, '%')
LIMIT _offset, _limit;
END
;;
DELIMITER ;
//简单的根据用户名和分页参数进行查询,返回总数和分页数据
List<SysUser> selectUserPage(Map<String,Object> params);
<select id="selectUserPage" resultMap="userMap" useCache="false" statementType="CALLABLE">
{call select_user_page(
#{userName,mode = IN},
#{_offset,mode = IN},
#{_limit,mode = IN},
#{total,mode = OUT,jdbcType = BIGINT}
)
}
</select>
这边还设置了resultMap和方法返回值因为存储过程不仅返回了total还返回了查询出来结果集
3.第三个和第四个存储过程
# 第三个存储过程
# 保存用户信息和角色关联信息
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS `insert_user_and_roles`;
DELIMITER ;;
CREATE PROCEDURE `insert_user_and_roles`(
OUT userId BIGINT,
IN userName VARCHAR(50),
IN userPassword VARCHAR(50),
IN userEmail VARCHAR(50),
IN userInfo TEXT,
IN headImg BLOB,
OUT createTime DATETIME,
IN roleIds VARCHAR(200)
)
BEGIN
# 设置当前时间
SET createTime = NOW();
# 插入数据
INSERT INTO sys_user(user_name, user_password, user_email, user_info, head_img, create_time)
VALUES (userName, userPassword, userEmail, userInfo, headImg, createTime);
# 获取自增主键
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID() INTO userId;
# 保存用户和角色关系数据
# roleIds 1,2,3这种形式 INSTR(roleIds, CONCAT(',',id,',')) 检测id是否在roleIds中
SET roleIds = CONCAT(',',roleIds,',');
INSERT INTO sys_user_role(user_id, role_id)
SELECT userId, id FROM sys_role
WHERE INSTR(roleIds, CONCAT(',',id,',')) > 0;
END
;;
DELIMITER ;
# 第四个存储过程
# 删除用户信息和角色关联信息
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS `delete_user_by_id`;
DELIMITER ;;
CREATE PROCEDURE `delete_user_by_id`(IN userId BIGINT)
BEGIN
DELETE FROM sys_user_role WHERE user_id = userId;
DELETE FROM sys_user WHERE id = userId;
END
;;
DELIMITER ;
//保存用户信息和角色关联信息
int insertUserAndRoles(@Param("user") SysUser user,@Param("roleIds") String roleIds);
//删除用户信息和角色关联信息
int deleteUserById(Long id);
<insert id="insertUserAndRoles" statementType="CALLABLE">
{call insert_user_and_roles(
#{user.id,mode = OUT,jdbcType = BIGINT},
#{user.userName,mode = IN},
#{user.userPassword,mode = IN},
#{user.userEmail,mode = IN},
#{user.userInfo,mode = IN},
#{user.headImg,mode = IN,jdbcType = BLOB},
#{user.createTime,mode = OUT,jdbcType = TIMESTAMP},
#{roleIds,mode = IN}
)}
</insert>
<delete id="deleteUserById" statementType="CALLABLE">
{call delete_user_by_id(
#{id,mode = IN}
)}
</delete>
4. Enum类型处理
在之前的例子中enable为1表示该角色有效,为0表示该角色无效。这种是通过手动校验是否合法的,那么值多了就不好判断了,这种情况用enum类比较合适
public enum Enabled {
enabled(1), //启用
disabled(0);//禁用
private final int value;
private Enabled(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
}
mybatis在处理java和数据库类型时,使用的时TypeHandler,处理enum默认的是EnumTypeHandler,他会将枚举类型转换为字符串字面值,例如Enabled.disabled会转换为“disabled”,另外一种就是org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumOrdinalTypeHandler顾名思义它会将枚举类型转换成索引来处理。
在mybatis-config.xml文件中配置
<typeHandlers>
<typeHandler handler="org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumOrdinalTypeHandler" javaType="com.yogurt.type.Enabled"/>
</typeHandlers>
在运行,不会报错了,但是返回的数据中数据库中的1对应的是disabled,这与需求不符合,那么就要自定义TypeHandler了
public class EnabledTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<Enabled> {
private final HashMap<Integer,Enabled> enabledMap = new HashMap<>();
public EnabledTypeHandler() {
for (Enabled enabled : Enabled.values()) {
enabledMap.put(enabled.getValue(),enabled);
}
}
//preparedStatement设置参数时需要进行类型转换
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, Enabled parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
ps.setObject(i,parameter.getValue());
}
//通过columnName从结果集中取出数据再做转换
@Override
public Enabled getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException {
Integer value = rs.getObject(columnName, Integer.class);
return enabledMap.get(value);
}
//通过columnIndex从结果集中取出数据再做转换
@Override
public Enabled getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
Integer value = rs.getObject(columnIndex, Integer.class);
return enabledMap.get(value);
}
//存储过程用的转换器
@Override
public Enabled getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
Integer value = cs.getObject(columnIndex, Integer.class);
return enabledMap.get(value);
}
}
再修改typeHanler配置即可达到需求