进程的描述与进程的创建
编程实现一个一个具有执行命令功能的shell
主要思路是通过利用exec函数族来实现用户输入的命令,但是调用exec函数族将会覆盖源程序,因此需要先使用fork()函数生成子进程,在子进程中调用exec函数族,而父进程则使用wait()函数等待子进程完成。
本程序使用的exec函数是execve(),函数原型为int execve(const char * filename,char * const argv[ ],char * const envp[ ]);:
- 第一个参数
filename存储的是执行命令的可执行文件,由于shell中命令的执行文件是存储在/bin/目录下,因此只需在字符串"/bin/"后拼接上输入的命令; - 第二个参数
argv[ ]类型为char * const,存储的是命令的各个参数,生成时把用户输入的命令中的各个参数存储在一个字符串数组中,将argv参数指向各个字符串,最后以NULL结尾; - 第三个参数
envp[ ]存储的则是传递给执行文件的新环境变量数组,直接定义为环境变量PATH。
程序代码如下:
//myshell.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <wait.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int main ()
{
pid_t pid;
int status = -1 ,flag =0,i=0,len=0,n=0,m=0;
char code[80],s_code[20][20];
char file[30]="/bin/";
char* argv[80]; //存储命令的参数
char* envp[ ]={"PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/snap/bin",0};//存储PATH
while (flag == 0)
{
printf("9205-myshell:/$ ");
fgets(code,80,stdin); //读取命令
if (code[0]=='e' && code[1]=='x' && code[2]== 'i' && code[3]== 't' ) flag = 1; //如果命令是exit则退出程序
else
{
//shell
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) printf("error1!!"); //分化进程错误
else if (pid > 0) //父进程
{
wait(&status); //父进程等待子进程完成
}
else if(pid==0) //子进程
{
//将命令中的各个参数存储进 argv
while (code[i] !='
' )
{
if (code[i]!=' ')
{
s_code[m][n]=code[i];
n++;
}
else
{
s_code[m][n]='�';
argv[m]=s_code[m];
m++;
n=0;
}
i++;
}
s_code[m][n]='�';
argv[m]=s_code[m];
m++;
n=0;
argv[m]=(char *)0;
//构成filename
strcat(file,s_code[0]);
//执行命令
execve(file, argv, envp);
//若执行到以下步骤则调用命令时发生错误
printf ("error2!!");
exit(0);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
程序执行效果如下图所示:
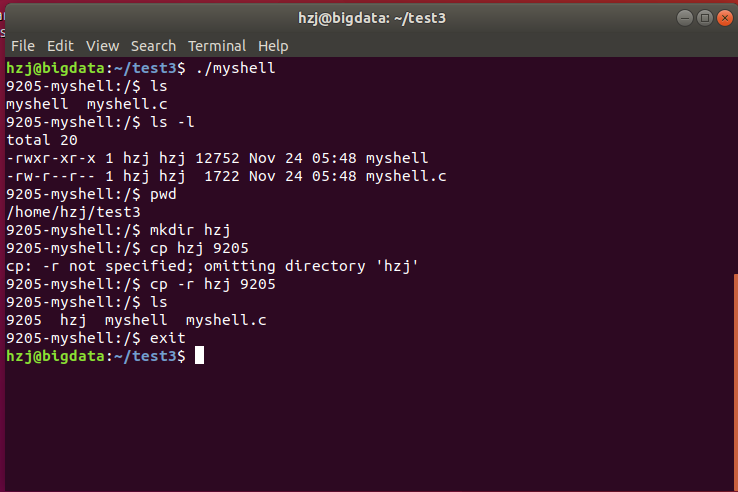
学习测试wait()、waitpid()函数
wait( )函数
其函数功能为等待子进程中断或结束,函数原型为pid_t wait (int * status);。
其参数 status 是一个整形指针。如果status不是一个空指针,则终止进程的终止状态将存储在该指针所指向的内存单元中。如果不关心终止状态,可以将 status参数设置为NULL。以下有几个宏可判别status中存储的结束情况:
- WIFEXITED(status)如果若为正常结束子进程返回的状态,则为真;对于这种情况可执行WEXITSTATUS(status),取子进程传给exit或_eixt的低8位。
- WEXITSTATUS(status)取得子进程 exit()返回的结束代码,一般会先用 WIFEXITED 来判断是否正常结束才能使用此宏。
- WIFSIGNALED(status)若为异常结束子进程返回的状态,则为真;对于这种情况可执行WTERMSIG(status),取使子进程结束的信号编号。
