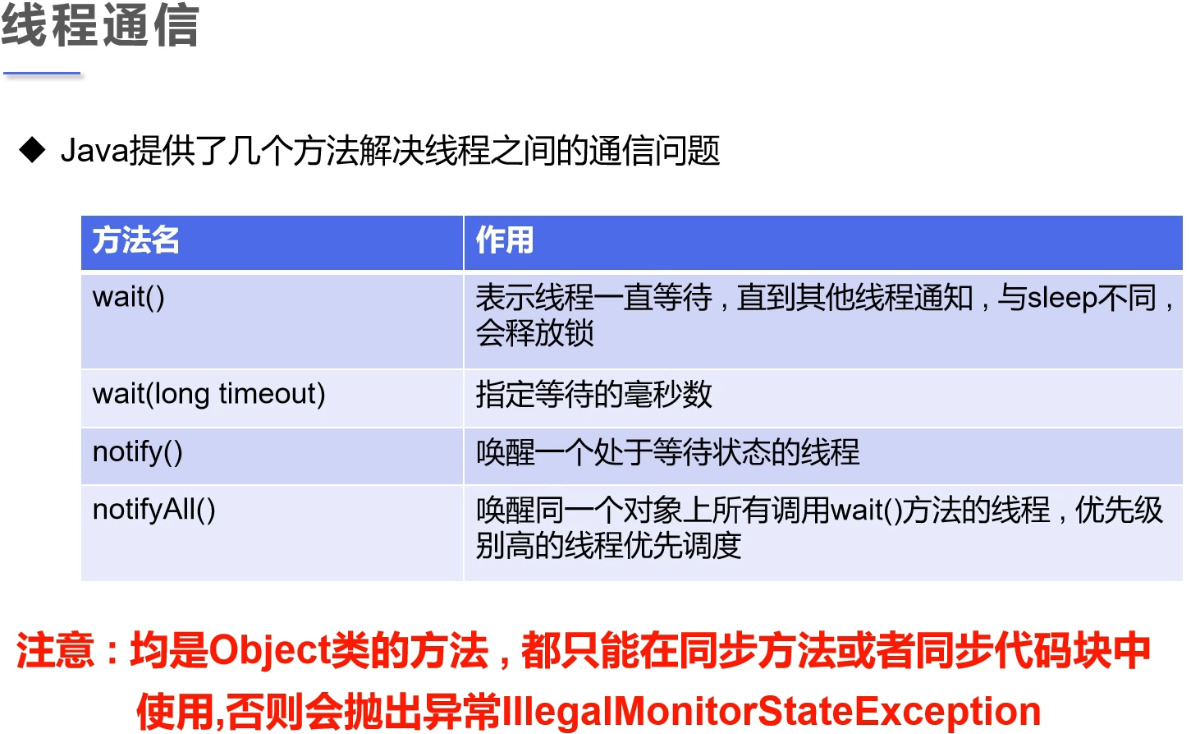
利用“生产者/消费者模式”去解决线程间的通信问题,这里整理“管程法”与“信号灯法”两种实现方式。
“管程法” 代码示例:
1 package com.huolongluo.coindemo; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by 火龙裸 on 2019/11/10. 5 * desc : 线程间的通信 6 * 生产者与消费者模式 -->利用缓冲区解决:管程法 7 * version: 1.0 8 */ 9 10 //生产者,消费者,产品,缓冲区 11 public class TestPC { 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 SynContainer container = new SynContainer(); 14 new Productor(container).start(); 15 new Consumer(container).start(); 16 } 17 } 18 19 //生产者 20 class Productor extends Thread { 21 SynContainer container; 22 23 public Productor(SynContainer container) { 24 this.container = container; 25 } 26 27 //生产 28 @Override 29 public void run() { 30 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { 31 container.push(new Chicken(i)); 32 System.out.println("生产了 " + i + " 只鸡"); 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 37 //消费者 38 class Consumer extends Thread { 39 SynContainer container; 40 41 public Consumer(SynContainer container) { 42 this.container = container; 43 } 44 45 //消费 46 @Override 47 public void run() { 48 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { 49 System.out.println("消费了第--> " + container.pop().id + " 只鸡"); 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 54 //产品 55 class Chicken { 56 int id;//产品编号 57 58 public Chicken(int id) { 59 this.id = id; 60 } 61 } 62 63 //缓冲区 64 class SynContainer { 65 66 //需要一个容器大小 67 Chicken[] chickens = new Chicken[10]; 68 //容器计数器 69 int count = 0; 70 71 //生产者放入产品 72 public synchronized void push(Chicken chicken) { 73 //如果容器满了,就需要等待消费者消费 74 if (count == chickens.length) { 75 //通知消费者消费,生产者等待 76 try { 77 this.wait(); 78 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 79 e.printStackTrace(); 80 } 81 } 82 //如果没有满,我们就需要丢入产品 83 chickens[count] = chicken; 84 count++; 85 86 //可以通知消费者消费了 87 this.notifyAll(); 88 } 89 90 //消费者消费产品 91 public synchronized Chicken pop() { 92 //判断能否消费 93 if (count == 0) { 94 //等待生产者生产,消费者等待 95 try { 96 this.wait(); 97 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 98 e.printStackTrace(); 99 } 100 } 101 102 //如果可以消费 103 count--; 104 Chicken chicken = chickens[count]; 105 106 //吃完了,通知生产者生产 107 this.notifyAll(); 108 return chicken; 109 } 110 }
“信号灯法” 代码示例:
1 package com.huolongluo.coindemo.morethread; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by 火龙裸 on 2019/11/10. 5 * desc : 测试生产者消费者问题2:信号灯法,标志位解决 6 * version: 1.0 7 */ 8 public class TestPc2 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 TV tv = new TV(); 11 new Player(tv).start(); 12 new Watcher(tv).start(); 13 } 14 } 15 16 //生产者-->演员 17 class Player extends Thread { 18 TV tv; 19 20 public Player(TV tv) { 21 this.tv = tv; 22 } 23 24 @Override 25 public void run() { 26 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 27 if (i % 2 == 0) { 28 this.tv.paly("快乐大本营"); 29 } else { 30 this.tv.paly("抖音:记录美好生活"); 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 36 //消费者-->观众 37 class Watcher extends Thread { 38 TV tv; 39 40 public Watcher(TV tv) { 41 this.tv = tv; 42 } 43 44 @Override 45 public void run() { 46 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 47 tv.watch(); 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 52 //产品-->节目 53 class TV { 54 //演员表演,观众等待 (flag为T,演员表演) 55 //观众观看,演员等待 (flag为F,演员等待) 56 String voice;//表演的节目 