5. Protocol
5.1 序列化
SerializerManager负责管理序列化类,默认起作用的是HessianSerializer
HessianSerializer实现了序列化接口Serializer,有两个方法
-
序列化
byte[] serialize(final Object obj) throws CodecException; -
反序列化
<T> T deserialize(final byte[] data, String classOfT) throws CodecException;
直接看实现
public class HessianSerializer implements Serializer {
private SerializerFactory serializerFactory = new SerializerFactory();
/**
* @see com.alipay.remoting.serialization.Serializer#serialize(java.lang.Object)
*/
@Override
public byte[] serialize(Object obj) throws CodecException {
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArray = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
Hessian2Output output = new Hessian2Output(byteArray);
output.setSerializerFactory(serializerFactory);
try {
output.writeObject(obj);
output.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new CodecException("IOException occurred when Hessian serializer encode!", e);
}
return byteArray.toByteArray();
}
/**
*
* @see com.alipay.remoting.serialization.Serializer#deserialize(byte[], java.lang.String)
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public <T> T deserialize(byte[] data, String classOfT) throws CodecException {
Hessian2Input input = new Hessian2Input(new ByteArrayInputStream(data));
input.setSerializerFactory(serializerFactory);
Object resultObject;
try {
resultObject = input.readObject();
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new CodecException("IOException occurred when Hessian serializer decode!", e);
}
return (T) resultObject;
}
}
Hessian的文档 http://hessian.caucho.com/doc/hessian-serialization.html
例如
对象RequestBody
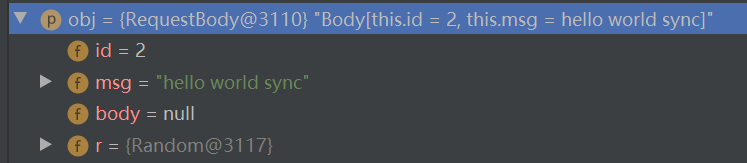
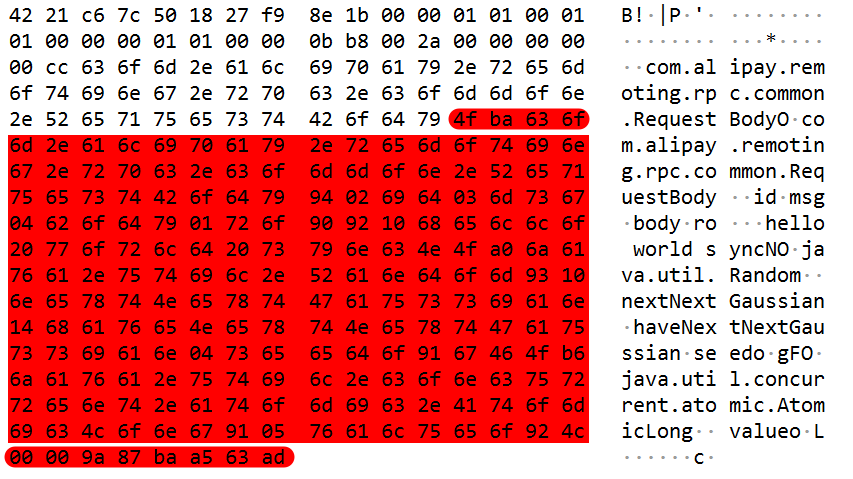
序列化结果为
5.2 编码
Bolt的编码处理器是ProtocolCodeBasedEncoder,当发送数据时,会调用encode方法
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Serializable msg, ByteBuf out)
throws Exception {
Attribute<ProtocolCode> att = ctx.channel().attr(Connection.PROTOCOL);
ProtocolCode protocolCode;
if (att == null || att.get() == null) {
protocolCode = this.defaultProtocolCode;
} else {
protocolCode = att.get();
}
Protocol protocol = ProtocolManager.getProtocol(protocolCode);
protocol.getEncoder().encode(ctx, msg, out);
}
该编码器并没有对数据进行直接处理,而是交给Protocol类处理
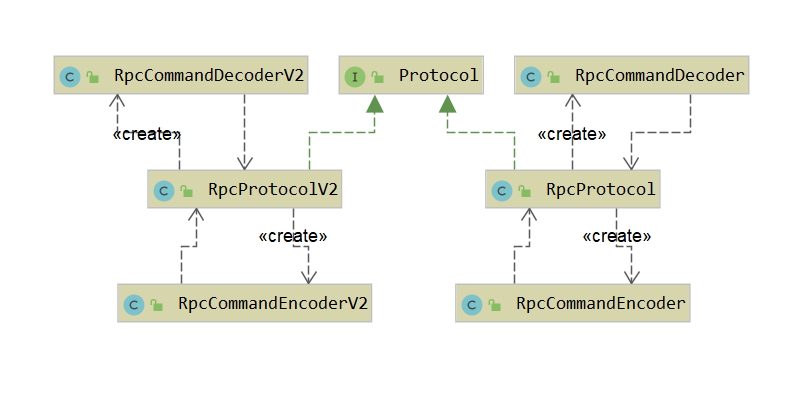
Protocol有两个实现类,可以在配置项或者连接的URL中指定协议的版本号。上面两个实现类的protocolCode分别是1和2。协议可以创建编码器和解码器。默认的协议号是1,因此默认的编码器是RpcCommandEncoder。
编码的代码如下:
public void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Serializable msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
try {
if (msg instanceof RpcCommand) {
/*
* ver: version for protocol
* type: request/response/request oneway
* cmdcode: code for remoting command
* ver2:version for remoting command
* requestId: id of request
* codec: code for codec
* (req)timeout: request timeout.
