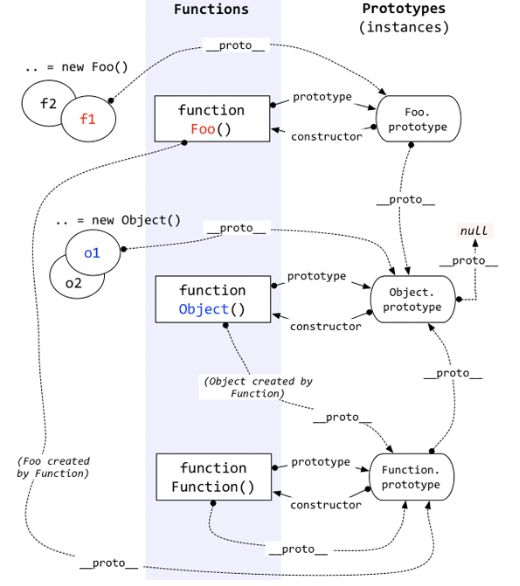
1.对象有属性__proto__,指向该对象的构造函数的原型对象。
2.方法除了有属性__proto__,还有属性prototype,prototype指向该方法的原型对象。
深入浅出妙用 Javascript 中 apply、call、bind
***两道面试题***
我们可以通过Array.prototype.slice.call(fakeArray)将伪数组转变为真正的Array对象。
1.如何利用splice方法实现数组去重
2.es6去重数组
// 去除数组的重复成员 [...new Set(array)] 或者 Array.from(new Set(array));
js日期格式化
function formatDate(date) { var fmt="yyyy-MM" var o = { "M+": date.getMonth() + 1, //月份 "d+": date.getDate(), //日 "h+": date.getHours(), //小时 "m+": date.getMinutes(), //分 "s+": date.getSeconds(), //秒 "q+": Math.floor((date.getMonth() + 3) / 3), //季度 "S": date.getMilliseconds() //毫秒 }; if (/(y+)/.test(fmt)) fmt = fmt.replace(RegExp.$1, (date.getFullYear() + "").substr(4 - RegExp.$1.length)); for (var k in o) if (new RegExp("(" + k + ")").test(fmt)) fmt = fmt.replace(RegExp.$1, (RegExp.$1.length == 1) ? (o[k]) : (("00" + o[k]).substr(("" + o[k]).length))); return fmt; }
getNowFormatDate(date) { var seperator1 = "-"; var seperator2 = ":"; var month = date.getMonth() + 1; var strDate = date.getDate(); if (month >= 1 && month <= 9) { month = "0" + month; } if (strDate >= 0 && strDate <= 9) { strDate = "0" + strDate; } var currentdate = date.getFullYear() + seperator1 + month + seperator1 + strDate + " " + date.getHours() + seperator2 + date.getMinutes() + seperator2 + date.getSeconds(); return currentdate; }
js Promise
简单测试一下, then函数可以返回新的promise。resolve()函数的返回值会传递到then(resolve, reject)函数中的resolve方法中。
Promise((resolve)=>{resolve(()=>{return 'xixi';})}).then((fun)=>{console.log(fun()); return Promise((resolve)=>{resolve(()=>{return 'haha'})}).then((fun)=>{console.log(fun())})});
//一个简单的Promise实现方案
function Promise(fn) { var value = null; var events = []; this.then = function(f) { events.push(f); return this; } function resolve(newValue) { var f = events.shift(); f(newValue, resolve); } fn(resolve); } function a() { return new Promise(function(resolve) { console.log("get..."); setTimeout(function() { console.log("get 1"); resolve(1); }, 1000) }); } a().then(function(value, resolve) { console.log("get..."); setTimeout(function() { console.log("get 2"); resolve(2); }, 1000) }).then(function(value, resolve) { console.log(value) }) 这样就得到控制台如下的结果 get... get 1 get... get 2 2
JavaScript进阶之路——认识和使用Promise,重构你的Js代码 。一个较为复杂的Promise实现方案如下。

// see => http://promises-aplus.github.io/promises-spec/ // see => https://github.com/cujojs/when/blob/master/lib/makePromise.js ;(function(root, factory) { if (typeof module !== 'undefined' && module.exports) {// CommonJS module.exports = factory(); } else if (typeof define === 'function' && define.amd) {// AMD / RequireJS define(factory); } else { root.Promise = factory.call(root); } }(this, function() { 'use strict'; function Promise(resolver) { if(!(this instanceof Promise)) return new Promise(resolver); this.status = 'pending'; this.value; this.reason; // then may be called multiple times on the same promise this._resolves = []; this._rejects = []; if(isFn(resolver)) resolver(this.resolve.bind(this), this.reject.bind(this)); return this; }; Promise.prototype.then = function(resolve, reject) { var next = this._next || (this._next = Promise()); var status = this.status; var x; if('pending' === status) { isFn(resolve) && this._resolves.push(resolve); isFn(reject) && this._rejects.push(reject); return