爬山算法(Hill Climbing )
爬山算法(Hill Climbing )是一种局部择优的方法,采用启发式方法,是对深度优先搜索的一种改进,它利用反馈信息帮助生成解的决策。 属于人工智能算法的一种。
有一些问题,是找全局最大值的。题目所述出自变量与值之间的关系是函数,而这函数图像往往像山的形状,可能有许多局部最大、局部最小。于是“爬山”、“高地”、“山脊”等词形象地表示了算法的作用与函数图像的某些部分.
解决这类问题一般有两种方法:爬山算法(Hill Climbing )与模拟退火(Simulated Annealing)。常用的为模拟退火,它往往可以得到最优解。不过这里先介绍爬山算法。
爬山算法是一种简单的贪心搜索算法,该算法每次从当前解的临近解空间中选择一个最优解作为当前解,直到达到一个局部最优解。
爬山算法的优点为:避免遍历,通过启发选择部分节点,从而达到提高效率的目的。但是有缺点:只能找到局部最优,一般找不到全局最优解;搜索一旦到达高地,就无法确定搜索最佳方向,会产生随机走动,使得搜索效率降低;搜索可能会在山脊的两面来回震荡,前进步伐很小。
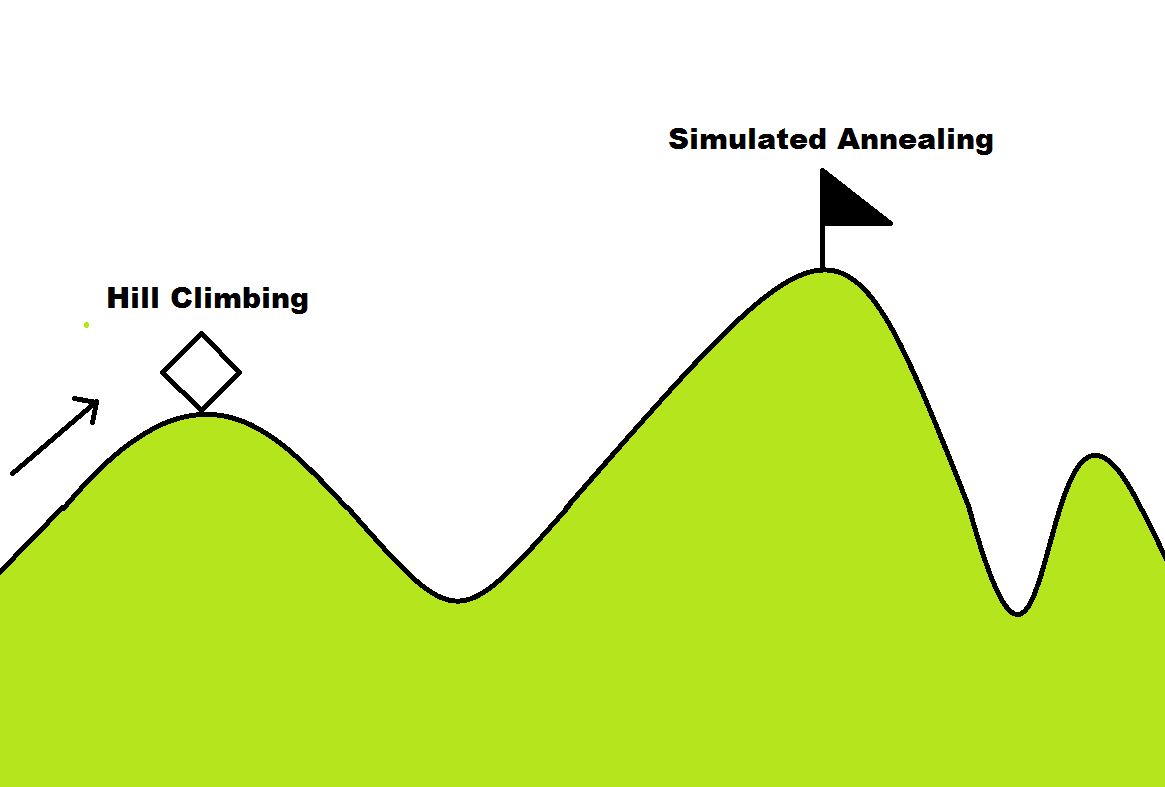
下图反应了爬山算法相对于模拟退火的目光短浅之处(模拟退火也是随机算法,不一定可以找到最优解,但大部分情况可以找到)
模拟退火(Simulated Annealing)
退火是物理热力学里的概念。退火是将金属加热到一定温度,保持足够时间,然后以适宜速度冷却的一种金属热处理工艺。我们把这个过程模拟一下,就叫模拟退火(Simulated Annealing)。
爬山算法就是贪心法。而模拟退火是一种随机搜索算法。它的描述是这样的:
若移动后得到更优解,则总是接受该移动
若移动后的解比当前解要差,则以一定的概率接受移动,而且这个概率随着时间推移逐渐降低。
根据热力学的原理,降温的概率(P)表示为:
(Delta E):新状态与当前状态的能量差
(k):常数
(T):时间
(Delta E<0)时,一定接受。(Delta E>0)时就不一定了,并且 (x) 越来越小的时,函数值越来越趋近于 (0),这也就是说随着 (T) 的增加,概率越来越小,趋向稳定。
我们要维护 (T),初始温度设置为 (T_0)(较大),降温系数为 (d),最终温度为 (T_k)。
首先令 (T = T_0);每次让 (T=dT);(T<T_k) 时降温结束,此时为最优解。
调参时一般会调 (d)((0<d<1))。(d) 过大降温慢,得到最优解的可能性大(容易 TLE);(d) 过小降温快,但得到最优解的可能性小(容易 WA);
那模拟退火具体怎么使用代码实现?
每次循环内有 4 步:
根据当前解找到下一个解
计算下一个解的 "能量"
决定是否要接受这个新解
降温
找下一个解时一般生成随机区间 ([−1,1]) 的随机数再乘上 (T) 作为差值. 得到一个 ([−T,T]) 的随机值作为差值,也就是说 (T) 越低,它随机到下一步的范围就越小。
伪代码:
当前温度 = 初始温度;
while 当前温度 > 终温:
根据 T 随机生成下一步;
计算出下一步的能量;
计算能量差;
if 接受:更新答案;
当前温度 乘以 降温系数;
推荐几道模拟退火的例题:
HDU 2899 比较好的入门题
HDU 3932 二维相关
NOIP2017 宝藏 骗分甚至AC
POJ 3311 TSP问题
例题讲解
HDU 2899 (求函数最值)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
double y;
double F(double x) {
return 6 * pow(x, 7) + 8 * pow(x, 6) + 7 * pow(x, 3)
+ 5 * pow(x, 2) - y * x;
}
double Rand01() {
return rand() / (double)RAND_MAX;
}
double Rand(double T) {
int f = rand() & 1;
return (f ? -1 : 1) * T * Rand01();