* (resp)respStatus: response status
* classLen: length of request or response class name
* headerLen: length of header
* cotentLen: length of content
* className
* header
* content
*/
RpcCommand cmd = (RpcCommand) msg;
out.writeByte(RpcProtocol.PROTOCOL_CODE);
out.writeByte(cmd.getType());
out.writeShort(((RpcCommand) msg).getCmdCode().value());
out.writeByte(cmd.getVersion());
out.writeInt(cmd.getId());
out.writeByte(cmd.getSerializer());
if (cmd instanceof RequestCommand) {
//timeout
out.writeInt(((RequestCommand) cmd).getTimeout());
}
if (cmd instanceof ResponseCommand) {
//response status
ResponseCommand response = (ResponseCommand) cmd;
out.writeShort(response.getResponseStatus().getValue());
}
out.writeShort(cmd.getClazzLength());
out.writeShort(cmd.getHeaderLength());
out.writeInt(cmd.getContentLength());
if (cmd.getClazzLength() > 0) {
out.writeBytes(cmd.getClazz());
}
if (cmd.getHeaderLength() > 0) {
out.writeBytes(cmd.getHeader());
}
if (cmd.getContentLength() > 0) {
out.writeBytes(cmd.getContent());
}
} else {
String warnMsg = "msg type [" + msg.getClass() + "] is not subclass of RpcCommand";
logger.warn(warnMsg);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Exception caught!", e);
throw e;
}
}
抓包结果分析

01 --ver
01 --request,表示请求
00 01 -- cmdcode
01 --ver2
00 00 00 01 -- requestId
01 -- codec
00 00 0b b8 -- timeout (=3000)
00 2a -- classLen(=42)
00 00 -- headerLen(=0)
00 00 00 cc -- cotentLen(=204)
63 6f 6d 2e 61 6c 69 70 61 79 2e 72 65 6d 6f 74 69 6e 67 2e
72 70 63 2e 63 6f 6d 6d 6f 6e 2e 52 65 71 75 65 73 74 42 6f
64 79 -- className(com.alipay.remoting.rpc.common.RequestBody)
4f ba ... -- content (序列化的对象)
5.3 解码
Bolt解码处理器是ProtocolCodeBasedDecoder
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
in.markReaderIndex();
//获取协议号ver
ProtocolCode protocolCode = decodeProtocolCode(in);
if (null != protocolCode) {
byte protocolVersion = decodeProtocolVersion(in);
if (ctx.channel().attr(Connection.PROTOCOL).get() == null) {
ctx.channel().attr(Connection.PROTOCOL).set(protocolCode);
if (DEFAULT_ILLEGAL_PROTOCOL_VERSION_LENGTH != protocolVersion) {
ctx.channel().attr(Connection.VERSION).set(protocolVersion);
}
}
Protocol protocol = ProtocolManager.getProtocol(protocolCode);
if (null != protocol) {
in.resetReaderIndex();
protocol.getDecoder().decode(ctx, in, out);
} else {
throw new CodecException("Unknown protocol code: [" + protocolCode
+ "] while decode in ProtocolDecoder.");
}
}
}
与编码一样交给Protocol来处理
直接看解码的实现类RpcCommandDecoder的decode方法
@Override
public void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
// the less length between response header and request header
if (in.readableBytes() >= lessLen) {
in.markReaderIndex();
byte protocol = in.readByte();
in.resetReaderIndex();
if (protocol == RpcProtocol.PROTOCOL_CODE) {
/*
* ver: version for protocol
* type: request/response/request oneway
* cmdcode: code for remoting command
* ver2:version for remoting command
* requestId: id of request
* codec: code for codec
* (req)timeout: request timeout
* (resp)respStatus: response status
* classLen: length of request or response class name
* headerLen: length of header
* contentLen: length of content
* className
* header
* content
*/
if (in.readableBytes() > 2) {
in.markReaderIndex();
in.readByte(); //version
byte type = in.readByte(); //type
if (type == RpcCommandType.REQUEST || type == RpcCommandType.REQUEST_ONEWAY) {
//decode request
if (in.readableBytes() >= RpcProtocol.getRequestHeaderLength() - 2) {