next; } if('resolved' === status) { if(!isFn(resolve)) { next.resolve(resolve); } else { try { x = resolve(this.value); resolveX(next, x); } catch(e) { this.reject(e); } } return next; } if('rejected' === status) { if(!isFn(reject)) { next.reject(reject); } else { try { x = reject(this.reason); resolveX(next, x); } catch(e) { this.reject(e); } } return next; } }; Promise.prototype.resolve = function(value) { if('rejected' === this.status) throw Error('Illegal call.'); this.status = 'resolved'; this.value = value; this._resolves.length && fireQ(this); return this; }; Promise.prototype.reject = function(reason) { if('resolved' === this.status) throw Error('Illegal call.'); this.status = 'rejected'; this.reason = reason; this._rejects.length && fireQ(this); return this; }; // shortcut of promise.then(undefined, reject) Promise.prototype.catch = function(reject) { return this.then(void 0, reject); }; // return a promise with another promise passing in Promise.cast = function(arg) { var p = Promise(); if(arg instanceof Promise) return resolvePromise(p, arg); else return Promise.resolve(arg); }; // return a promise which resolved with arg // the arg maybe a thanable object or thanable function or other Promise.resolve = function(arg) { var p = Promise(); if(isThenable(arg)) return resolveThen(p, arg); else return p.resolve(arg); }; Promise.all = function(promises) { ; }; // return a promise which reject with reason // reason must be an instance of Error object Promise.reject = function(reason) { if(!(reason instanceof Error)) throw Error('reason must be an instance of Error'); var p = Promise(); p.reject(reason); return p; }; function resolveX(promise, x) { if(x === promise) promise.reject(new Error('TypeError')); if(x instanceof Promise) return resolvePromise(promise, x); else if(isThenable(x)) return resolveThen(promise, x); else return promise.resolve(x); }; function resolvePromise(promise, promise2) { var status = promise2.status; if('pending' === status) { promise2.then(promise.resolve.bind(promise), promise.reject.bind(promise)); } if('resolved' === status) promise.resolve(promise2.value); if('rejected' === status) promise.reject(promise2.reason); return promise; }; function resolveThen(promise, thanable) { var called; var resolve = once(function(x) { if(called) return; resolveX(promise, x); called = true; }); var reject = once(function(r) { if(called) return; promise.reject(r); called = true; }); try { thanable.then.call(thanable, resolve, reject); } catch(e) { if(!called) throw e; else promise.reject(e); } return promise; }; function fireQ(promise) { var status = promise.status; var queue = promise['resolved' === status ? '_resolves' : '_rejects']; var arg = promise['resolved' === status ? 'value' : 'reason']; var fn; var x; while(fn = queue.shift()) { x = fn.call(promise, arg); resolveX(promise._next, x); } return promise; }; function noop () {}; function isFn(fn) { return 'function' === type(fn); }; function isObj(o) { return 'object' === type(o); }; function type(obj) { var o = {}; return o.toString.call(obj).replace(/[object (w+)]/, '$1').toLowerCase(); }; function isThenable(obj) { return obj && obj.then && isFn(obj.then); }; function once(fn) { var called; return function() { if(called) return; fn.apply(this, arguments); called = true; }; }; return Promise; }));
