失败者,往往是热度只有五分钟的人;成功者,往往是坚持最后五分钟的人。
你好,我是梦阳辰,期待与你相遇!
10年前单核CPU电脑,假的多线程,像马戏团小丑玩多个球,CPU需要来回切换。现在是多核电脑,多个线程各自跑在独立的CPU上,不用切换效率高。
线程池的优势:
线程池做的工作只要是控制运行的线程数量,处理过程中将任务放入队列,然后在线程创建后启动这些任务,如果线程数量超过了最大数量,超出数量的线程排队等候,等其他线程执行完毕,再从队列中取出任务来执行。
它的主要特点为:线程复用;控制最大并发数;管理线程。
第一:降低资源消耗。通过重复利用已创建的线程降低线程创建和销毁造成的销耗。
第二:提高响应速度。当任务到达时,任务可以不需要等待线程创建就能立即执行。
第三:提高线程的可管理性。线程是稀缺资源,如果无限制的创建,不仅会销耗系统资源,还会降低系统的稳定性,使用线程池可以进行统一的分配,调优和监控。
java.util.concurrent
Interface Executor
子接口:
java.util.concurrent
Interface ExecutorService

Executors是一个辅助工具类。
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(int)执行长期任务性能好,创建一个线程池,—池
有N个固定的线程,有固定线程数的线程
package Part5;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ThreadPoolDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);//一个池5个受理线程,类似于一个银行有五个受理窗口
try{
//模拟20个顾客办理业务
for(int i = 1;i<=20;i++){
threadPool.execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 在办理业务!");
});
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
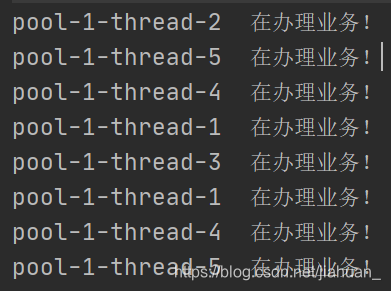
2.Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor()一个任务一个任务的执行,一池一线程
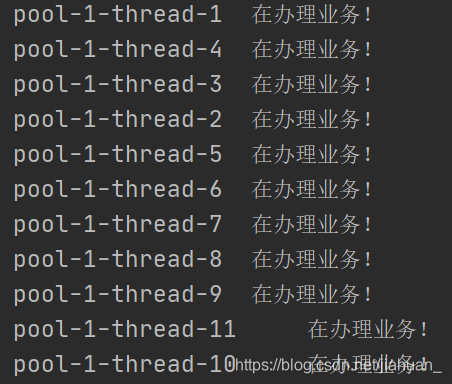
3.Executors.newCachedThreadPool()执行很多短期异步任务,线程池根据需要创建新线程,
但在先前构建的线程可用时将重用它们。可扩容,遇强则强
package Part5;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ThreadPoolDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);//一个池5个受理线程,类似于一个银行有五个受理窗口
//ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();//一个池1个受理线程,类似于一个银行有1个受理窗口
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();//一个池N个受理线程,类似于一个银行有N个受理窗口
try{
//模拟20个顾客办理业务
for(int i = 1;i<=20;i++){
threadPool.execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 在办理业务!");
});
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ?
