2018-03-17 18:15:47
A*搜索算法是最短路径问题中另一个非常经典的算法。A*算法常用于游戏中的NPC的移动计算,或网络游戏的BOT的移动计算上。
该算法综合了Best-First Search和Dijkstra算法的优点:在进行启发式搜索提高算法效率的同时,可以保证找到一条最优路径(基于评估函数)。

下面举例说明这个算法的过程,举例用的网络如下,从S - > G:
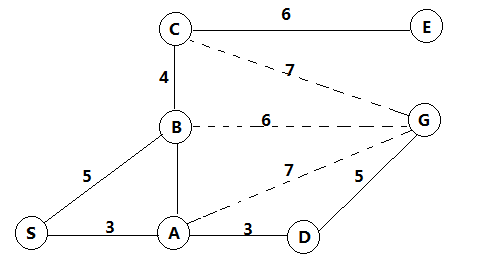
方法一、仅采用积累距离
算法流程:
Get the end,break
|
Initial Queue --> Test First Path --> Extend First Path , sorted by ACC
|——————————|
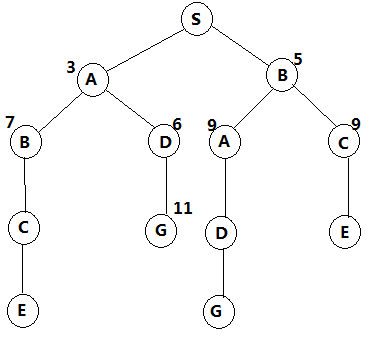
由于我每次都扩展的最小的积累距离值,所以第取出G的时候,就是G为最短路确定的时候,因为任何其他的路都比S - ›G长,而且日后也不可能更短。
其实这就是Dijkstra算法。当然在这里,我做了很多无效的extend,如果维护一个extend表,那么效率将会有很大的提升。
方法二、启发式距离 + 扩展列表
上面的Dijkstra方法不好的地方是很明显的,这种方法没有方向性,是一种发散式的搜索,事实上,运行一遍Dijkstra可以将源点到其他所有点的最短路径求出来。
然而,在很多问题中,我们并不需要源点到其他结点的距离信息,我们只关系源点到目的地的最短路径,这时候就可以使用启发式的距离,来让路径的生成变得有方向性。
具体做法就是将上面的选择过程中积累长度变成积累长度 + 启发式距离。
在找到一条路径后还需向下探查,直到其他路都绝无可能为止。

另外,这里加上了扩展列表,也就是已经扩展过的不会再继续扩展,这就是A*算法的思路。
A* = 分支限界 + 扩展列表 + 可容许启发式路径。
function A*(start,goal)
closedset := the empty set //已经被估算的节点集合
openset := set containing the initial node //将要被估算的节点集合,初始只包含start
came_from := empty map
g_score[start] := 0 //g(n)
h_score[start] := heuristic_estimate_of_distance(start, goal) //通过估计函数 估计h(start)
f_score[start] := h_score[start] //f(n)=h(n)+g(n),由于g(n)=0,所以省略
while openset is not empty //当将被估算的节点存在时,执行循环
x := the node in openset having the lowest f_score[] value //在将被估计的集合中找到f(x)最小的节点
if x = goal //若x为终点,执行
return reconstruct_path(came_from,goal) //返回到x的最佳路径
remove x from openset //将x节点从将被估算的节点中删除
add x to closedset //将x节点插入已经被估算的节点
for each y in neighbor_nodes(x) //循环遍历与x相邻节点
if y in closedset //若y已被估值,跳过
continue
tentative_g_score := g_score[x] + dist_between(x,y) //从起点到节点y的距离
if y not in openset //若y不是将被估算的节点
add y to openset //将y插入将被估算的节点中
tentative_is_better := true //暂时判断为更好
elseif tentative_g_score < g_score[y] //如果起点到y的距离小于y的实际距离
tentative_is_better := true //暂时判断为更好
else
tentative_is_better := false //否则判断为更差
if tentative_is_better = true //如果判断为更好
came_from[y] := x //将y设为x的子节点
g_score[y] := tentative_g_score //更新y到原点的距离
h_score[y] := heuristic_estimate_of_distance(y, goal) //估计y到终点的距离
f_score[y] := g_score[y] + h_score[y]
return failure
function reconstruct_path(came_from,current_node)
if came_from[current_node] is set
p = reconstruct_path(came_from,came_from[current_node])
return (p + current_node)
else
return current_node