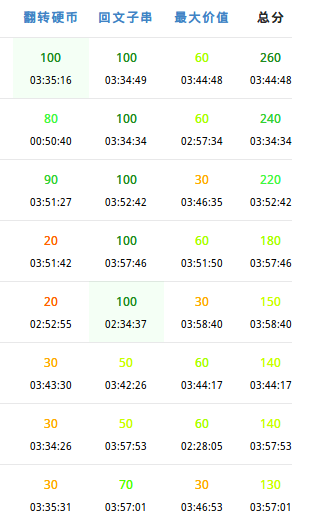
这次考得相对不错,但是没什么水准。
只不过记得T1这道原题而已。虽说我忘了怎么做,而且数据范围不一样。。。差不多是从头想的。
但是并没有AC,像个弱智一样,有两个细节写的完全不对还有80分运气也是真好。
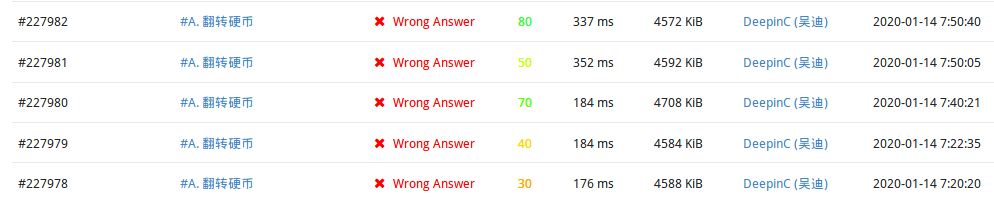
其实挂了不止两个细节。。。以为是原题于是上来就写20分钟写完,然后过一会出一个锅。。。
然后看T2,感觉$O(nk^2)$也许差不多?常数很大。。。但也不会别的。挺好想但是不是很好写。
于是乎强烈谴责cbx没素质暴力水题考后还不改正解的无脸行径
于是就开始写,写了一个半小时。

看T3,绝对大神题啊除了skyh谁会做啊(%%%大神打表)。60分暴力乱弄一个不会证的结论过样例(啥?归纳??)
花了半个小时。还有一个小时。直接放弃T3正解,自知T2板子容易爆炸于是老老实实写个对拍。
暴力疯狂出锅,修好之后发现了正解的锅。修啊修半个小时之后就AC了。
其实是发挥的不错的一次考试。对拍也挺明智的。只不过T1不注重细节单求速度的问题也有所暴露。
今天考试时难得状态上线。。。所以考试结束后累的一匹。。。
顺及:
昨天清了清博客的动态,从32页删到了10页。顺便看了看我联赛前的动态。
我怎么那么颓啊!!!
也活该联赛爆炸。想想最近一段时间也颓的不轻,效率挺低的(虽说最近的确是又累又闷但这并不是合适的理由)
自我督促一下。现在我没有放松的资本。。。
尽量更紧张一些吧。。。
T1:翻转硬币
题意:n硬币正面朝上,每次对一个长为$a_i$的区间翻转(共$m$种$a$),最后要求$k$个特定位置反面朝上其余正面。问最少翻转次数
$n le 10000,mle 100,kle 10$。
0811NOIP模拟测试17的T3《星空》。数据范围略有变化。
然而当时并没有写题解,所以现在再说一说。
区间异或不难想到做差分。于是每次是对相距$a$的点同时操作。最多有$2k$个位置需要操作。
做$2k$次$BFS$找到点对之间相互到达的最少次数,然后做一个状压$dp$。
考场上挂的两个细节:
1,要注意差分之后数列实际上用到了$n+1$位所以上限不要只开到$n$。
2,状压$dp$时每次选出的点对不能与当前状态有交集。
其中状压$dp$的部分可以用那种钦定最小点的思路,这样复杂度会低一些。
最终复杂度$O(2knm+4^kn)$

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 int n,m,k,dt[11111],bp[22][22],sp[11111],p[22],pc,dp[1048577],q[66666],stp[111]; 4 int main(){ 5 scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&k,&m); 6 for(int i=1,x;i<=k;++i)scanf("%d",&x),sp[x]^=1,sp[x+1]^=1; 7 for(int i=1;i<=n+1;++i)if(sp[i])p[pc]=i,pc++; 8 for(int i=1;i<=m;++i)scanf("%d",&stp[i]); 9 for(int i=0,h,t;i<pc;++i){ 10 memset(dt,0x3f,sizeof dt);dt[p[i]]=0;q[h=t=1]=p[i]; 11 for(;h<=t;++h){ 12 for(int j=1;j<=m;++j){ 13 if(q[h]+stp[j]<=n+1&&dt[q[h]+stp[j]]>dt[q[h]]+1)dt[q[++t]=q[h]+stp[j]]=dt[q[h]]+1; 14 if(q[h]-stp[j]>0&&dt[q[h]-stp[j]]>dt[q[h]]+1)dt[q[++t]=q[h]-stp[j]]=dt[q[h]]+1; 15 } 16 }for(int j=0;j<pc;++j)bp[i][j]=dt[p[j]]; 17 } 18 memset(dp,0x3f,sizeof dp);dp[0]=0; 19 for(int s=0;s<(1<<pc)-1;++s){ 20 int fs; 21 for(int j=0;j<pc;++j)if(!(s&1<<j)){fs=j;break;} 22 for(int j=fs+1;j<pc;++j)if(!(s&1<<j))dp[s|1<<fs|1<<j]=min(dp[s|1<<fs|1<<j],dp[s]+bp[j][fs]); 23 } 24 printf("%d ",dp[(1<<pc)-1]>6666666?-1:dp[(1<<pc)-1]); 25 }
T2:回文子串
题意:给定一个字符串,支持区间改为某一个字符,询问区间长度小于等于$k$的回文串个数。$n,mle 50000,kle 50$
突破口自然在$k$。除非你像cbx大神直接n2过。
维护i一个数组$a_{i,j}$表示以$j$结尾的长度为$i$的回文串是否存在$(0/1)$。查询就直接区间$k$次区间和。
如果修改的区间很长,那么对于$[l+k-1,r]$这些位置它们一定都是$1$。区间赋值。
而对于$[l,l+k-1],[r+1,r+k]$这两部分暴力重构,长度很短所以复杂度可以接受。
维护$50$个线段树。对于查询字符串,于是再开个线段树维护字符串。

