一 什么是Semaphore、Semaphore用来做什么
semaphore是计数信号量,可用于多线程并发执行时,限制获取资源的线程数量。常用场景为:限流。
二 Semaphore用法

1 public class SemaphoreTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 // 声明5个窗口 state: 资源数 5 Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3); 6 7 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { 8 new Thread(new Runnable() { 9 @Override 10 public void run() { 11 try { 12 // 占用窗口 13 semaphore.acquire(2); 14 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": 开始买票"); 15 //模拟买票流程 16 Thread.sleep(5000); 17 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": 购票成功"); 18 // 释放窗口 19 semaphore.release(2); 20 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } 23 } 24 }).start(); 25 } 26 } 27 }
执行结果为:
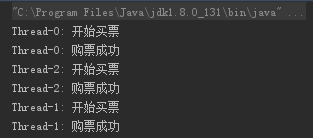
为什么会出现这种情况呢?

三 Semaphore源码解析
看上图执行结果和执行过程,我们会提出三个疑问:
1、Semaphore如何获取信号量
2、Semaphore获取信号量失败,又如何进入等待队列
3、等待队列线程如何阻塞的
4、release信号量时,又如何唤醒下一个线程的。

看上图可以解答如何获取信号量、获取信号量失败时如何添加到等待队列
1、Semaphore如何获取信号量
核心逻辑在Sync.nonfairTryAcquireShared()方法,首先getState(),state为volatitle变量,remaining>0且cas更新成功,代表获取信号量成功

1 abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer { 2 final int nonfairTryAcquireShared(int acquires) { 3 for (;;) { 4 int available = getState(); 5 int remaining = available - acquires; 6 if (remaining < 0 || 7 compareAndSetState(available, remaining)) 8 return remaining; 9 } 10 } 11 }
2、Semaphore获取信号量失败,又如何进入等待队列
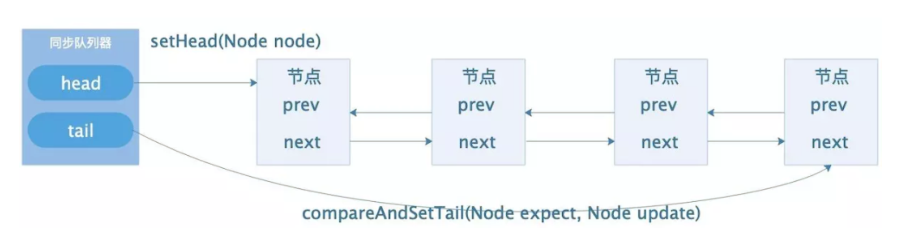
首先等待队列是一个双向链表。
thread2插入的时候,链表为空,需要初始化head节点,然后把thread2放到head节点的next
thread3,可以快速插入,放到thread2的next节点。

1 private Node addWaiter(Node mode) { 2 // 以给定的模式来构建节点, mode有两种模式 3 // 共享式SHARED, 独占式EXCLUSIVE; 4 Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode); 5 // 尝试快速将该节点加入到队列的尾部 6 Node pred = tail; 7 if (pred != null) { 8 node.prev = pred; 9 if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { 10 pred.next = node; 11 return node; 12 } 13 } 14 // 如果快速加入失败,则通过 anq方式入列 15 enq(node); 16 return node; 17 } 18 private Node enq(final Node node) { 19 // CAS自旋,直到加入队尾成功 20 for (;;) { 21 Node t = tail; 22 if (t == null) { // 如果队列为空,则必须先初始化CLH队列,新建一个空节点标识作为 23 Hader节点,并将tail 指向它 24 if (compareAndSetHead(new Node())) 25 tail = head; 26 } else {// 正常流程,加入队列尾部 27 node.prev = t; 28 if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) { 29 t.next = node; 30 return t; 31 } 32 出队操作 33 同步队列(CLH)遵循FIFO,首节点是获取同步状态的节点,首节点的线程释放同步状态后,将会唤醒 34 它的后继节点(next),而后继节点将会在获取同步状态成功时将自己设置为首节点 35 Condition队列 36 Condition 将 Object 监视器方法(wait、notify 和 notifyAll)分解成截然不同的对象,以便通过将这些 37 对象与任意 Lock 实现组合使用,为每个对象提供多个等待 set(wait-set)。其中,Lock 替代了 38 synchronized 方法和语句的使用,Condition 替代了 Object 监视器方法的使用。 39 } 40 } 41 }
3、等待队列线程如何阻塞的
加入等待队列成功后,调用shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire方法把等待队列waitStatus置为-1(等待被通知执行状态),然后调用parkAndCheckInterrupt方法阻塞当前线程。