short cmdCode = in.readShort();
byte ver2 = in.readByte();
int requestId = in.readInt();
byte serializer = in.readByte();
int timeout = in.readInt();
short classLen = in.readShort();
short headerLen = in.readShort();
int contentLen = in.readInt();
byte[] clazz = null;
byte[] header = null;
byte[] content = null;
if (in.readableBytes() >= classLen + headerLen + contentLen) {
if (classLen > 0) {
clazz = new byte[classLen];
in.readBytes(clazz);
}
if (headerLen > 0) {
header = new byte[headerLen];
in.readBytes(header);
}
if (contentLen > 0) {
content = new byte[contentLen];
in.readBytes(content);
}
} else {// not enough data
in.resetReaderIndex();
return;
}
RequestCommand command;
if (cmdCode == CommandCode.HEARTBEAT_VALUE) {
command = new HeartbeatCommand();
} else {
command = createRequestCommand(cmdCode);
}
command.setType(type);
command.setVersion(ver2);
command.setId(requestId);
command.setSerializer(serializer);
command.setTimeout(timeout);
command.setClazz(clazz);
command.setHeader(header);
command.setContent(content);
out.add(command);
} else {
in.resetReaderIndex();
}
} else if (type == RpcCommandType.RESPONSE) {
//decode response
if (in.readableBytes() >= RpcProtocol.getResponseHeaderLength() - 2) {
short cmdCode = in.readShort();
byte ver2 = in.readByte();
int requestId = in.readInt();
byte serializer = in.readByte();
short status = in.readShort();
short classLen = in.readShort();
short headerLen = in.readShort();
int contentLen = in.readInt();
byte[] clazz = null;
byte[] header = null;
byte[] content = null;
if (in.readableBytes() >= classLen + headerLen + contentLen) {
if (classLen > 0) {
clazz = new byte[classLen];
in.readBytes(clazz);
}
if (headerLen > 0) {
header = new byte[headerLen];
in.readBytes(header);
}
if (contentLen > 0) {
content = new byte[contentLen];
in.readBytes(content);
}
} else {// not enough data
in.resetReaderIndex();
return;
}
ResponseCommand command;
if (cmdCode == CommandCode.HEARTBEAT_VALUE) {
command = new HeartbeatAckCommand();
} else {
command = createResponseCommand(cmdCode);
}
command.setType(type);
command.setVersion(ver2);
command.setId(requestId);
command.setSerializer(serializer);
command.setResponseStatus(ResponseStatus.valueOf(status));
command.setClazz(clazz);
command.setHeader(header);
command.setContent(content);
command.setResponseTimeMillis(System.currentTimeMillis());
command.setResponseHost((InetSocketAddress) ctx.channel()
.remoteAddress());
out.add(command);
} else {
in.resetReaderIndex();
}
} else {
String emsg = "Unknown command type: " + type;
logger.error(emsg);
throw new RuntimeException(emsg);
}
}
} else {
String emsg = "Unknown protocol: " + protocol;
logger.error(emsg);
throw new RuntimeException(emsg);
}
}
}
解码时根据type的类型,将字节流分装成RequestCommand或ResponseCommand的对象。
5.4 流程分析

服务器的数据流转过程总结一下:
- decoder将字节流解码成RequestCommand或ResponseCommand的对象
- idleStateHandler更新read时间
- serverIdleHandler未接收到空闲事件,pass
- connectionEventHandler,pass
- handler根据协议号获取commandHandler
- commandHandler根据msg(第1步保证肯定是RpcCommand的实现类)的cmdCode获取具体的命令处理器RemotingProcessor。
- 心跳 HeartbeatCommand -> RpcHeartBeatProcessor
- 请求 RpcRequestCommand-> RpcRequestProcessor
- 响应 RpcResponseCommand -> RpcResponseProcessor
- 以请求RpcRequestCommand为例,RpcRequestProcessor根据requestClass获取具体的UserProcessor,处理自定义业务后封装响应为RpcResponseCommand 并写入到channel中
- connectionEventHandler,pass
- serverIdleHandler未接收到空闲事件,pass
- idleStateHandler更新write时间
- encoder将对象编码成字节流发送给客户端