57 boolean flag = true; 58 59 //表演 60 public synchronized void paly(String voice) { 61 if (!flag) { 62 try { 63 this.wait(); 64 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 65 e.printStackTrace(); 66 } 67 } 68 System.out.println("演员表演了: " + voice); 69 //通知观众观看 70 this.notifyAll();//通知唤醒 71 this.voice = voice; 72 this.flag = !this.flag; 73 } 74 75 //观看 76 public synchronized void watch() { 77 if (flag) { 78 try { 79 this.wait(); 80 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 81 e.printStackTrace(); 82 } 83 } 84 System.out.println("观众观看了: " + voice); 85 //通知演员表演 86 this.notifyAll(); 87 this.flag = !this.flag; 88 } 89 }
线程池

- JDK5.0起提供了线程池相关API:ExecutorService和Executors
- ExecutorService:真正的线程池接口。常见子类ThreadPoolExecutor
1. void execute(Runnable command):执行任务/命令,没有返回值,一般用来执行Runnable
2. <T>Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task):执行任务,有返回值,一般用来执行Callable
3. void shutdown():关闭连接池
- Executors:工具类、线程池的工厂类,用于创建并返回不同类型的线程池
线程池 代码示例:
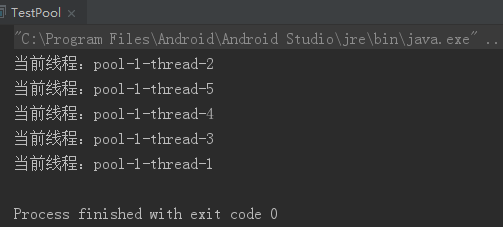
1 package com.huolongluo.coindemo; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 4 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 5 6 /** 7 * Created by 火龙裸 on 2019/11/10. 8 * desc : 线程池 9 * version: 1.0 10 */ 11 public class TestPool { 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 //1.创建服务,创建线程池 14 //newFixedThreadPool 参数为:线程池大小 15 ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); 16 17 //执行 18 service.execute(new MyThread()); 19 service.execute(new MyThread()); 20 service.execute(new MyThread()); 21 service.execute(new MyThread()); 22 service.execute(new MyThread()); 23 24 //2.关闭链接 25 service.shutdown(); 26 } 27 } 28 29 class MyThread implements Runnable { 30 31 @Override 32 public void run() { 33 System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 34 } 35 }
运行结果:
总结:
线程的实现方式,代码示例如下:
1 package com.huolongluo.coindemo; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.Callable; 4 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; 5 import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; 6 7 /** 8 * Created by 火龙裸 on 2019/11/10. 9 * desc :回顾线程的创建 10 * version: 1.0 11 */ 12 public class ThreadNew { 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 //启动线程 MyThread1 15 new MyThread1().start(); 16 17 //启动线程 MyThread2 18 new Thread(new MyThread2()).start(); 19 20 //启动线程 MyThread3 (通过Callable接口启动线程的方式有很多,这里只简单介绍一种) 21 //FutureTask的构造参数可以是一个Callable接口,也可以是一个Runnable接口 22 FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<Integer>(new MyThread3()); 23 new Thread(futureTask).start();//FutureTask本身RunnableFuture接口,而RunnableFuture接口又是继承的Runnable接口,所以可以这样启动 24 try { 25 Integer integer = futureTask.get();//通过get()方法获得返回值 26 System.out.println("获得的返回值:" + integer); 27 } catch (ExecutionException e) { 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 35 //1.继承Thread类 36 class MyThread1 extends Thread { 37 @Override 38 public void run() { 39 System.out.println("Thread1"); 40 } 41 } 42 43 //2.实现Runnable接口 44 class MyThread2 implements Runnable { 45 46 @Override 47 public void run() { 48 System.out.println("MyThread2"); 49 } 50 } 51 52 //3.实现Callable接口 53 class MyThread3 implements Callable<Integer> { 54 @Override 55 public Integer call() throws Exception { 56 System.out.println("MyThread3"); 57 return 100; 58 } 59 }
运行结果:
