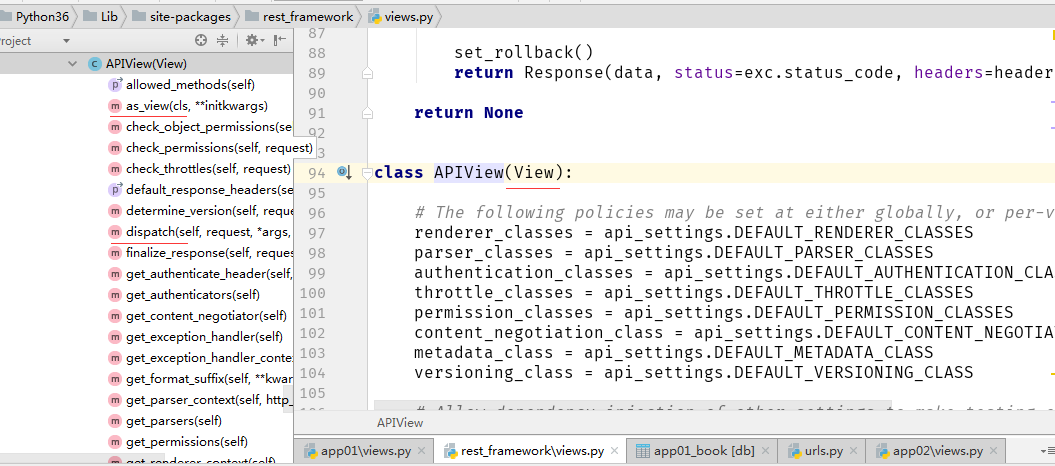
导入restful 的API
from rest_framework.views import APIView
def as_view(cls, **initkwargs): """ Store the original class on the view function. This allows us to discover information about the view when we do URL reverse lookups. Used for breadcrumb generation. """ if isinstance(getattr(cls, 'queryset', None), models.query.QuerySet): def force_evaluation(): raise RuntimeError( 'Do not evaluate the `.queryset` attribute directly, ' 'as the result will be cached and reused between requests. ' 'Use `.all()` or call `.get_queryset()` instead.' ) cls.queryset._fetch_all = force_evaluation view = super(APIView, cls).as_view(**initkwargs) view.cls = cls view.initkwargs = initkwargs # Note: session based authentication is explicitly CSRF validated, # all other authentication is CSRF exempt. return csrf_exempt(view)
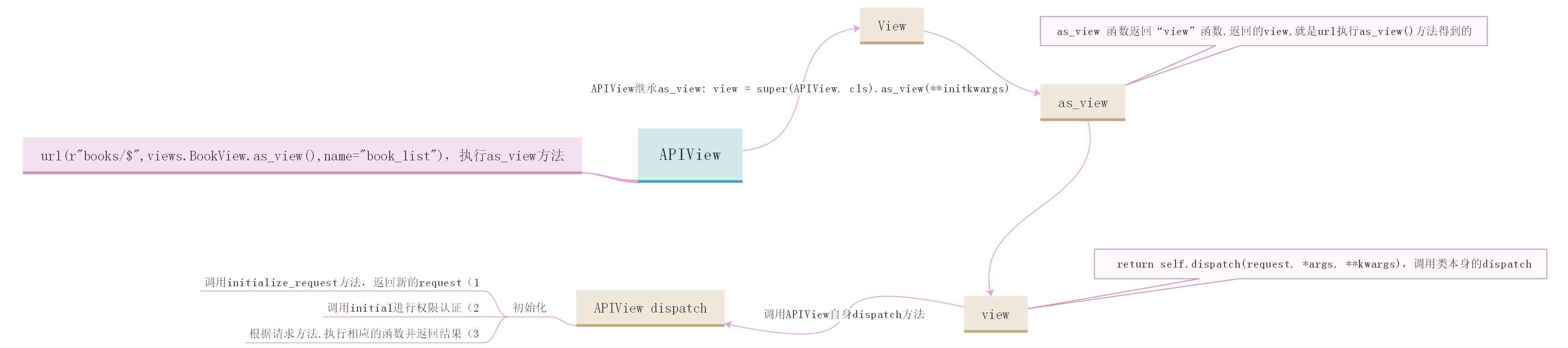
如上所示,APIView继承View,且重些dispath,as_view方法
看下View中的as_view
@classonlymethod def as_view(cls, **initkwargs): """ Main entry point for a request-response process. """ for key in initkwargs: if key in cls.http_method_names: raise TypeError("You tried to pass in the %s method name as a " "keyword argument to %s(). Don't do that." % (key, cls.__name__)) if not hasattr(cls, key): raise TypeError("%s() received an invalid keyword %r. as_view " "only accepts arguments that are already " "attributes of the class." % (cls.__name__, key)) def view(request, *args, **kwargs): self = cls(**initkwargs) if hasattr(self, 'get') and not hasattr(self, 'head'): self.head = self.get self.request = request self.args = args self.kwargs = kwargs return self.dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs) #注意这里调用类自身的dispatch方法。 view.view_class = cls view.view_initkwargs = initkwargs # take name and docstring from class update_wrapper(view, cls, updated=()) # and possible attributes set by decorators # like csrf_exempt from dispatch update_wrapper(view, cls.dispatch, assigned=()) return view
由于APIView继承了View的as_view, as_view在执行的过程中,调用自身的dispatch方法。而APIView 自身又重写了dispatch方法,所以APIView在执行as_view时,调用dispatch方法,调用的是APIView的自己重写后的dispatch
APIView 中的dispatch
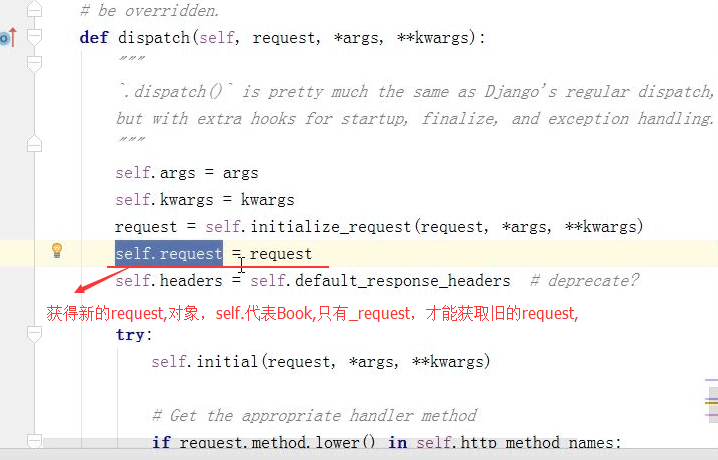
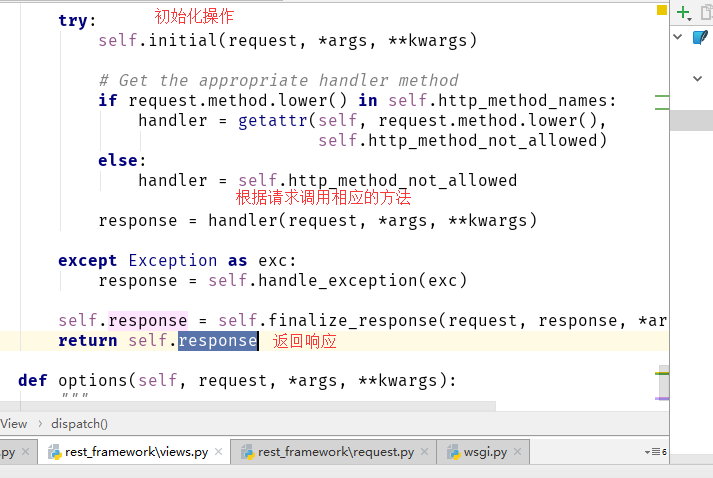
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs): """ `.dispatch()` is pretty much the same as Django's regular dispatch, but with extra hooks for startup, finalize, and exception handling. """ self.args = args self.kwargs = kwargs request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs) #注意这里调用了一个方法,返回request self.request = request self.headers = self.default_response_headers # deprecate? try: self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs) # Get the appropriate handler method if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names: handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(), self.http_method_not_allowed) else: handler = self.http_method_not_allowed response = handler(request, *args, **kwargs) except Exception as exc: response = self.handle_exception(exc) self.response = self.finalize_response(request, response, *args, **kwargs) return self.response