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define lc p<<1 4 #define rc p<<1|1 5 #define md (cl+cr>>1) 6 #define S 222222 7 char rs[S];int k,q,s[S],ss[S],n;unsigned long long h1[S],h2[S],pw[S]; 8 int palin(int l,int r){return h1[r]-h1[l-1]*pw[r-l+1]==h2[l]-h2[r+1]*pw[r-l+1];} 9 void build_str(int p,int cl,int cr){ 10 if(cl==cr){s[p]=rs[cl]-'a'+1;return;} 11 build_str(lc,cl,md); 12 build_str(rc,md+1,cr); 13 } 14 void down_str(int p){if(s[p])s[lc]=s[p],s[rc]=s[p],s[p]=0;} 15 void ask_str(int l,int r,int p=1,int cl=1,int cr=n){ 16 if(cl==cr){ss[cl]=s[p];return;} 17 down_str(p); 18 if(l<=md)ask_str(l,r,lc,cl,md); 19 if(r>md)ask_str(l,r,rc,md+1,cr); 20 } 21 void chg_str(int l,int r,int w,int p=1,int cl=1,int cr=n){ 22 if(l<=cl&&cr<=r){s[p]=w;return;} 23 down_str(p); 24 if(l<=md)chg_str(l,r,w,lc,cl,md); 25 if(r>md)chg_str(l,r,w,rc,md+1,cr); 26 } 27 struct Segment_Tree{ 28 int w[S];bool lz[S]; 29 void chg(int l,int r,int p=1,int cl=1,int cr=n){ 30 if(l<=cl&&cr<=r){w[p]=cr-cl+1;lz[p]=1;return;} 31 if(l<=md)chg(l,r,lc,cl,md); 32 if(r>md)chg(l,r,rc,md+1,cr); 33 w[p]=w[lc]+w[rc]; 34 } 35 void rebuild(int l,int r,int p=1,int cl=1,int cr=n){ 36 if(cl==cr){w[p]=ss[cl];return;} 37 if(lz[p])w[lc]=md-cl+1,w[rc]=cr-md,lz[lc]=lz[rc]=1,lz[p]=0; 38 if(l<=md)rebuild(l,r,lc,cl,md); 39 if(r>md)rebuild(l,r,rc,md+1,cr); 40 w[p]=w[lc]+w[rc]; 41 } 42 int ask(int l,int r,int p=1,int cl=1,int cr=n){ 43 if(r<l)return 0; 44 if(l<=cl&&cr<=r)return w[p]; 45 if(lz[p])w[lc]=md-cl+1,w[rc]=cr-md,lz[lc]=lz[rc]=1,lz[p]=0; 46 return (l<=md?ask(l,r,lc,cl,md):0)+(r>md?ask(l,r,rc,md+1,cr):0); 47 } 48 }T[55]; 49 int main(){//freopen("2.in","r",stdin);freopen("A.out","w",stdout); 50 scanf("%s%d%d",rs+1,&k,&q);n=strlen(rs+1);build_str(1,1,n); 51 pw[0]=1;for(int i=1;i<=k+1;++i)pw[i]=pw[i-1]*29; 52 for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)h1[i]=h1[i-1]*29+rs[i]-'a'+1; 53 for(int i=n;i;--i)h2[i]=h2[i+1]*29+rs[i]-'a'+1; 54 for(int len=2;len<=k;++len){ 55 for(int i=len;i<=n;++i)ss[i]=palin(i-len+1,i); 56 T[len].rebuild(len,n); 57 } 58 while(q-->0){ 59 int opt,l,r,L,R;scanf("%d%d%d",&opt,&l,&r); 60 if(opt==1){ 61 scanf("%s",rs);chg_str(l,r,rs[0]-'a'+1);L=max(1,l+1-k);R=min(n,r+k-1); 62 if(r-l+1<=k){ 63 ask_str(L,R); 64 for(int i=L;i<=R;++i)h1[i]=h1[i-1]*29+ss[i]; 65 for(int i=R;i>=L;--i)h2[i]=h2[i+1]*29+ss[i]; 66 for(int len=2;len<=k;++len){ 67 for(int i=l;i<=R;++i)ss[i]=i>=len?palin(i-len+1,i):0; 68 T[len].rebuild(l,R); 69 } 70 }else{ 71 ask_str(L,l+k-1); 72 for(int i=L;i<=l+k-1;++i)h1[i]=h1[i-1]*29+ss[i]; 73 for(int i=l+k-1;i>=L;--i)h2[i]=h2[i+1]*29+ss[i]; 