}
int main() {
srand(time(NULL));
int Case;
scanf("%d", &Case);
while(Case --) {
scanf("%lf", &y);
double T = 100, T_end = 1e-6, d = 0.85, ans = F(0);
double x_now = 0, x_next;
while(T > T_end) {
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i ++) {
x_next = x_now + Rand(T);
if(x_next < 0 || x_next > 100) continue;
double f_next = F(x_next), f_now = F(x_now);
double delta = f_next - f_now;
if(delta < 0 || Rand01() < exp(- delta / T)) {
x_now = x_next;
ans = min(ans, f_next);
}
}
T *= d;
}
printf("%.4f
", ans);
}
return 0;
}
HDU 3932 (矩形中找距离和最小点)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
int X, Y, N;
int px[1010], py[1010];
double pw(double x) {
return x * x;
}
double calc(double x, double y) {
double dis = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i ++)
dis = max(dis, sqrt(pw(x - px[i]) + pw(y - py[i])));
return dis;
}
double Rand01() {
return rand() / (double) RAND_MAX;
}
double Rand() {
int f = rand() & 1;
return (f ? -1 : 1) * Rand01();
}
int main() {
srand(12834917);
while(~ scanf("%d%d%d", &X, &Y, &N)) {
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i ++)
scanf("%d%d", &px[i], &py[i]);
double x = 0, y = 0;
double ans = calc(x, y), ansx = x, ansy = y;
double T = sqrt(X * X + Y * Y), T_end = 1e-4, d = 0.99;
while(T > T_end) {
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i ++) {
double theta = Rand01() * 2 * PI;
double nx = x + T * cos(theta);
double ny = y + T * sin(theta);
if(nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx > X || ny > Y) continue;
double next_ans = calc(nx, ny);
double now_ans = calc(x, y);
double delta = next_ans - now_ans;
if(delta < 0 || Rand01() < exp(- delta / T)) {
x = nx, y = ny;
if(next_ans < ans) {
ans = next_ans;
ansx = x, ansy = y;
}
}
}
T *= d;
}
printf("(%.1f,%.1f).