initialize_request
def initialize_request(self, request, *args, **kwargs): """ Returns the initial request object. """ parser_context = self.get_parser_context(request) return Request( #这里创建 request, parsers=self.get_parsers(), authenticators=self.get_authenticators(), negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(), parser_context=parser_context )
下面看一下Request类
class Request(object): """ Wrapper allowing to enhance a standard `HttpRequest` instance. Kwargs: - request(HttpRequest). The original request instance. - parsers_classes(list/tuple). The parsers to use for parsing the request content. - authentication_classes(list/tuple). The authentications used to try authenticating the request's user. """ def __init__(self, request, parsers=None, authenticators=None, negotiator=None, parser_context=None): assert isinstance(request, HttpRequest), ( 'The `request` argument must be an instance of ' '`django.http.HttpRequest`, not `{}.{}`.' .format(request.__class__.__module__, request.__class__.__name__) ) self._request = request #这里吧request 赋值给_request self.parsers = parsers or () self.authenticators = authenticators or () self.negotiator = negotiator or self._default_negotiator() self.parser_context = parser_context self._data = Empty self._files = Empty self._full_data = Empty self._content_type = Empty self._stream = Empty if self.parser_context is None: self.parser_context = {} self.parser_context['request'] = self self.parser_context['encoding'] = request.encoding or settings.DEFAULT_CHARSET force_user = getattr(request, '_force_auth_user', None) force_token = getattr(request, '_force_auth_token', None) if force_user is not None or force_token is not None: forced_auth = ForcedAuthentication(force_user, force_token) self.authenticators = (forced_auth,) def _default_negotiator(self): return api_settings.DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_CLASS() @property def content_type(self): meta = self._request.META return meta.get('CONTENT_TYPE', meta.get('HTTP_CONTENT_TYPE', '')) .......
所以dispatch得到的类是经过处理的requeset。
上面的 initial 方法 涉及到权限认证相关的操作
经过初始化操作,

def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs): """ Runs anything that needs to occur prior to calling the method handler. """ self.format_kwarg = self.get_format_suffix(**kwargs) # Perform content negotiation and store the accepted info on the request neg = self.perform_content_negotiation(request) request.accepted_renderer, request.accepted_media_type = neg # Determine the API version, if versioning is in use. version, scheme = self.determine_version(request, *args, **kwargs) request.version, request.versioning_scheme = version, scheme # Ensure that the incoming request is permitted self.perform_authentication(request) self.check_permissions(request) self.check_throttles(request)
initial 是对用户认证和权限相关的验证/