74 for(int len=2;len<=k;++len){ 75 for(int i=l;i<=l+len-2;++i)ss[i]=palin(i-len+1,i); 76 T[len].rebuild(l,l+len-2); 77 } 78 ask_str(r-k+1,R); 79 for(int i=r-k+1;i<=R;++i)h1[i]=h1[i-1]*29+ss[i]; 80 for(int i=R;i>=r-k+1;--i)h2[i]=h2[i+1]*29+ss[i]; 81 for(int len=2;len<=k;++len){ 82 for(int i=r+1;i<=r+len-1&&i<=n;++i)ss[i]=palin(i-len+1,i); 83 T[len].rebuild(r+1,min(n,r+len-1)); 84 } 85 for(int len=2;len<=k;++len)T[len].chg(l+len-1,r); 86 } 87 }else{ 88 int ans=r-l+1; 89 for(int i=2;i<=k&&i<=r-l+1;++i)ans+=T[i].ask(l+i-1,r); 90 printf("%d ",ans); 91 } 92 } 93 }
T3:最大权值
题意:$n$物品有参数$a,b$,选出$k$件任意排列的价值为$sum b+a imes (p-1)$。求对所有$1le k le n$的最大价值。
$n le 300000, a le 10^6,b le 10^{12}$
大神都用$\% d$读$long long$。
显然(?)选$k$个物品时的集合是$k+1$时的子集,其实只是插入一个元素其余相对位置不变。
设$dp_{i,j}$表示考虑前$i$个物品选出$j$个的最大收益,做个差分就是每个元素的贡献,设为$g$。
打表发现$dp$转移时两种转移之间有一个明确的分界。考虑二分。
每个点的贡献就是按照题意那么维护,插入一个点之后它左端的点权值不变,右端的要增加一个$a_i$。
插入,区间加,二分。$splay$
不难写。不好想。
$splay$上二分以及$dp$打表都是挺好的思路,记一下。

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define S 333333 4 struct ps{ 5 long long a,b; 6 friend bool operator<(ps x,ps y){return x.a<y.a;} 7 }P[S]; 8 int n,c[2][S],f[S],sz[S],s[S],rt,I,C;long long lz[S],w[S],g[S]; 9 void down(int p){ 10 if(!lz[p])return; 11 w[c[0][p]]+=lz[p];lz[c[0][p]]+=lz[p]; 12 w[c[1][p]]+=lz[p];lz[c[1][p]]+=lz[p]; 13 lz[p]=0; 14 } 15 void up(int p){sz[p]=sz[c[0][p]]+sz[c[1][p]]+1;} 16 void spin(int p){ 17 int F=f[p],G=f[F],d=c[1][F]==p,B=c[!d][p]; 18 if(G)c[c[1][G]==F][G]=p; c[d][c[!d][p]=F]=B; 19 if(B)f[B]=F; f[f[F]=p]=G; 20 up(p);up(F); 21 } 22 void splay(int p){ 23 int F=p,tp=0;while(F)s[++tp]=F,F=f[F];while(tp)down(s[tp]),tp--; 24 for(;F=f[p];spin(p))if(f[F])spin(c[1][f[F]]==F^c[1][F]==p?p:F);rt=p; 25 } 26 void find(int p){ 27 int lp,tsz=0,d; 28 while(p){ 29 down(p); 30 if(w[p]>P[I].a*(tsz+sz[c[0][p]])+P[I].b)tsz+=sz[c[0][p]]+1,p=c[d=1][lp=p]; 31 else p=c[d=0][lp=p]; 32 } 33 f[I]=lp;c[d][lp]=I;w[I]=P[I].a*tsz+P[I].b;sz[I]=1; 34 splay(I);lz[c[1][I]]+=P[I].a;w[c[1][I]]+=P[I].a; 35 } 36 void dfs(int p){ 37 if(!p)return; 38 down(p); 39 dfs(c[0][p]); 40 g[++C]=w[p]; 41 dfs(c[1][p]); 42 } 43 int main(){//freopen("1.in","r",stdin); 44 scanf("%d",&n); 45 for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)scanf("%lld%lld",&P[i].a,&P[i].b); 46 sort(P+1,P+1+n); 47 rt=1;w[1]=P[1].b;sz[1]=1; 48 for(I=2;I<=n;++I)find(rt); 49 dfs(rt); 50 for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)g[i]+=g[i-1],printf("%lld ",g[i]); 51 }