null :
AccessController.getContext();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}


1、在创建了线程池后,开始等待请求。
2、当调用execute()方法添加一个请求任务时,线程池会做出如下判断:
2.1如果正在运行的线程数量小于corePoolSize,那么马上创建线程运行这个任务;2.2如果正在运行的线程数量大于或等于corePoolSize,那么将这个任务放入队列;
2.3如果这个时候队列满了且正在运行的线程数量还小于maximumPoolSize,那么还是要创建非核心线程立2.4如果队列满了且正在运行的线程数量大于或等于maximumPoolSize,那么线程池会启动饱和拒绝策略来
3、当一个线程完成任务时,它会从队列中取下一个任务来执行。
4、当一个线程无事可做超过一定的时间(keepAliveTime)时,线程会判断:
如果当前运行的线程数大于corePoolSize,那么这个线程就被停掉。
所以线程池的所有任务完成后,它最终会收缩到corePoolSize的大小。
强制线程池不允许使用Executors 去创建,而是通过ThreadPoolExecutor的方式这样的处理方式让写的同学更加明确线程池的运行规则,规避资源耗尽的风险。
说明: Executors返回的线程池对象的弊端如下:
-
FixedThreadPool和 singleThreadPool:
允许的请求队列长度为Integer.MAx_VALUE,可能会堆积大量的请求,从而导致OOM -
cachedThreadPool和 ScheduledThreadPool:
允许的创建线程数量为Integer.NAX_VALUE,可能会创建大量的线程,从而导致OOM。
等待队列已经排满了,再也塞不下新任务了同时,
线程池中的max线程也达到页,无法继续为新任务服务。
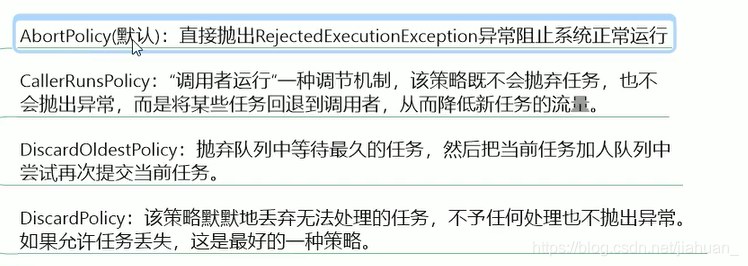
这个是时候我们就需要拒绝策略机制合理的处理这个问题。
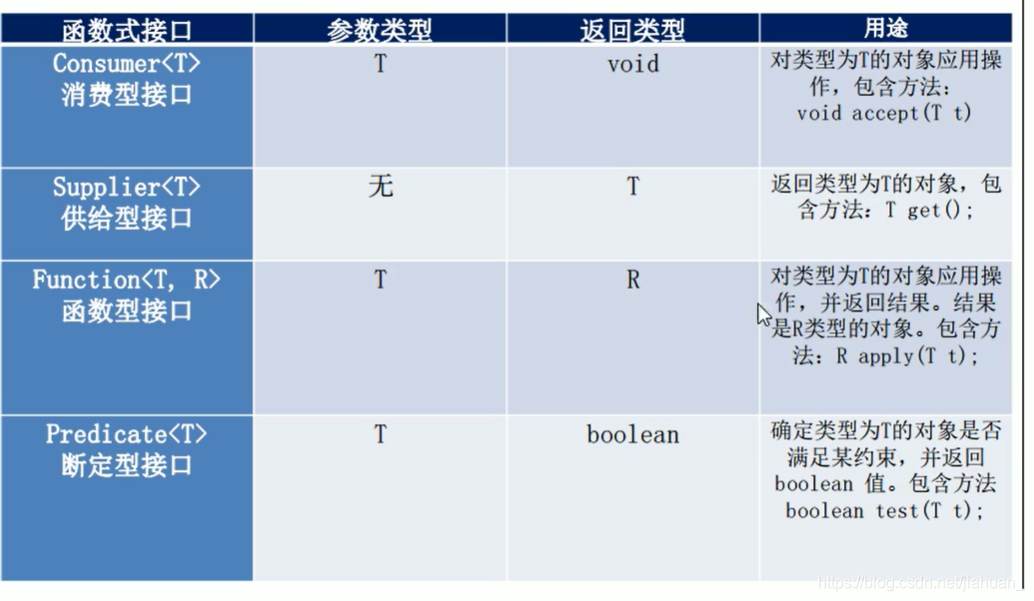
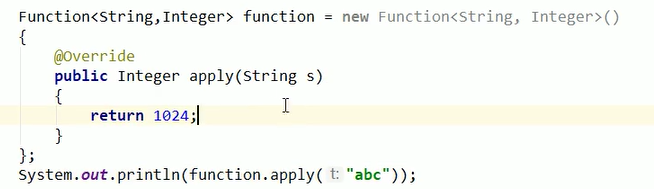

流(Stream)到底是什么呢?
是数据渠道,r用于操作数据源(集合、数组等)所生成的元素序列。
“集合讲的是数据,流讲的是计算!”
Stream自己不会存储元素,Stream不会改变源对象。
相反他们会返回一个持有结果的新Stream。
Stream操作是延迟执行的。
这意味着他们会等到需要结果的时候才执行。
创建一个Stream: 一个数据源(数组、集合)
中间操作:一个中间操作,处理数据源数据
终止操作:一个终止操作,执行中间操作链,产生结果
源头=>中间流水线=>结果
package Part5;
import com.sun.xml.internal.ws.api.model.wsdl.WSDLOutput;
import org.w3c.dom.ls.LSOutput;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class StreamDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User u1 = new User(11,"a",23);
User u2 = new User(12,"b",24);
User u3 = new User(13,"c",22);
User u4 = new User(14,"d",28);
User u5 = new User(16,"e",26);
List<User> list = Arrays.asList(u1,u2,u3,u4,u5);
list.stream().filter(t->{return t.getId()%2 == 0;})
.filter(t->{return t.getAge()>24;})
.map(m->{return m.getName().toUpperCase();})
.sorted((o1,o2)->{return o2.compareTo(o1);}).limit(1)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
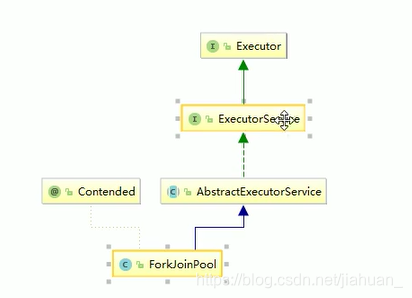
java.lang.Object
java.util.concurrent.AbstractExecutorService
java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool
java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask<V>
java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask<V> //递归抽象类
package Part5;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask;
class MyTask extends RecursiveTask<Integer>{//资源类,RecursiveTask抽象类为递归
private static final Integer ADD_VALUE = 10;
private int begin;
private int end;
private int result;
public MyTask(int begin, int end) {
this.begin = begin;
this.end = end;
}
@Override
protected Integer compute() {
if((end-begin)<=ADD_VALUE){
for(int i=begin;i<=end;i++){
result = result + i;
}
}else{
int middle = (end+begin)/2;
MyTask task1 = new MyTask(begin,middle);
MyTask task2 = new MyTask(middle+1,end);
task1.fork();//分
task2.fork();//分支
result = task1.join()+task2.join();//合并结果
}
return result;
}
}
public class ForkJoinDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
MyTask myTask = new MyTask(0,100);
ForkJoinPool threadPool = new ForkJoinPool();
ForkJoinTask<Integer> forkJoinTask = threadPool.submit(myTask);//提交任务
System.out.println(forkJoinTask.get());//获取结果
threadPool.shutdown() ;
}
}
java.lang.Object
java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture<T>
测试:
package Part5;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class CompletableFutrueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
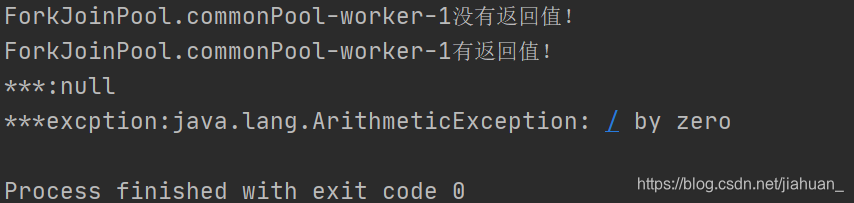
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"没有返回值!");
});
completableFuture.get();
//异步回调
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"有返回值!");
int f = 5/0;
return 1;
});
completableFuture2.whenComplete((t,u)->{//正常时的情况
System.out.println("***:"+t);
}).exceptionally(f->{//异常时情况
System.out.println("***excption:"+f.getMessage());
return 444;
});
}
}
Don’t look forward to tomorrow, don’t miss yesterday, to grasp today.