1 private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() { 2 LockSupport.park(this); 3 return Thread.interrupted(); 4 }
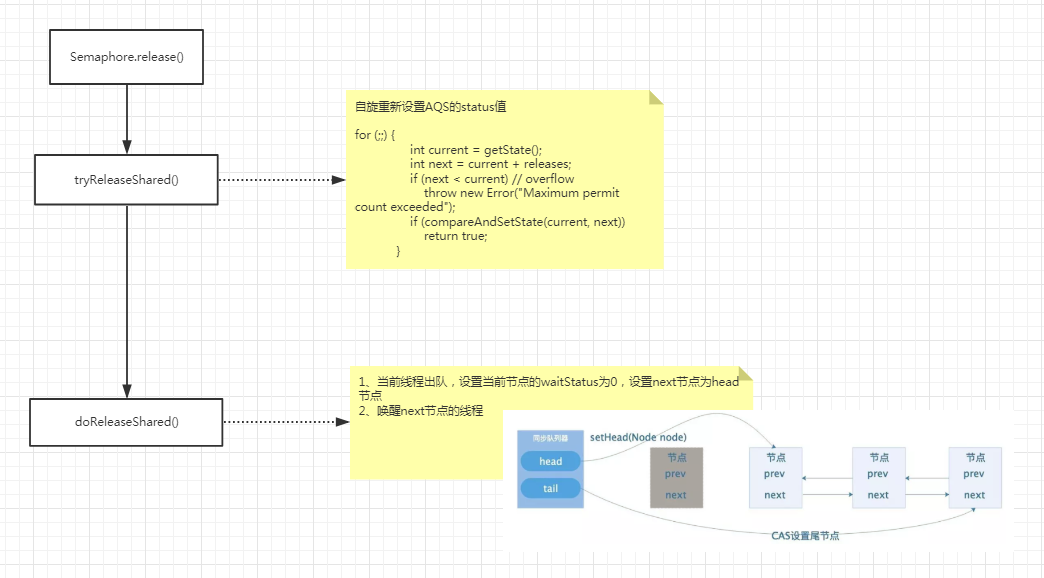
4、release信号量时,又如何唤醒下一个线程的
1、自旋为aqs的state值cas添加释放的信号量

1 protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) { 2 for (;;) { 3 int current = getState(); 4 int next = current + releases; 5 if (next < current) // overflow 6 throw new Error("Maximum permit count exceeded"); 7 if (compareAndSetState(current, next)) 8 return true; 9 } 10 }
2、当前线程出队,next节点为head节点,并且唤醒next线程

1 private void doReleaseShared() { 2 //移除当前节点,设置next接单为head 3 for (;;) { 4 Node h = head; 5 if (h != null && h != tail) { 6 int ws = h.waitStatus; 7 if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) { 8 if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0)) 9 continue; // loop to recheck cases 10 //唤醒next线程 11 unparkSuccessor(h); 12 } 13 else if (ws == 0 && 14 !compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE)) 15 continue; // loop on failed CAS 16 } 17 if (h == head) // loop if head changed 18 break; 19 } 20 }
unparkSuccessor---->LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);