%.1f
", ansx, ansy, ans);
}
return 0;
}
NOIP2017 宝藏
PS:调参十分麻烦。听说有人考试的时候骗了95分(雾
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
const int N = 12;
const int INF = 1 << 29;
int n, m, s;
int G[N][N], K[N], a[N], b[N];
int calc(int *a) { //O(n^2)
int ans = 0;
K[ a[0] ] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i ++) {
int j = a[i], mc = INF, mk;
for(int k = 0; k < i; k ++) {
if(G[a[k]][j] < INF && mc > K[a[k]] * G[a[k]][j])
mc = (mk = K[a[k]]) * G[a[k]][j];
}
if(mc == INF) return INF;
K[j] = mk + 1;
ans += mc;
}
return ans;
}
double Rand01() {
return rand() / (double) RAND_MAX;
}
void Change(int times) {
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) b[i] = a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= times; i ++)
swap(b[rand() % n], b[rand() % n]);
}
int main() {
srand(time(NULL));
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(G, 127, sizeof G);
for(int i = 1, u, v, w; i <= m; i ++) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &u, &v, &w);
-- u, -- v;
G[u][v] = G[v][u] = min(G[u][v], w);
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) a[i] = i;
int ans = calc(a);
double T = 6e6, T_end = 100, d = 0.98;
while(T > T_end) {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i ++) {
Change(T / 100);
int now_ans = calc(a), next_ans = calc(b);
int delta = next_ans - now_ans;
if(delta < 0 || Rand01() < exp(- delta / T)) {
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) a[i] = b[i];
if(next_ans < ans) ans = next_ans;
}
}
T *= d;
}
printf("%d
", ans);
return 0;
}
POJ 3311 TSP
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int n, G[20][20], a[20], b[20];
int calc(int *a) {
int now = 1, ans = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; now = a[i ++])
ans += G[now][ a[i] ];
return ans + G[now][1];
}
int Rand() {
return rand() % (n - 1) + 2;
}
double Rand01() {
return rand() / (double) RAND_MAX;
}
void Change(int times) {
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i ++) b[i] = a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= times; i ++)
swap(b[Rand()], b[Rand()]);
}
int main() {
srand(91874899);
while(scanf("%d", &n), n ++ != 0) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; a[i] = i, i ++)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++)
scanf("%d", &G[i][j]);
for(int k = 1; k <= n; ++ k)
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++ j)
if(G[i][k] + G[k][j] < G[i][j])
G[i][j] = G[i][k] + G[k][j];
int ans = calc(a);
double T = n * 10, T_end = 1e-4, d = 0.98;
while(T > T_end) {
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i ++) {
if((int)T == 0) break;
Change(T);
int now_ans = calc(a);
int next_ans = calc(b);
int delta = next_ans - now_ans;
if(delta < 0 || Rand01() < exp(-delta / T)) {
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i ++) a[i] = b[i];
if(next_ans < ans) ans = next_ans;
}
}
T *= d;
}
printf("%d
", ans);
}
return 0;
}