- WTERMSIG(status) 取得子进程因信号而中止的信号代码,一般会先用 WIFSIGNALED 来判断后才使用此宏。
- WIFSTOPPED(status) 若为当前暂停子进程返回的状态,则为真;对于这种情况可执行WSTOPSIG(status),取使子进程暂停的信号编号。
- WSTOPSIG(status) 取得引发子进程暂停的信号代码,一般会先用 WIFSTOPPED 来判断后才使用此宏。
调用 wait 函数时,调用进程将会出现下面的情况:
- 如果其所有子进程都还在运行,则阻塞。
- 如果一个子进程已经终止,正等待父进程获取其终止状态,则获取该子进程的终止状态然后立即返回。
- 如果没有任何子进程,则立即出错返回。
wait( )函数如果执行成功则返回子进程识别码(PID),如果有错误发生则返回-1。失败原因存于errno 中。
waitpid()函数
其函数功能为:暂时停止目前进程的执行,直到有信号来到或子进程结束。与wait( )函数相似但功能比其更加强大。
其函数原型为pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid,int * status,int options);;
第一个参数pid为欲等待的子进程识别码,其数值意义如下:
- pid<-1 等待进程组识别码为 pid 绝对值的任何子进程。
- pid=-1 等待任何子进程,相当于 wait()。
- pid=0 等待进程组识别码与目前进程相同的任何子进程。
- pid>0 等待任何子进程识别码为 pid 的子进程。
第二个参数status将存储子进程的终止状态。
第三个参数options提供了一些额外的选项来控制waitpid,参数 option 可以为 0 或可以用"|"运算符把它们连接起来使用,其选项包括如下:
WNOHANG 若pid指定的子进程没有结束,则waitpid()函数返回0,不予以等待。若结束,则返回该子进程的ID。
WUNTRACED 若子进程进入暂停状态,则马上返回,但子进程的结束状态不予以理会。
WIFSTOPPED(status)宏确定返回值是否对应与一个暂停子进程。
waitpid( )函数如果执行成功则返回子进程识别码(PID),如果有错误发生则返回-1。失败原因存于errno 中。
测试程序
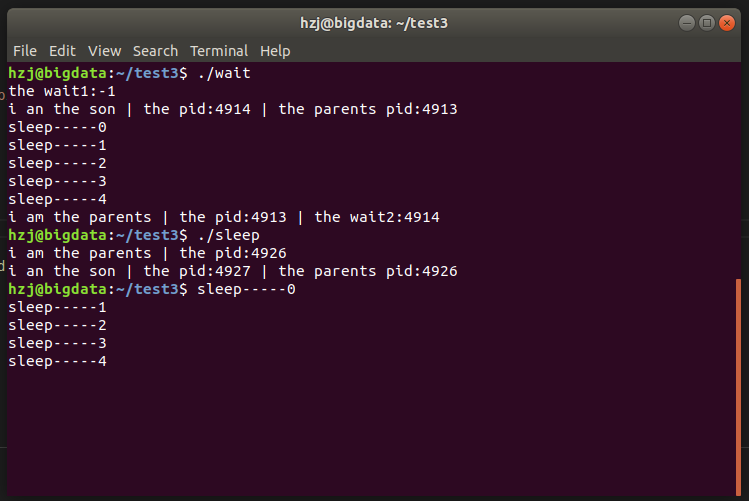
包括了使用了wait( )函数的wait测试程序和没事用函数的sleep对比程序,以对照查看wait( )函数的运行结果。
//wait测试程序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
int num1,num2,status=0;
//在无子进程的状态下执行wait()
num1=wait(&status);
printf("the wait1:%d
",num1);
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) printf("error 1!!");
else if (pid == 0) //子进程
{
int i;
printf("i an the son | the pid:%d | the parents pid:%d
",getpid(),getppid());
for (i=0; i<5 ;i++) //子进程sleep
{
sleep(1);
printf ("sleep-----%d
",i);
}
}
else if (pid > 0) //父进程
{
num2=wait(&status); //父进程wait()
printf ("i am the parents | the pid:%d | the wait2:%d
",getpid(),num2);
}
return 0;
}
//对比sleep程序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
int num1,num2,status=0;
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) printf("error 1!!");
else if (pid == 0) //子进程
{
int i;
printf("i an the son | the pid:%d | the parents pid:%d
",getpid(),getppid());
for (i=0; i<5 ;i++)
{
sleep(1);
printf ("sleep-----%d
",i);
}
}
else if (pid > 0) //父进程
{
printf ("i am the parents | the pid:%d
",getpid());
}
return 0;
}
运行结果如图所示: