Given the root of a binary tree, the depth of each node is the shortest distance to the root.
Return the smallest subtree such that it contains all the deepest nodes in the original tree.
A node is called the deepest if it has the largest depth possible among any node in the entire tree.
The subtree of a node is tree consisting of that node, plus the set of all descendants of that node.
Note: This question is the same as 1123: https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-deepest-leaves/
Example 1:
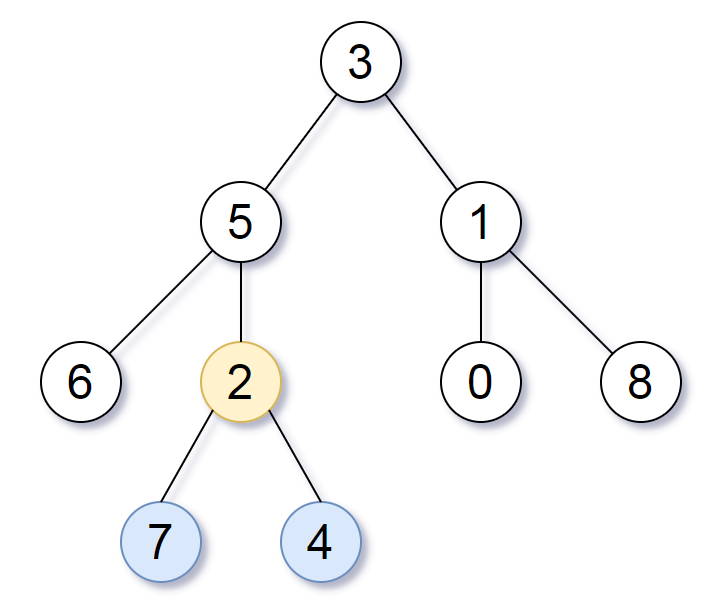
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4] Output: [2,7,4] Explanation: We return the node with value 2, colored in yellow in the diagram. The nodes coloured in blue are the deepest nodes of the tree. Notice that nodes 5, 3 and 2 contain the deepest nodes in the tree but node 2 is the smallest subtree among them, so we return it.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: [1] Explanation: The root is the deepest node in the tree.
Example 3:
Input: root = [0,1,3,null,2] Output: [2] Explanation: The deepest node in the tree is 2, the valid subtrees are the subtrees of nodes 2, 1 and 0 but the subtree of node 2 is the smallest.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[1, 500]. 0 <= Node.val <= 500- The values of the nodes in the tree are unique.
具有所有最深节点的最小子树。
给定一个根为 root 的二叉树,每个节点的深度是 该节点到根的最短距离 。
如果一个节点在 整个树 的任意节点之间具有最大的深度,则该节点是 最深的 。
一个节点的 子树 是该节点加上它的所有后代的集合。
返回能满足 以该节点为根的子树中包含所有最深的节点 这一条件的具有最大深度的节点。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/smallest-subtree-with-all-the-deepest-nodes
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
这道题的思路类似236题,思路是DFS + memorization,这里我先提供一个遍历两次的思路。既然找的是一棵最小的子树,但是这棵子树包含一个深度最大的节点(也就是距离根节点最远的节点),那么首先我们要做的就是记录下树中每个节点的深度,这里我选择用hashmap记录。第二次遍历的时候我们用dfs分别去看左子树和右子树,看哪个子树上返回的深度更大,则递归去看那个子树。
时间O(n)
空间O(n)
Java实现
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode() {} 8 * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 9 * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { 10 * this.val = val; 11 * this.left = left; 12 * this.right = right; 13 * } 14 * } 15 */ 16 class Solution { 17 public TreeNode subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode root) { 18 // corner case 19 if (root == null) { 20 return null; 21 } 22 // normal case 23 HashMap<TreeNode, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); 24 depth(root, map); 25 return dfs(root, map); 26 } 27 28 private int depth(TreeNode root, HashMap<TreeNode, Integer> map) { 29 if (root == null) { 30 return 0; 31 } 32 if (map.containsKey(root)) { 33 return map.get(root); 34 } 35 int max = Math.max(depth(root.left, map), depth(root.right, map)) + 1; 36 map.put(root, max); 37 return max; 38 } 39 40 private TreeNode dfs(TreeNode root, HashMap<TreeNode, Integer> map) { 41 int left = depth(root.left, map); 42 int right = depth(root.right, map); 43 if (left == right) { 44 return root; 45 } 46 if (left > right) { 47 return dfs(root.left, map); 48 } else { 49 return dfs(root.right, map); 50 } 51 } 52 }
相关题目
235. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree